Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2006/07 - Gruppe 03 - Aufgabe 1 - InfoZoom
Definition
InfoZoom is an application, developed by the company humanIT a spin-off of Fraunhofer Society, for analyzing and displaying large amounts of data in an easy-to-understand format.
History
InfoZoom evolved from another system called FOCUS, a focus+context table layout [Kort, 2004].
Description
Overview
Primarily, InfoZoom was developed for manipulating tables. By default it uses parallel bargrams for larger sizes of data sets and special focus+context tables for smaller ones [Wittenburg et al, 2001]. So it is possible to present information in table or distribution oriented formats.
When displaying relational data tables, InfoZoom uses one row for each record. This data can be sorted sequential, hierarchical or in any other way the user wants it to be sorted. If necessary, the user can "zoom" into the information. This happens for example by doubleclicking on attribute values or sets/ranges of values [Mark et al, 2003]. This "zooming" can also be done by selecting columns of a row interactively and then promoting them into qualified records. All other records except those marked as qualified records are hidden instantly, enabling a "zoomed" view on the information.
[Wittenburg et al, 2001]
Data source
The user can import data either with the import tool for Excel or text files or use an ODBC or OLE DB connection.
View Modes
InfoZoom offers three modes for data analysis: wide table, compressed table and overview
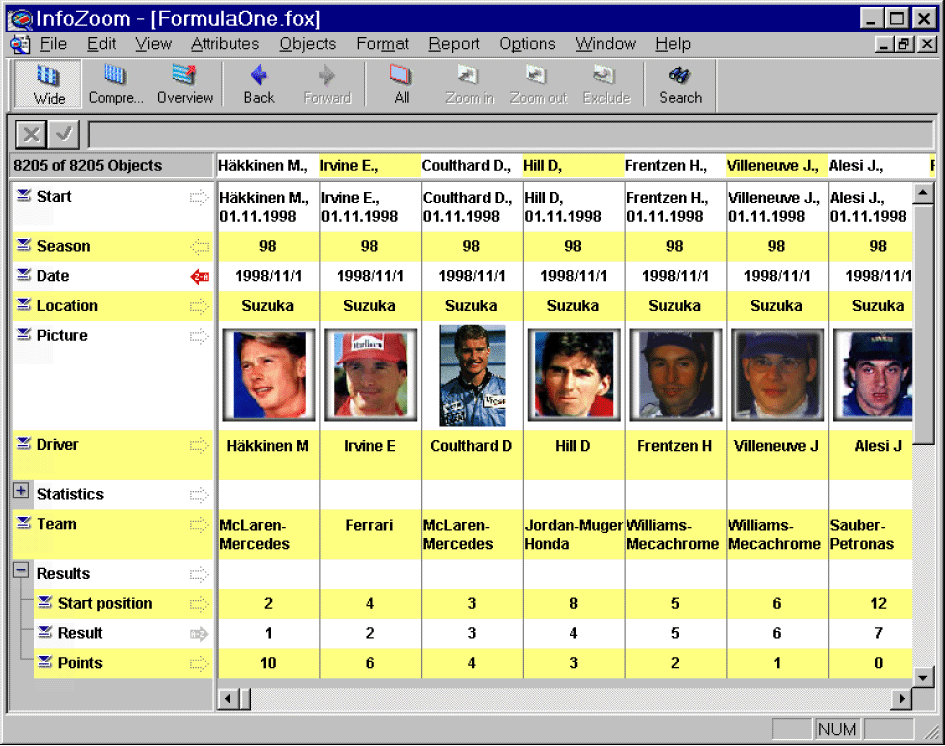
Wide Table
The wide table looks like a table we know from spreadsheets or database tables. Every attribute is shown as a row and the objects as columns. If the windows is not big enough to show all records or attributes you can scroll vertically or horizontally
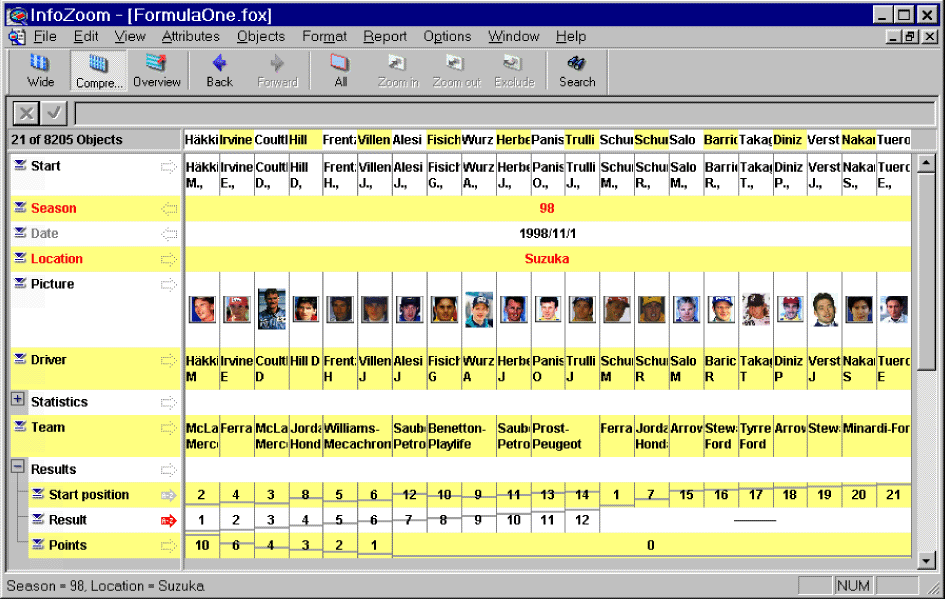
Compressed Table
The compressed table shows all objects pushed together to fit on the screen. Numerical values are represented by the vertical position of dots. The data can be sorted by individual attributes in ascending or descendig order.
