Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2008/09 - Gruppe 02 - Aufgabe 1 - Scatterplot: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A scatterplot (also called a ''scatter chart'', ''scatter diagram'' or ''scatter graph'' [Wikipedia]) is a diagram in which the values of two ''metric'' variables are applied to the horizontal and vertical axes of a cartesian coordinate system. The resulting point in the graph represents one record from a data set. The distribution pattern of points from multiple records reveals, among other qualities, the correlation between the selected variables in the data set. The scatterplot is not to be confused with the ''correlation plot'' [Information Technology Lab, NIST #2] which treats already adopted correlation coefficients in different data groups, while the term ''correlation diagram'' does not seem to be bound. | A scatterplot (also called a ''scatter chart'', ''scatter diagram'' or ''scatter graph'' [Wikipedia]) is a diagram in which the values of two ''metric'' variables are applied to the horizontal and vertical axes of a cartesian coordinate system. The resulting point in the graph represents one record from a data set. The distribution pattern of points from multiple records reveals, among other qualities, the correlation between the selected variables in the data set. The scatterplot is not to be confused with the ''correlation plot'' [Information Technology Lab, NIST #2] which treats already adopted correlation coefficients in different data groups, while the term ''correlation diagram'' does not seem to be bound. | ||
=Revealed Information= | ===Revealed Information=== | ||
Perfect linear correlation results in all samples lying on the regression line with positive or negative incline dependent on the sign of the correlation coefficient [University of Illinois]. Note, that the nonzero incline of the line is insignificant in this kind of diagram [Wikipedia Correlation, EN] since it is dependent on axis scales. | |||
An example of perfect correlation can be seen on the right together with other patterns: strong positive, weak negative and one example of variables without significant correlation. | |||
[[Image:SomeScatterplots.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Some scatterplots.]] | |||
The plot below features a regression line to further increase expressiveness. The regression function is not necessarily chosen linear as in this example. Any kind of curve may fit a plot (quadratic, splines, ...). Generally, the curve with the smallest sum of squared distances to the points is sought after, [NetMBA]. | |||
[Wikipedia Linear Regression] | |||
[[Image:WeakNegativeCorrelationLine.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Regression line.]] | |||
Generally: refer to regression analysis for further ... | Generally: refer to regression analysis for further ... | ||
Further properties of data sets that are easily discovered are the presence of clusters and outlyers. | |||
density (-> cluster analysis) & outlyers | density (-> cluster analysis) & outlyers | ||
*1 image for clusters | *1 image for clusters and outlyers | ||
===Scatterplots of Higher Dimensions=== | |||
