Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2008/09 - Gruppe 10 - Aufgabe 1 - Hyperbolic Tree
Hyperbolic Tree[edit]
Definition[edit]
A mathematical point of view[edit]
A Hyperbolic Tree, sometimes called a Hypertree, is a visualization method based on the hyperbolic geometry. In this geometry the parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced. That parallel postulate says, that for any given line l and any point P it can only exist exactly one line which does not intersect l and runs through P. This line is called a parallel line. In a hyperbolic space these two lines would diverge. [Wikipedia, 2008a] Because of this characteristic the circumference grows exponentially as a function of the circle's radius. Similarly the number of leaves in a tree grow exponentially as a function of it's depth. [Wikipedia, 2008b]
Information visualization[edit]
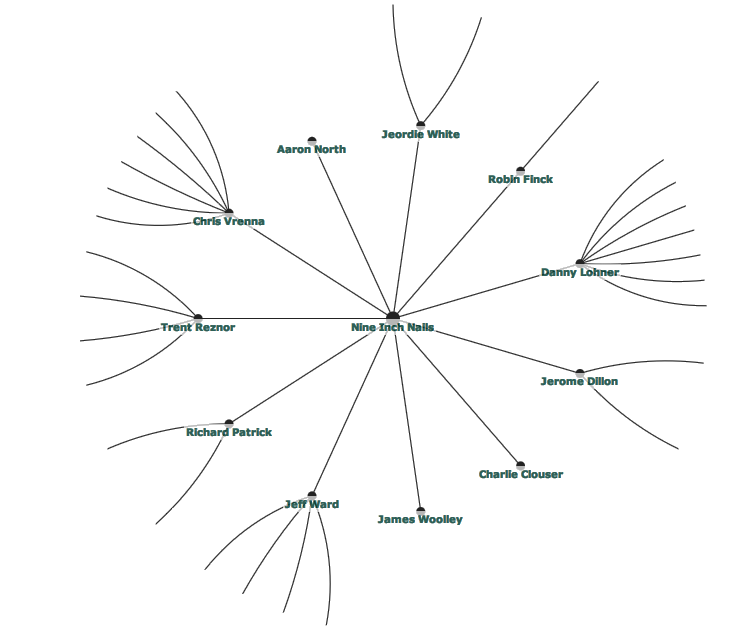
A Hyperbolic Tree is a concept which makes use of the properties discussed before. It can be classified as a focus + context technique. Only a small number of data is shown on the most expansive area in and near the center. Information in this area is stretched and is the part where the focus is caught. The peripheral area of the circle is used for all other nodes - the context. Information in this part is "squeezed". [Pirolli et al, 2003] Generally a hypertree is known as a "fisheye representation of information".
User interaction[edit]
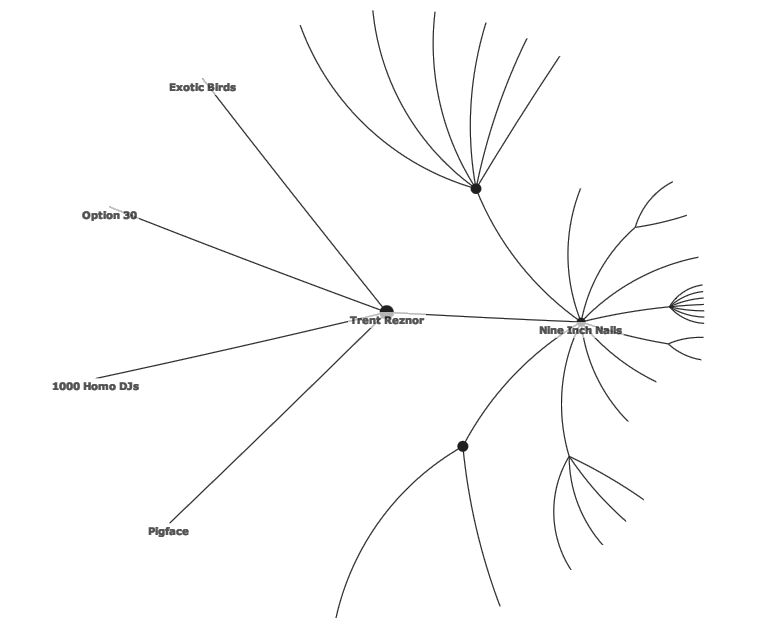
The root-node is placed in the center of the circle. [Figure 1] Child nodes are positioned in other fictive concentric circles. Users can click within the tree to focus the desired area. As a result the user might be presented with something like that shown in [Figure 2]. Typically the part of bringing other nodes into focus, the user is shown a smooth transformation of the display. [Pirolli et al, 2003; Huang and Quan, 2004]
Comparison[edit]
Compared to other conventional tree browsers, the hyperbolic tree shows all of the information at once, where other techniques force the user to scroll. For this reason it could be expected, that browsing performance will increase. The answer is both yes and no. In retrieval tasks, where users simply search for specific nodes, the performance is very good. It is fuerthermore increased through strong practice effects. In comparison tasks, where users have access to nodes in different parts of the tree to compare information. In this task a Hyperbolic tree cannot aim any advantage. On tasks with poor information scent cues, tests can end up with loss of efficiency. [Pirolli et al, 2003] Other limitations in navigation efficiency occur for trees with a large number of children. Also the concept of focus+context can be lost in specific situations where the "context-part" is pushed in any corner and therefore meaningless. [Huang and Quan, 2004]
Bibliography[edit]
[Wikipedia, 2008a] Wikipedia contributors, Hyperbolic Geometry, Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia., Retrieved at: November, 6 2008. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperbolic_geometry
[Wikipedia, 2008b] Wikipedia contributors, Hyperbolic Tree, Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia., Retrieved at: November, 6 2008. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperbolic_tree
[Pirolli et al, 2003] Peter Pirolli and Stuart K. Card and Mija M. Van Der Wege, The effects of information scent on visual search in the hyperbolic tree browser in ACM Trans. Comput.-Hum. Interact., pages 20-53, 2003, ACM
[Huang and Quan, 2004] Mao Lin Huang and Wu Quan, 21DF-browser: a multiple fisheye distortion technique for visualizing and navigating hierarchies with large number of leaves, In Information Visualisation, 2004. IV 2004. Proceedings. Eighth International Conference on, pages 277-284, July 2004
[Garcia, 2008] Nicolas Garcia, JavaScript Information Visualization, Retrieved at: November, 6 2008. http://blog.thejit.org/wp-content/jit-1.0a/examples/hypertree.html[1]
Footnotes and references[edit]
- ↑ Colors were changed, inverted to suit wiki better