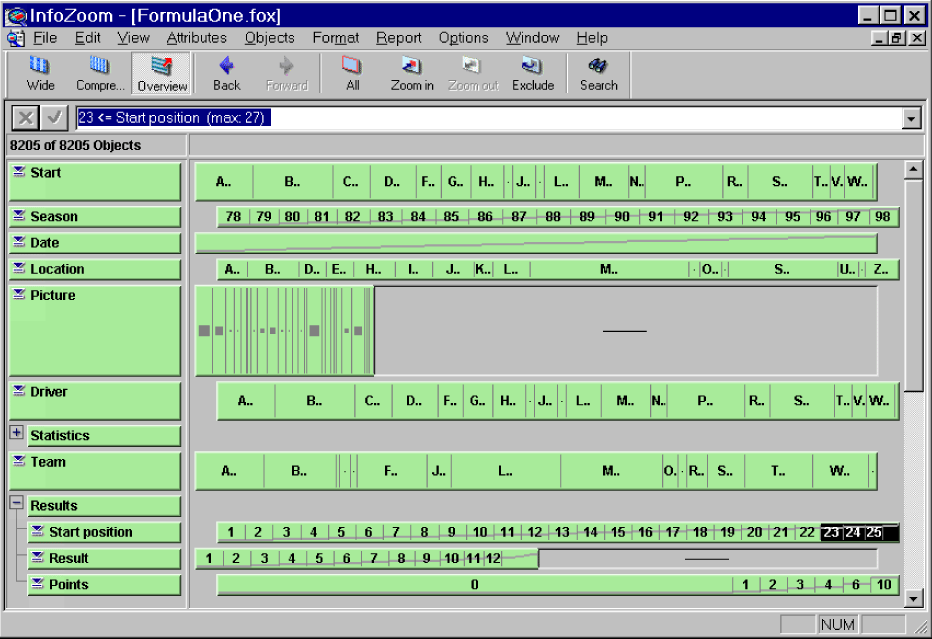
Overview Mode
The overview mode allows that the content of each attributes row are sorted independently. The identical values are placed together in a cell. The width of the cell represents the frequency of this value.
Filter
With filter the user can search data or find patterns in a dataset. You can search after a specific value or value range on an attribute.
Derived Attribute
The user can combine attributes with derived attributes. The new value is calculated from the values of one or two already existing attributes.
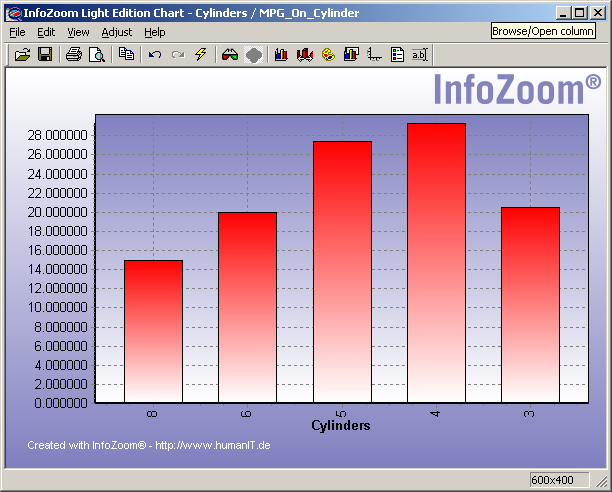
Graphics Report
Graphic Reports can be created with different styles, e.g. Pie, Donut, Bar, Horiz Bar, Line, Area, Point, Bubble, Volume, ...
Use
InfoZoom is often used for Visual Data Mining (VDM), a process which aims at the recognition of patterns in data by an human expert. VDM makes use of an technique called focus+context. Here, it's possible for the expert to show focused and contextual information at the same time. [Kort, 2004]
References
[humanIT, 2006] Author unknown: InfoZoom; humanIT Software GmbH; Access Date: 30 Oct 2006; URL: http://www.infozoom.com/enu/infozoom/index.htm
[Kort, 2004] Alexander Kort. Visual Data Mining and Zoomable Interfaces. In Proceedings of the 9th international conference on Intelligent user interface. pages 274-276, New York, NY, 2004. ACM Press
[Mark et al, 2003] Gloria Mark, Keri Carpenter, Alfred Kobsa. Are There Benefits in Seeing Double? A Study of Collaborative Information Visualization. In CHI '03 extended abstracts on Human factors in computing systems, pages 840-841, Irvine, CA, April 2003. ACM Press
[Spenke, 2000] Michael Spenke and Christian Beilken. InfoZoom - Analysing Formula One Racing Results With an Interactive Data Mining and Visualisation Tool. Second Conference on Data Mining 2000; URL: http://www.ifs.tuwien.ac.at/~silvia/wien/vu-infovis/articles/spenke00infozoom.pdf
[Wittenburg et al, 2001] Kent Wittenburg, Tom Lanning, Michael Heinrichs, Michael Stanton. Parallel bargrams for consumer-based information exploration and choice. In Proceedings of the 14th annual ACM symposium on User interface software and technology, pages 51-60, Waltham, MA, November 2001. ACM Press
[Xie, 2006] Zaixian Xie: Review on InfoZoom; Worcester Polytechnic Insitute: Course Data Visualization; Creation Date: 1. Feb. 2006 Access date: 30. Oct. 2006; URL: http://users.wpi.edu/~xiezx/courses/cs525d/infozoom/infozoom.htm