Scatterplots are not restricted to records with only two variables. Higher dimensional data can be displayed by adding the third axis to the plotspacially or by point properties (color, size, shape) | |||
=Treating Discrete Data= | TODO: add figure with colored 3D plot, | ||
[Wikipedia, EN] | |||
Nice example of plotting multidimensional data: [AI Lab] | |||
===Treating Discrete Data=== | |||
For continuously distributed data, scatterplots do well in visualizing density. The problem with discrete data is the possibility of more than one record sharing one point in the diagram (''overplotting''). One solution is to alter the point representation according to density, as is achieved by ''sun flower plots'' in which each point symbol gains radial segments as a consequence, [Wikipedia, DE]. Examples can be found here: [York University], [addictedtor.free.fr]. | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
| Line 42: | Line 45: | ||
*Wikipedia, DE: http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streudiagramm | *Wikipedia, DE: http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streudiagramm | ||
*Wikipedia Correlation, EN: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Correlation | *Wikipedia Correlation, EN: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Correlation | ||
*Wikipedia Linear Regression, EN:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_regression | |||
*University of Illinois: http://www.mste.uiuc.edu/courses/ci330ms/youtsey/scatterinfo.html | *University of Illinois: http://www.mste.uiuc.edu/courses/ci330ms/youtsey/scatterinfo.html | ||
*Information Technology Lab, NIST #1: http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda33q.htm | *Information Technology Lab, NIST #1: http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda33q.htm | ||
| Line 47: | Line 51: | ||
*NetMBA: http://www.netmba.com/statistics/plot/scatter/ | *NetMBA: http://www.netmba.com/statistics/plot/scatter/ | ||
*ChartItNow: http://www.chartitnow.com/scatter%20diagram.html | *ChartItNow: http://www.chartitnow.com/scatter%20diagram.html | ||
*addictedtor.free.fr: http://addictedtor.free.fr/graphiques/graphcode.php?graph=59 | *addictedtor.free.fr: http://addictedtor.free.fr/graphiques/graphcode.php?graph=59 | ||
*York University: http://www.math.yorku.ca/SCS/sasmac/sunplot.html | *York University: http://www.math.yorku.ca/SCS/sasmac/sunplot.html | ||
*NLVM: http://matti.usu.edu/nlvm/nav/frames_asid_144_g_4_t_5.html | *NLVM: http://matti.usu.edu/nlvm/nav/frames_asid_144_g_4_t_5.html | ||
*AI Lab: www.ailab.si/janez/visualizations.html | |||
Revision as of 23:02, 2 November 2008
A scatterplot (also called a scatter chart, scatter diagram or scatter graph [Wikipedia]) is a diagram in which the values of two metric variables are applied to the horizontal and vertical axes of a cartesian coordinate system. The resulting point in the graph represents one record from a data set. The distribution pattern of points from multiple records reveals, among other qualities, the correlation between the selected variables in the data set. The scatterplot is not to be confused with the correlation plot [Information Technology Lab, NIST #2] which treats already adopted correlation coefficients in different data groups, while the term correlation diagram does not seem to be bound.
