Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2008/09 - Gruppe 09 - Aufgabe 4: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
=== Technologies Used === | === Technologies Used === | ||
Tags | |||
Zoom | |||
MouseOver | |||
reduce substances and detailed | |||
Multiuse flow graph (substance/fluids) | |||
=== Interaction === | === Interaction === | ||
*Zoom Bar | *Zoom Bar | ||
*Mouse | [[Image:G09_UE4_Zoombar.jpg]]<br> | ||
Above the Flow graph there is a small bar with two sliders on it. This is the "Zoom Bar". If you grab one of the two sliders and move him closer to, or farther away from the other slider, you thereby set the zoom factor in the flow graph. If you, for example, move the a slider directly next to the other, the flow graph is totally zoomed in - meaning only one day is displayed. The bigger the distance between the two sliders, the smaller the zoom factor in the graph (and hence the bigger the zoomed period of time).<br> | |||
If you grab the line between the two sliders, you can move toe zoomed area in the flow graph left and right. | |||
*Grab and move Flow graph | |||
[[Image:G09_UE4_Grab.jpg]]<br> | |||
Another way to move the zoomed area in the flow graph left and right (besides moving the Zoom Bar) is done by simply grabbing a point in the zoomed area of the flow graph and then move around. | |||
*Mouse over | |||
[[Image:G09_UE4_Popup.jpg]]<br> | |||
Almost all displayed data also has a MouseOver menu. Hovering the mouse above a line in the flow graph for example, makes a popup field appear, which describes the actual amount of the fluid, the date and all tags for this date. Another example is are the tags listed in the Detail table. Moving the mouse cursor over one of those will show the periods of time in which they are set. | |||
*Mouse over: Substances | |||
[[Image:G09_UE4_Substances.jpg]][[Image:G09_UE4_SubstancesMouseOver.jpg]]<br> | |||
A special case for a MouseOver action is found in the substance part-to-whole bar chart. By moving the mouse over a bar, all other bars turn grey and the composition of the current bar is displayed. That way, one can dive deeper into the data with just a simple interaction.<br> | |||
*Zoom on .. | *Zoom on .. | ||
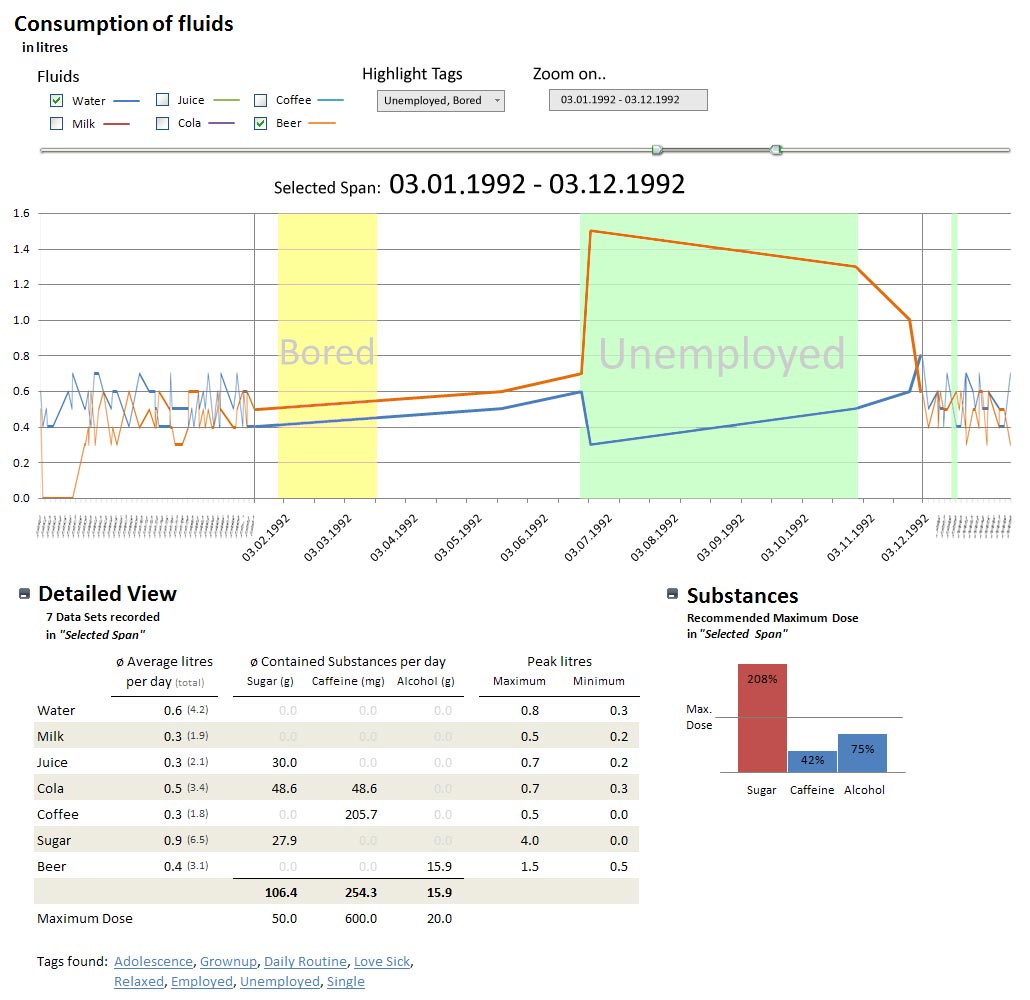
