Cone Trees
Authors
Short description
The task of managing and accessing large information spaces is a problem in large scale cognition. Emerging technologies for 3D visualization and interactive animation offer potential solutions to this problem, especially when the structure of the information can be visualized. We describe one of these Information Visualization techniques, called the Cone Tree, which is used for visualizing hierarchical information structures. The hierarchy is presented in 3D to maximize effective use of available screen space and enable visualization of the whole structure. Interactive animation is used to shift some of the user's cognitive load to the human perceptual system.
Suitable Datatypes
Suitable Datatypes are hierarchical information structures.
Figures
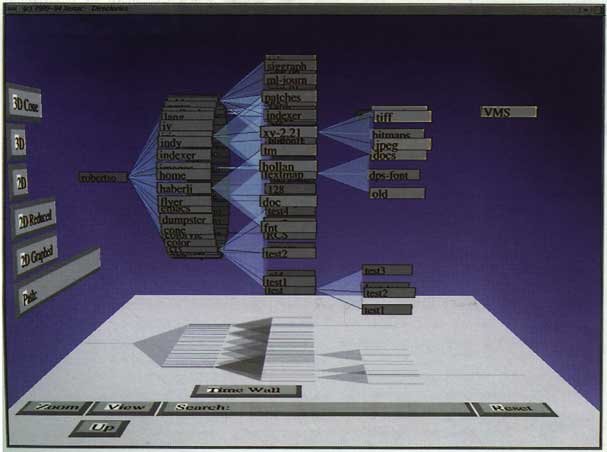
Each tree node is the apex of a cone. The children of each node are drawn around the base of its associated cone.
Examples and use cases
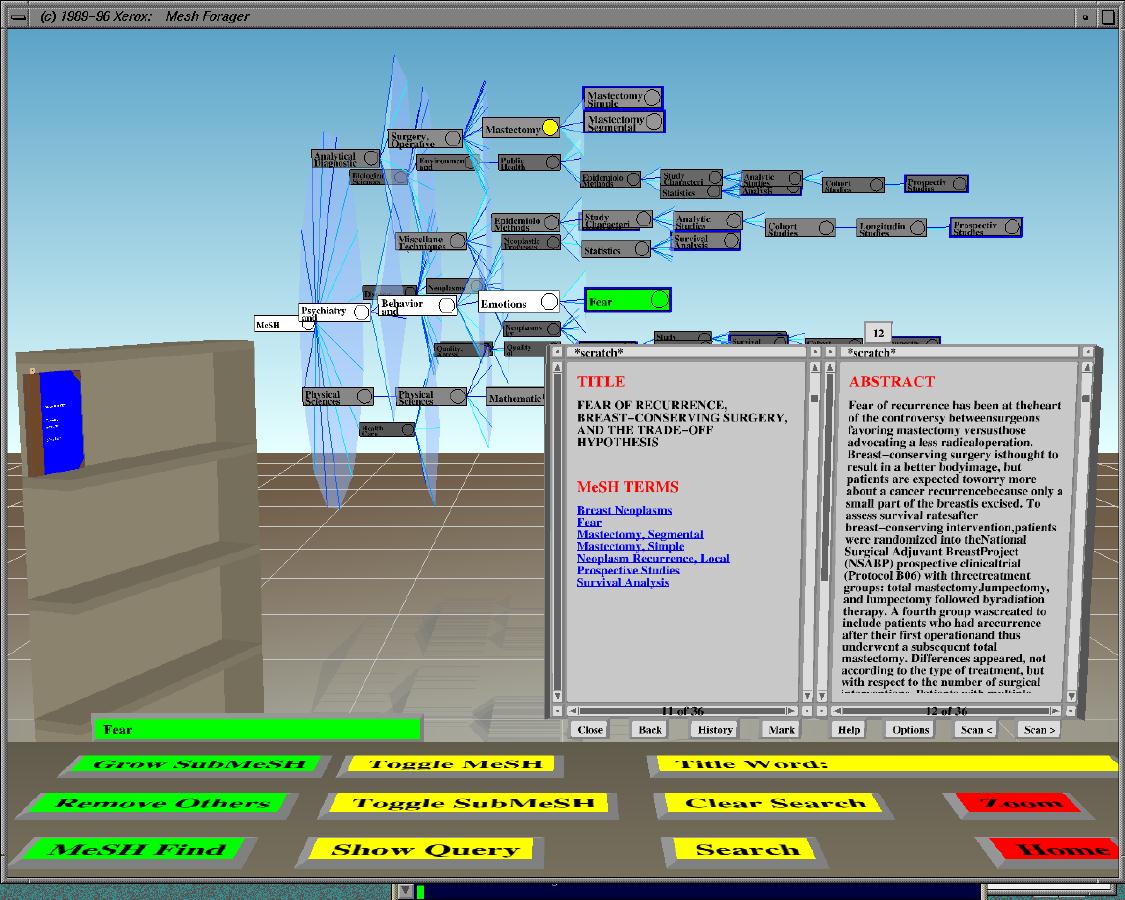
Cat-a-Cone (Hearst & Karadi 1997)
The Cat-a-Cone interface.
The Cat-a-Cone is a novel user interface that integrates search and browsing of very large category hierarchies with their associated text collections. One key insight is the separation of the representation of category labels from documents, which allows the display of multiple categories per document. Another key component is the display of multiple selected categories simultaneously, complete with their hierarchical context.
Shown are the results of a search on category labels Mastectomy and Radiation Therapy in conjunction with the text word lumpectomy on a breast cancer subset of the MEDLINE collection. A ConeTree displays category labels and a WebBook shows retrieval results. The lefthand page shows the title and the category labels associated with the document. The righthand page shows the abstract associated with the document. Books that are the results of previous searches are stored in the workspace on the bookshelf, thus acting as a memory aid.
Lyberworld (Matthias Hemmje et al 1994)
LyberWorld is a 3D visualization user interface supporting fulltext retrieval.
Example 1: A UNIX file-system displayed as cone-tree
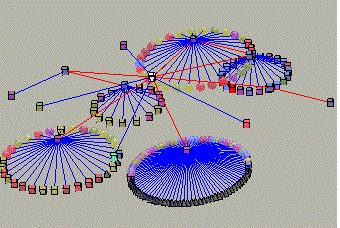
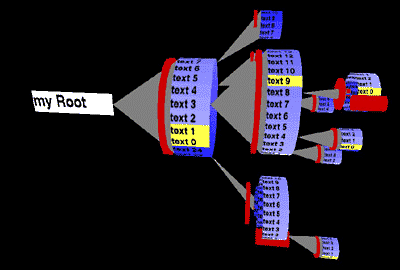
Example 2: Layout of a simple Cone Tree