Revealed Information
Perfect linear correlation results in all samples lying on the regression line with positive or negative incline dependent on the sign of the correlation coefficient [University of Illinois]. Note, that the nonzero incline of the line is insignificant in this kind of diagram [Wikipedia Correlation, EN] since it is dependent on axis scales.
An example of perfect correlation can be seen on the right together with other patterns: strong positive, weak negative and one example of variables without significant correlation.
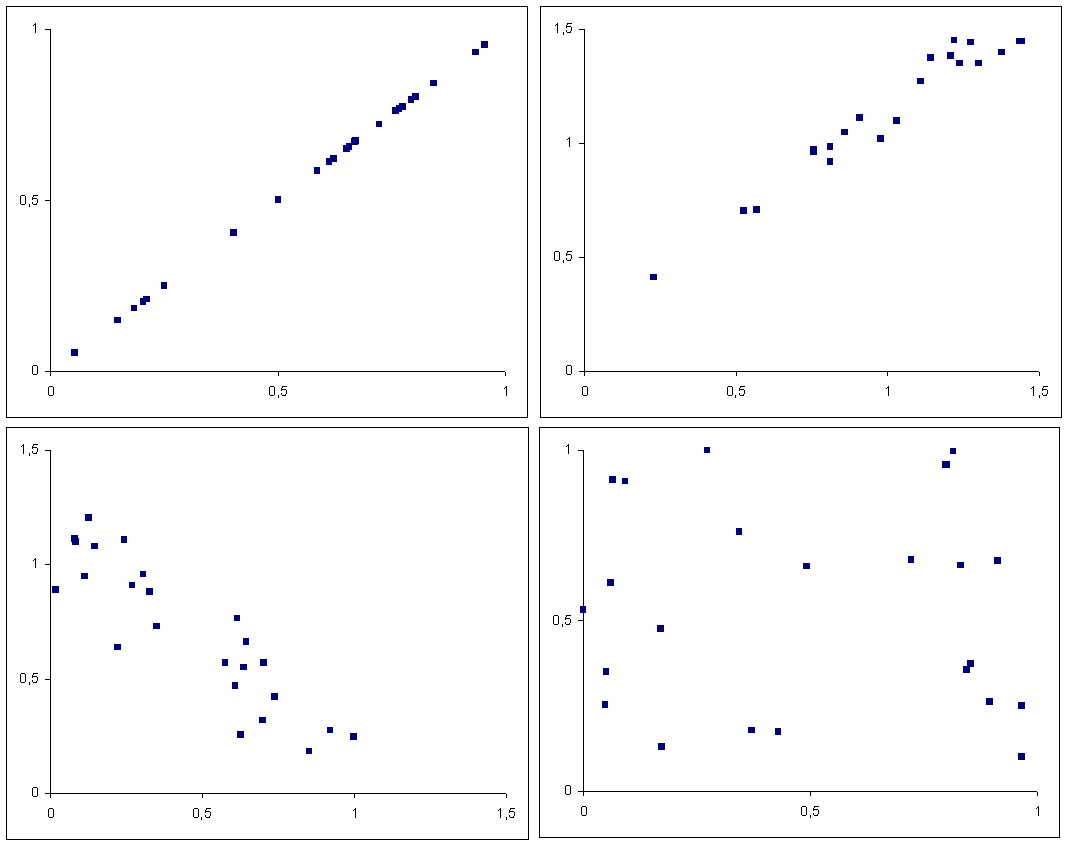
The plot below features a regression line to further increase expressiveness. The regression function is not necessarily chosen linear as in this example. Any kind of curve may fit a plot (quadratic, splines, ...). Generally, the curve with the smallest sum of squared distances to the points is sought after, [NetMBA].
[Wikipedia Linear Regression]
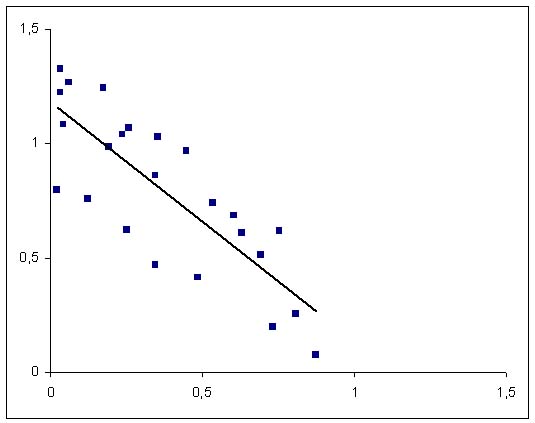
Generally: refer to regression analysis for further ...
Further properties of data sets that are easily discovered are the presence of clusters and outlyers.
density (-> cluster analysis) & outlyers
- 1 image for clusters and outlyers
Scatterplots of Higher Dimensions
Scatterplots are not restricted to records with only two variables. Higher dimensional data can be displayed by adding the third axis to the plotspacially or by point properties (color, size, shape)
TODO: add figure with colored 3D plot,
[Wikipedia, EN]
Nice example of plotting multidimensional data: [AI Lab]
Treating Discrete Data
For continuously distributed data, scatterplots do well in visualizing density. The problem with discrete data is the possibility of more than one record sharing one point in the diagram (overplotting). One solution is to alter the point representation according to density, as is achieved by sun flower plots in which each point symbol gains radial segments as a consequence, [Wikipedia, DE]. Examples can be found here: [York University], [addictedtor.free.fr].
References
- Wikipedia, EN: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scatterplot
- Wikipedia, DE: http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streudiagramm
- Wikipedia Correlation, EN: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Correlation
- Wikipedia Linear Regression, EN:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_regression
- University of Illinois: http://www.mste.uiuc.edu/courses/ci330ms/youtsey/scatterinfo.html
- Information Technology Lab, NIST #1: http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda33q.htm
- Information Technology Lab, NIST #2: http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/linecorr.htm
- NetMBA: http://www.netmba.com/statistics/plot/scatter/
- ChartItNow: http://www.chartitnow.com/scatter%20diagram.html
- addictedtor.free.fr: http://addictedtor.free.fr/graphiques/graphcode.php?graph=59
- York University: http://www.math.yorku.ca/SCS/sasmac/sunplot.html
- NLVM: http://matti.usu.edu/nlvm/nav/frames_asid_144_g_4_t_5.html
- AI Lab: www.ailab.si/janez/visualizations.html