With the "Zoom on.." field above the flow graph, the user can set the zoomed area for the graph. Usually the user will enter a date or a period of time into it. Doing so will set the zoomed area according to the input. The zoomed area can then be moved / changed through the Zoom Bar. Via the "Zoom on.." field, the user can also zoom the specific Tags. For example, by entering "Unemployed" into the field, the flow graph will zoom to all periods of time in which Homer Simpson was not exmployed. If there where several periods in which he was unemployed, the flow graph would zoom onto several periods of time. | |||
*Select fluids | *Select fluids | ||
By clicking the Checkboxes above the flow graph the user can add/remove the lines for the specific fluids in the flow graph. | |||
*Highlight tags | |||
All Tags typed into the "Highlight Tags" field will be highlighted in the flow graph by coloring the background of the periods in which a tag was found. | |||
*Click tags | |||
By clicking a tag in the Detail table the specified tag is sent to the "Zoom on.." field. So, if a user is interested in relations between different tags, e.g. if Homer Simpson is always 'Relaxed' when he has 'Holidays', one can easily switch between the different tags in order to get an overview when and where they are found. | |||
*Draw Substances into Flow graph | |||
By clicking a (substance) bar in the Substance part-to-whole bar chart, all data is removed from the Flow graph and the selected substance data is filled into it. This means that the Flow graph can display not only data on fuilds, but also data on substances. | |||
=== Fake Screenshot === | |||
=== | |||
[[Image:G09_UE4_VerlaufLarge.jpg]]<br> | [[Image:G09_UE4_VerlaufLarge.jpg]]<br> | ||
=== Discussion === | === Discussion === | ||
*Advantages | *Advantages | ||
*Disadvantages | *Disadvantages | ||
=== Improvements === | === Improvements === | ||
Revision as of 18:35, 7 January 2009
Aufgabenstellung
Gegebene Daten
Homer Simpson's Trinkverhalten in Abhängigkeit von seinen Lebensumständen
...Visualisierung von Homer's Lebensabschnitten bzw. Ereignissen mit Einfluss auf sein
Trinkverhalten (zB.: Kindheit, Pubertät, Arbeitslosigkeit, Beziehungen, Hochzeit, Geburt
der Kinder, Liebeskummer, Alltag, etc.) von seiner Geburt bis Jetzt + mögliche
Zukunftsszenarien (mind. 3).
