Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2007/08 - Gruppe 08 - Aufgabe 1 - Spatial Analysis
Definition[edit]
Spatial analysis is the process creating visual images or models from data to help understand or interpret that data. The data has to refer to a phenomena distributed in some form of space, this could for example be data relating to physical locations on a map. It is therefore frequently used as a tool for statistical and geographical purposes, such as to create predictions or evaluating the suitability of a particular location for a purpose. [Wood, 1984]
While spatial analysis is essentially not new, as it was already used by civilisations such as the 2nd century Eygptians in early forms of world mapping, recent advances in the field of computing have empowered society to perform far more complex analysis then previously possible. This in turn has lead to an increased intrest in spatial analysis tools in the recent years. [Fotheringham et al., 2000]
Examples[edit]
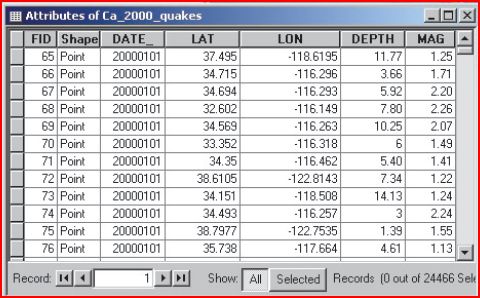
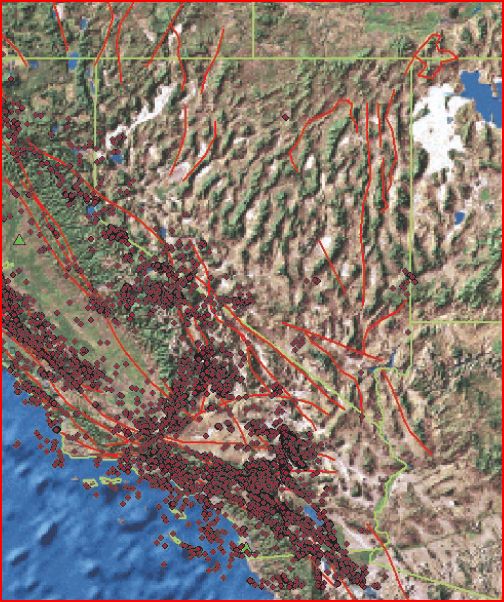
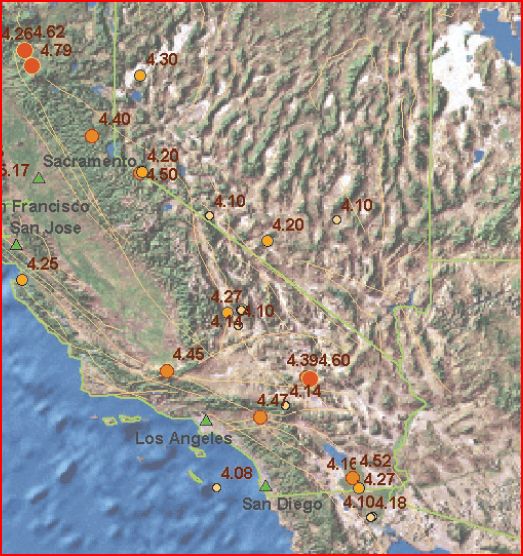
A typical approach to get new information from existent data using spatial analysis is to find patterns and correlations in the data by mapping them with their geographic location. The example below illustrates this. The first illustration shows a table of earthquake data. By visualizing this data one can better understand it (see figure 2) but one can gain even more useful knowledge with further spatial analysis, for example by filtering out the smaller earthquakes and then combining the larger earthquakes (see figure 3). [Pratt, 2003]
-
Figure 1
-
Figure 2
-
Figure 3
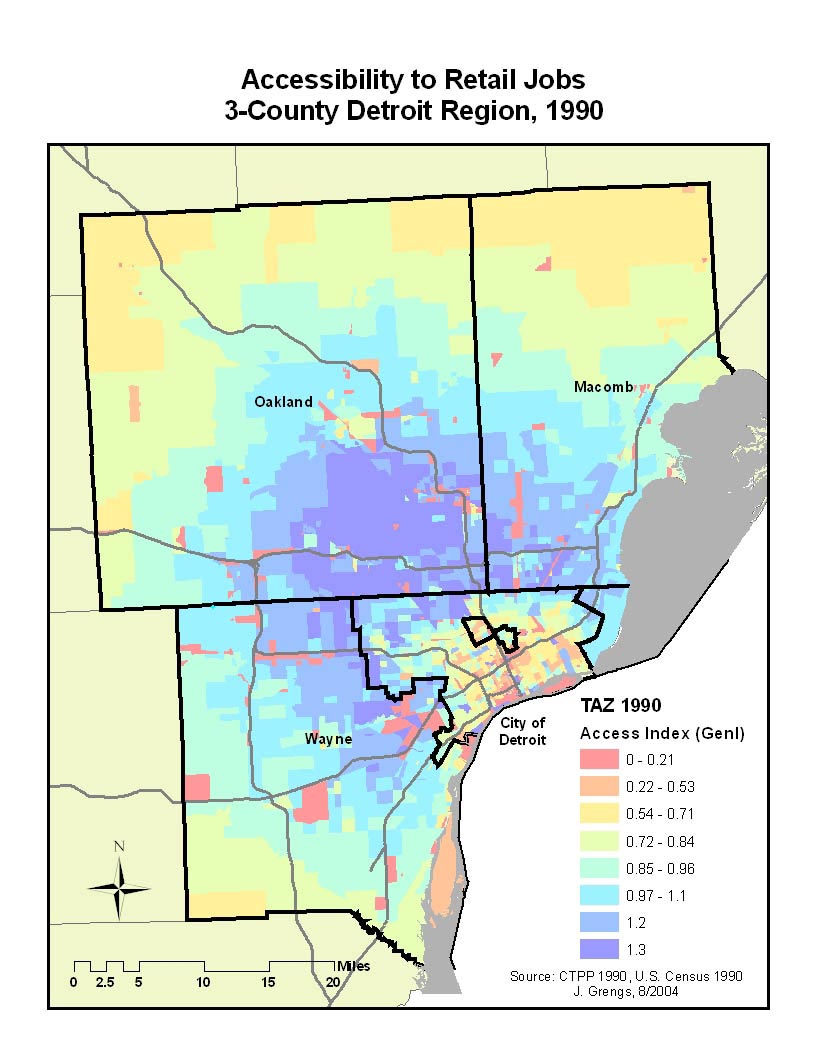
Further examples of spatial data analysis can be found in every day life
References[edit]
- [Fotheringham et al., 2000] A. Stewart Fotheringham, Chris Brunsdon, Martin Charlton. Quantitative Geography: Perspectives on Spatial Data Analysis. Sage Publications, London, 2000. Pages 15-16
- [Green, 2006] Richard Green, MCAG GIS: - Glossary of GIS Terms. Created at: December 21, 2006. Retrieved at: November 8, 2007. http://www.mcaggis.com/Glossary.html#S
- [Pratt, 2003] Monica Pratt. Beginning spatial Analysis. ArcUser, October-December 2003: 58-59, October 2003
- [Wood, 1984] Stearns J. Wood, GIS Glossary h-t. Created at: 1984. Retrieved at: November 8, 2007. http://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia_term/0,2542,t=GIS+glossary+h-t&i=43796,00.asp