Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2007/08 - Gruppe 07 - Aufgabe 1 - Boxplot
Definitions
In descriptive statistics, a boxplot (also known as a box-and-whisker diagram or plot or candlestick chart) is a convenient way of graphically depicting groups of numerical data through their five-number summaries (the smallest observation, lower quartile (Q1), median, upper quartile (Q3), and largest observation). A boxplot also indicates which observations, if any, might be considered outliers. The boxplot was invented in 1977 by the American statistician John Tukey.
Boxplots are able to visually show different types of populations, without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution. The spacings between the different parts of the box help indicate variance, skewness and identify outliers. Boxplots can be drawn either horizontally or vertically.
Boxplots are able to visually show different types of populations, without making any assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution. The spacings between the different parts of the box help indicate variance, skewness and identify outliers. Boxplots can be drawn either horizontally or vertically.
[Wikipedia, 2007]
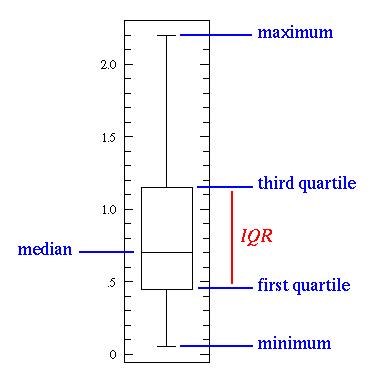
Explanation
TODO PETER ... WEBSTERs ...
Example
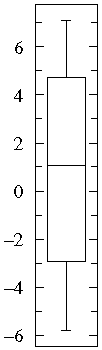
As an example we consider values given from the table on the right to create a boxplot (right image). Notice that the dataset is approximately balanced around zero. Evidently the mean is near zero. However there is a variation in the dataset which ranges approximately from -6 to 6. The maximum and minimum values are showed as whiskers. Hence it is obvious that the boxplot is a powerful visualisation that has the ability to outframe characteristic attributes of the given dataset, in a way that viewers can quickly gain important informations from the visualisation that characterise the data.
|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Related Links
References
- [Wikipedia, 2007] Wikipedia, Box plot. Retrieved at: November 01, 2007. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Box_plot