- Die Menge folgender Getränke soll für die jeweiligen Lebensumstände ablesbar sein
(ml oder Liter - je nachdem - pro Tag, Monat, Jahr (z.B.: Fokus+Kontext Methoden):
a) Wasser
b) Milch
c) Fruchtsaft
d) Cola
e) Kaffee (Würfelzucker?)
f) Bier
(vereinfacht angenommen, Homer trinkt ausschließlich diese Getränke)
- Die folgenden Werte sollen abhängig von den konsumierten Getränken ablesbar sein:
1) g oder kg konsumierter Zucker (aus Getränken) + empfohlene Maximaldosis pro Tag, Monat, Jahr (empfohlene Maximaldosis/Tag: 50g; enthaltener Zucker: 10g/100 ml Cola; 10g/100 ml Fruchtsaft; 3g/Würfelzucker).
2) mg konsumiertes Coffein + empfohlene Maximaldosis pro Tag, Monat, Jahr (empfohlene Maximaldosis/Tag: 600mg; enthaltenes Coffein: 10 mg/100 ml Cola; 80 mg/100 ml Kaffee).
3) g konsumierter Alkohol + empfohlene Maximaldosis pro Tag, Monat, Jahr (empfohlene Maximaldosis/Tag: 20g; enthaltener Alkohol: 3,6 g/100ml Bier)
- Die Daten sollen zur medizinischen/psychologischen Analyse visualisiert werden.
- Die bisher erlernten Design-Prinzipien sollen umgesetzt werden (z.B.: Optimierung der Data-ink ratio).
- Die Mockups sollten zumindest 1) Homer's Leben im Überblick 2) und eine Detailansicht wiedergeben.
- Alle nicht angeführten Daten können frei erfunden werden.
Analysis
Concept
Visualization
2. Use Graphs when the document you produce will be used to reveal relationships among multiple values.
Following the principles of Stephen Few, the main graphic of the visualization is a graph. In order to get an overview of Homer Simpsons drinking habits this visualization method seems superior to any other. Since becoming an overview is this visualizations main task, no detailed information is needed. This, and the fact the there are simply too many values to compare, makes the graph superior to a table. The graph also allows to browse Homer Simpsons life quite easily for any special events. To make this browsing more effecive several interactive technologies where applied. (see "Interaction").
When it comes to analysing detailed information we need an other method. [Few, 2004] recommends using Tables when "The document you produce will be used to look up individual values." For a doctor who wants to set up a therapy or medication, a graph wont be sufficient. He will want detailed and exact data. Therefore, the visualization should also hold a detailed table view (in addition to the overview graph).
Finally, to look up if a maximum dose was exceeded, a part-to-whole bar chart is also contained in the visualization. This visualization method "Measures [..] individual categorical subdivisions as ratios to the whole." [Few, 2004] Since the task is to compare given values to a maximum values and display theri ratios, this methods seems appropriate.
The visualization now holds:
- Flow graph
- Detail table
- Substance part-to-whole bar chart
Visual Mapping
- Flow graph [Figure 1]
In the Flow graph the consumed amount of Fluids (in litres) is mapped to the y-axis while Homer Simpsons age/life-period is mapped to the x-axis. The key events in his life (described by "Tags") are mapped as an area to both axes.
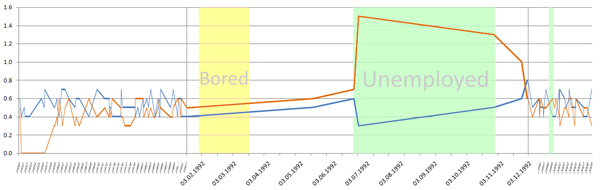
- Detail table [Figure 2]
In the detailed view table things are relatively simple: all values are directly mapped into a table values.
