Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2008/09 - Gruppe 01 - Aufgabe 1 - Visual Encoding: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
*[Card et al., 1999] Stuart K. Card, Jock D. Mackinlay, and Ben Schneiderman. ''Readings in Information Visualization. Using Vision to Think.''Morgan Kaufman Publ Inc, San Diego, 1990. | |||
* [Dürsteler, 2005] Juan C. Dürsteler, Web Content Mining Visualisation. Created at: November 7. http://www.infovis.net/printMag.php?num=175&lang=2. | * [Dürsteler, 2005] Juan C. Dürsteler, Web Content Mining Visualisation. Created at: November 7. http://www.infovis.net/printMag.php?num=175&lang=2. | ||
* [Ignatius and Senay, 1999] Ignatius Eve, and Senay Hikmet, Data,vocabulary,marks,composition rules and visual perception rules. Created at: ?. http://cose.math.bas.bg/Sci_Visualization/visConcepts/concepts/marks.htm. | * [Ignatius and Senay, 1999] Ignatius Eve, and Senay Hikmet, Data,vocabulary,marks,composition rules and visual perception rules. Created at: ?. http://cose.math.bas.bg/Sci_Visualization/visConcepts/concepts/marks.htm. | ||
*[Jacko and Sears, 2002] Julie A. Jacko, and Andrew Sears.''The Human-computer Interaction Handbook: Fundamentals, Evolving Technologies.''Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc in, NY, 2002. | *[Jacko and Sears, 2002] Julie A. Jacko, and Andrew Sears.''The Human-computer Interaction Handbook: Fundamentals, Evolving Technologies.''Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc in, NY, 2002. | ||
*[ | * [Munzner, 2000] Tamara Munzner, Interactive Visualization of Large Graphs and Networks. Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University. June 2000, http://graphics.stanford.edu/papers/munzner_thesis/. | ||
* [Waloszek, 2008] Gerd Waloszek, SAP AG, SAP User Experience,Selecting Objects By Attributes – Part II. Created at: October 3. http://www.sapdesignguild.org/.../attributes_2.asp . | * [Waloszek, 2008] Gerd Waloszek, SAP AG, SAP User Experience,Selecting Objects By Attributes – Part II. Created at: October 3. http://www.sapdesignguild.org/.../attributes_2.asp . | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 7 November 2008
Visual Encoding
Definition
Visual encoding is the set of techniques enabling the representation of data on a screen or on paper. It comprises of the use of shapes, colours, areas and other visual variables that make it possible to associate data variables to graphic variables [Dürsteler, 2005]. Visual encodings are mappings of information to display elements [Munzner, 2000].
Techniques of Visual Encoding
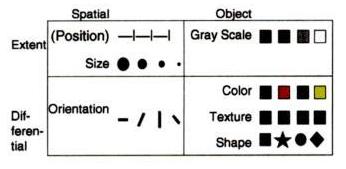
The fundamental substrate of visualizations is spatial position. Marks such as points, lines, or area-covering elements can be placed on this substrate. These marks can carry additional information independent of their spatial position, such as size, greyscale luminance (brightness) value, surface texture density, color hue, color saturation, curvature, angle, and shape [Munzner, 2000].
- Space
- Marks
- Connections & Enclosures
- Retinal Properties
- Temporal Encoding
- Viewpoint Transformation
Space
When you think about an empty paper as the beginning of a visualisation, the space between some possible object is one of the most powerful aspects to give something an important note.
Marks
Marks are the visible things that occur in space [Card et al., 1999], and are simply any graphical symbol visible on a display medium [Ignatius and Senay, 1999]. There are four types of simple Marks :
- Points
- Lines
- Areas
- Volumes
Connections & enclosures
Connections and enclosures build the important dependencies between the objects (marks). Connections show a relationship between objects, while enclosures can also indicate related objects.
Retinal properties
A retinal encoding is any variation of the marks that the retina of the eye can perceive besides position [Ignatius and Senay, 1999]. They are the informations that are carried by marks, such as crispness, shape, resolution, transperancy, color(value,hue & saturation), grayscale [Munzner, 2000]. Retinal properties describe how objects (marks) look like.
Temporal encoding
A temporal encoding shows how the marks' properties vary over time. It's the encoding which depends on the temporal changes of marks (mark position and their retinal properties) [Ignatius and Senay, 1999].
Viewpoint transformations
Viewpoint transformations modify interactively and augment Visual Structures to turn static presentations into visualizations by establishing graphical parameters to create Views of Visual Structures [Card et al., 1999; Jacko and Sears, 2002] in other words it is the modification of the view position of the viewer (or in general the modification of viewing parameters), thus enhancing the visual perception.
There are three common view transformations :
- Location Probes : Usage of Location in the visual structures to reveal additional info
- Viewpoint control : Moving the viewpoint to create visualisation : Pan,zoom,clip the viewpoint.
- Distortion : Creating a focus area and context area.
References
- [Card et al., 1999] Stuart K. Card, Jock D. Mackinlay, and Ben Schneiderman. Readings in Information Visualization. Using Vision to Think.Morgan Kaufman Publ Inc, San Diego, 1990.
- [Dürsteler, 2005] Juan C. Dürsteler, Web Content Mining Visualisation. Created at: November 7. http://www.infovis.net/printMag.php?num=175&lang=2.
- [Ignatius and Senay, 1999] Ignatius Eve, and Senay Hikmet, Data,vocabulary,marks,composition rules and visual perception rules. Created at: ?. http://cose.math.bas.bg/Sci_Visualization/visConcepts/concepts/marks.htm.
- [Jacko and Sears, 2002] Julie A. Jacko, and Andrew Sears.The Human-computer Interaction Handbook: Fundamentals, Evolving Technologies.Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc in, NY, 2002.
- [Munzner, 2000] Tamara Munzner, Interactive Visualization of Large Graphs and Networks. Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University. June 2000, http://graphics.stanford.edu/papers/munzner_thesis/.
- [Waloszek, 2008] Gerd Waloszek, SAP AG, SAP User Experience,Selecting Objects By Attributes – Part II. Created at: October 3. http://www.sapdesignguild.org/.../attributes_2.asp .