Cone Trees: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Figures == | == Figures == | ||
[[Image:cone1.GIF]]<br/><br/> | |||
[[Image:cone2.GIF]]<br/><br/> | |||
== Examples and use cases == | == Examples and use cases == | ||
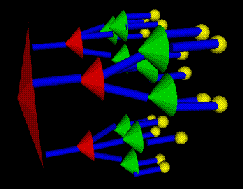
Each tree node is the apex of a cone. The children of each node are drawn around the base of its associated cone. <br/><br/> | Each tree node is the apex of a cone. The children of each node are drawn around the base of its associated cone. <br/><br/> | ||
[[Image:cones.gif]]<br/><br/> | |||
''Example 1: A UNIX file-system displayed as cone-tree''<br/><br/> | ''Example 1: A UNIX file-system displayed as cone-tree''<br/><br/> | ||
[[Image:conetree.jpg]]<br/> | |||
''Example 2: Layout of a simple Cone Tree''<br/> | ''Example 2: Layout of a simple Cone Tree''<br/> | ||
Revision as of 16:59, 17 April 2006
BUILDING SITE
Authors
Short description
The task of managing and accessing large information spaces is a problem in large scale cognition. Emerging technologies for 3D visualization and interactive animation offer potential solutions to this problem, especially when the structure of the information can be visualized. We describe one of these Information Visualization techniques, called the Cone Tree, which is used for visualizing hierarchical information structures. The hierarchy is presented in 3D to maximize effective use of available screen space and enable visualization of the whole structure. Interactive animation is used to shift some of the user's cognitive load to the human perceptual system.
Suitable Datatypes
Suitable Datatypes are hierarchical information structures.
Figures
Examples and use cases
Each tree node is the apex of a cone. The children of each node are drawn around the base of its associated cone.
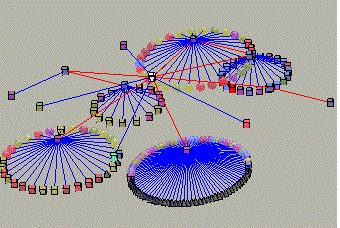
Example 1: A UNIX file-system displayed as cone-tree
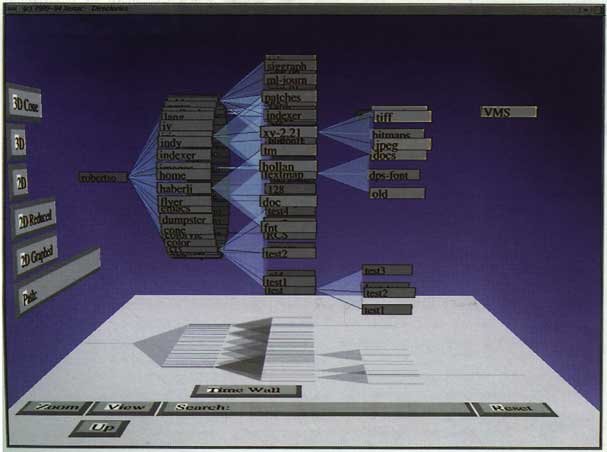
Example 2: Layout of a simple Cone Tree