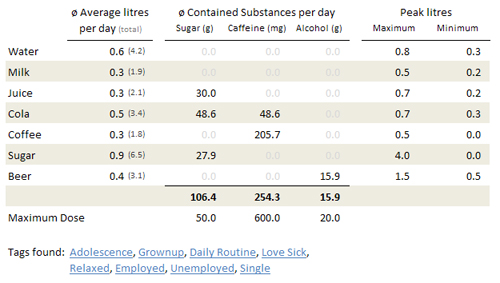
The table holds the average consumpted litres, the average thereby consumpted substances and the peak values for a given period of time. It also contains a list of all tags which where found in this period of time (e.g. "Unemployed"). In order to grant interpretation of this data, the table also holds the maximum doses for substances.
For the task of checking wheter a maximum dose was exceeded or not, one can also take look at the..
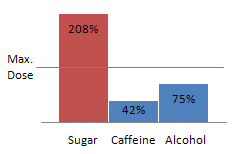
- Substance part-to-whole bar chart [Figure 3]
Like mentioned above, this chart holds the values of all consumpted substances and their maximum value. To make the comparison more easy, the values are displayed as a bar and compared against a line which describes the maximum doses.
Technologies Used
Tags Zoom MouseOver reduce substances and detailed Multiuse flow graph (substance/fluids)
Interaction
- Zoom Bar
![]()
Above the Flow graph there is a small bar with two sliders on it. This is the "Zoom Bar". If you grab one of the two sliders and move him closer to, or farther away from the other slider, you thereby set the zoom factor in the flow graph. If you, for example, move the a slider directly next to the other, the flow graph is totally zoomed in - meaning only one day is displayed. The bigger the distance between the two sliders, the smaller the zoom factor in the graph (and hence the bigger the zoomed period of time).
If you grab the line between the two sliders, you can move toe zoomed area in the flow graph left and right.
- Grab and move Flow graph
Another way to move the zoomed area in the flow graph left and right (besides moving the Zoom Bar) is done by simply grabbing a point in the zoomed area of the flow graph and then move around.
- Mouse over
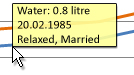
Almost all displayed data also has a MouseOver menu. Hovering the mouse above a line in the flow graph for example, makes a popup field appear, which describes the actual amount of the fluid, the date and all tags for this date. Another example is are the tags listed in the Detail table. Moving the mouse cursor over one of those will show the periods of time in which they are set.
- Mouse over: Substances


A special case for a MouseOver action is found in the substance part-to-whole bar chart. By moving the mouse over a bar, all other bars turn grey and the composition of the current bar is displayed. That way, one can dive deeper into the data with just a simple interaction.
- Zoom on ..
With the "Zoom on.." field above the flow graph, the user can set the zoomed area for the graph. Usually the user will enter a date or a period of time into it. Doing so will set the zoomed area according to the input. The zoomed area can then be moved / changed through the Zoom Bar. Via the "Zoom on.." field, the user can also zoom the specific Tags. For example, by entering "Unemployed" into the field, the flow graph will zoom to all periods of time in which Homer Simpson was not exmployed. If there where several periods in which he was unemployed, the flow graph would zoom onto several periods of time.
- Select fluids
By clicking the Checkboxes above the flow graph the user can add/remove the lines for the specific fluids in the flow graph.
- Highlight tags
All Tags typed into the "Highlight Tags" field will be highlighted in the flow graph by coloring the background of the periods in which a tag was found.
- Click tags
By clicking a tag in the Detail table the specified tag is sent to the "Zoom on.." field. So, if a user is interested in relations between different tags, e.g. if Homer Simpson is always 'Relaxed' when he has 'Holidays', one can easily switch between the different tags in order to get an overview when and where they are found.
- Draw Substances into Flow graph
By clicking a (substance) bar in the Substance part-to-whole bar chart, all data is removed from the Flow graph and the selected substance data is filled into it. This means that the Flow graph can display not only data on fuilds, but also data on substances.
Fake Screenshot
Discussion
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
Improvements
References
- [Few, 2004]:Stephen Few, Show Me the Numbers: Designing Tables and Graphs to Enlighten, Analytics Press, 2004, Appendix A - Table and Graph Design at a Glance.