Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2008/09 - Gruppe 01 - Aufgabe 1 - Cartogram: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
{{Quotation|A cartogram is a map in which some thematic mapping variable – such as travel time or Gross National Product – is substituted for land area. The geometry or space of the map is distorted in order to convey the information of this alternate variable.|[Wikipedia, 2009]}} | {{Quotation|A cartogram is a map in which some thematic mapping variable – such as travel time or Gross National Product – is substituted for land area. The geometry or space of the map is distorted in order to convey the information of this alternate variable.|[Wikipedia, 2009]}} | ||
== More about Cartogram == | == More about Cartogram == | ||
A Cartogram is a small diagram, on the face of a map, showing quantitative information or an abstracted and simplified map the base of which is not true to scale. Simply we can say cartograms are unique representations of geographical space. They use cartographic outlines to represent data which depends on the source of the chosen country('s). [Bortis and Demers, 2002]. | A Cartogram is a small diagram, on the face of a map, showing quantitative information or an abstracted and simplified map the base of which is not true to scale. Simply we can say cartograms are unique representations of geographical space. They use cartographic outlines to represent data which depends on the source of the chosen country('s). [Bortis and Demers, 2002]. <br/> | ||
[[Image:USA2.jpg| | [[Image:USA2.jpg|right|300px|thumb|Figure 1: [Kocmound, 1997] a) traditional choropleth thematic map b) Cartogram]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
In non-continuous cartograms the regions on the map don't have to be connected to their neighbors. In this type of cartogram it is important to see the shape of the original map. User will recognize the map just because of their borders. The regions in the map are displaying the content with their own size. For an example a region with a smaller population will be smaller than a sector with a higher population [Kocmoud, 1997]. | In non-continuous cartograms the regions on the map don't have to be connected to their neighbors. In this type of cartogram it is important to see the shape of the original map. User will recognize the map just because of their borders. The regions in the map are displaying the content with their own size. For an example a region with a smaller population will be smaller than a sector with a higher population [Kocmoud, 1997]. | ||
[[Image:noncont.jpg| | [[Image:noncont.jpg|right|300px|thumb|Figure 2: [Kocmound, 1997] non-continous cartogram - a) overlapping b) non-overlapping]] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
Different to the non-continuous cartograms, the important point is that the regions in the map are connected to each other. Accordingly the shape of each region is changing their size [Bortis and Demers, 2002]. Therefore the outline of the hole map changes. For example as we can see in the picture below, France is very distorted but still connected to his neighbors. With changing the shape of this country, the outlines of the whole map has changed [Wikipedia, 2008]. | Different to the non-continuous cartograms, the important point is that the regions in the map are connected to each other. Accordingly the shape of each region is changing their size [Bortis and Demers, 2002]. Therefore the outline of the hole map changes. For example as we can see in the picture below, France is very distorted but still connected to his neighbors. With changing the shape of this country, the outlines of the whole map has changed [Wikipedia, 2008]. | ||
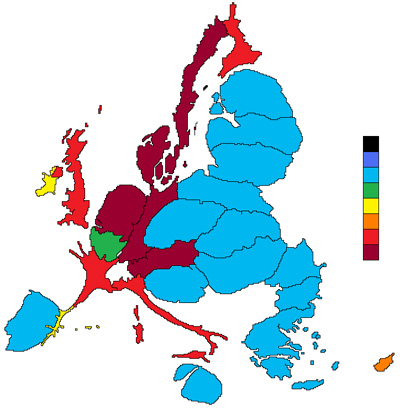
[[Image:europe.jpg| | [[Image:europe.jpg|right|300px|thumb|Figure 3: [Wikipedia, 2008] Cartogram of europe net budget expenditure in euros for the whole period 2007-2013 per capita using continuos cartograms]] | ||
* Perimeter-Preserving Cartograms | * Perimeter-Preserving Cartograms | ||
Revision as of 00:29, 3 November 2009
Cartogram
Definition
More about Cartogram
A Cartogram is a small diagram, on the face of a map, showing quantitative information or an abstracted and simplified map the base of which is not true to scale. Simply we can say cartograms are unique representations of geographical space. They use cartographic outlines to represent data which depends on the source of the chosen country('s). [Bortis and Demers, 2002].
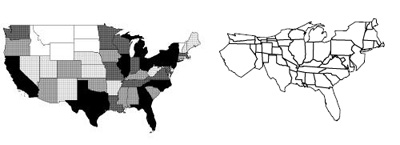
For example on the left side of Figure 1. you can see a traditional map of the United states and on the right side a Cartogram of USA depending on the population density. Sometimes it is enough to just color a map, like in Figure 1 on the left, to see some statistical data like the population but if you want to show a thing like the size of state it is sometimes better to use the same value (the size) to show the difference between the values.
The size of a cartogram is depending on the value of the part shown in the picture. For example in Figure 1 the state california is in the cartogram bigger then in the original because it has a high population. On the other side Ohio seems to be smaller on the right side then on the left because it is a big state from the area but has a low population.
Types of Cartograms
- Non-Continuous Cartograms
In non-continuous cartograms the regions on the map don't have to be connected to their neighbors. In this type of cartogram it is important to see the shape of the original map. User will recognize the map just because of their borders. The regions in the map are displaying the content with their own size. For an example a region with a smaller population will be smaller than a sector with a higher population [Kocmoud, 1997].
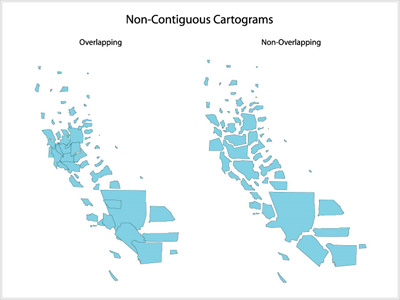
- Continuos Cartograms
Different to the non-continuous cartograms, the important point is that the regions in the map are connected to each other. Accordingly the shape of each region is changing their size [Bortis and Demers, 2002]. Therefore the outline of the hole map changes. For example as we can see in the picture below, France is very distorted but still connected to his neighbors. With changing the shape of this country, the outlines of the whole map has changed [Wikipedia, 2008].
- Perimeter-Preserving Cartograms
In this version the outline of the map is the same as in the original image. The regions in it are still connected to each other, so the only change is the border of the regions which is moving but still connected to his neighbors [Kocmoud, 1997].
- The usage of different shapes for representation of the regions
One type that can be used is the Dorling Cartogram. In this form the original regions are replaced with circles of varying size. With this kind of shape it is easier to see the difference between the regions. The same strategy is used by Demers which is use squares instead of circles. The positive effect of this is, that there are no free spaces between them [Florisson et al., 2005].
References
- [Bortis and Demers, 2002]Ian Bortis, and Steve Demers, USGS, Cartogram Central. Created at: December 7, 2002. http://www.ncgia.ucsb.edu/projects/Cartogram_Central/index.html .
- [Kocmoud, 1997] Christopher James Kocmoud, Constructing Continuous Cartograms:
A Constraint-Based Approach. Created at: December, 1997. http://www-viz.tamu.edu/faculty/house/cartograms/Thesis.html .
- [Florisson et al., 2005] Sander Florisson, Marc van Kreveld, and Bettina Speckmann. Rectangular Cartograms : Construction & Animation. 'Annual Symposium on Computational Geometry'.372–373, 2005.
- [Wikipedia, 2008] Wikipedia. Cartogramm. Retrieved at: October 5, 2008. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cartogram .