Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2008/09 - Gruppe 09 - Aufgabe 1 - Types of Data (quantitative vs. qualitative): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Definition= | ==Definition== | ||
===Qualitative | ===Qualitative data=== | ||
{{Quotation | The term qualitative is used to describe certain types of information. Qualitative data are described in terms of quality (that is, 'informal' or relative characteristics such as warmth and flavour). This is the converse of quantitative, which more precisely describes data in terms of quantity and often using a numerical figure to represent something in a statement.| | {{Quotation | The term qualitative is used to describe certain types of information. Qualitative data are described in terms of quality (that is, 'informal' or relative characteristics such as warmth and flavour). This is the converse of quantitative, which more precisely describes data in terms of quantity and often using a numerical figure to represent something in a statement.| Wikipedia, Nov 2008 }} | ||
===Quantitative | ===Quantitative data=== | ||
{{Quotation | [...] Quantitative data is data measured or identified on a numerical scale. Numerical data can be analysed using statistical methods, and results can be displayed using tables, charts, histograms and graphs. For example, a researcher will ask a questions to a participant that include words how often, how many or percentage. The answers from the questions will be numerical. [...] After the data is collected the researcher will make an analysis of the quantitative data and produce statistics.| | {{Quotation | [...] Quantitative data is data measured or identified on a numerical scale. Numerical data can be analysed using statistical methods, and results can be displayed using tables, charts, histograms and graphs. For example, a researcher will ask a questions to a participant that include words how often, how many or percentage. The answers from the questions will be numerical. [...] After the data is collected the researcher will make an analysis of the quantitative data and produce statistics.| Wikipedia, Nov 2008 }} | ||
<br> | |||
---- | |||
==Field of Application== | |||
===Quantitative research=== | |||
Quantitative research is done by systematically collecting and analyzing numerical data concerning the subject. The researcher knows clearly in advance what he/she is looking for, i.e. all aspects of the study have to be carefully designed before the data is collected. One advantage of quantitative research is, that it tends to stay more objective than qualitative research. Furthermore statistical models can be constructed or hypotheses can be developed based on the collected quantitative data.<br> | |||
Quantitative research is widely used in both, natural and social sciences. Because quantitative methods are only supplied with numerical data, the results most of the times lack contextual details. | |||
===Qualitative research=== | |||
Qualitative research is used when the goal is a complete and detailed description of the subject. The data is not presented in form of numbers an statistics as in quantitative data, but in the form of words, pictures and objects. Contrary to quantitative methods it is much more subjective, because the observations which are made during a research a strongly dependent on the researcher's interpretation.<br> | |||
In most cases qualitative methods aim to gather an in-depth understanding of human behavior and the causes that affect human behavior. There are many different ways of doing qualitative research. Qualitative data can be gained through in-depth interviews with persons or groups, direct observation or even through referring to existing written papers. | |||
---- | ---- | ||
==Example: Qualitative data vs. quantitative data== | |||
===Oil Painting=== | |||
<table> | <table> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 54: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
<br><br> | |||
---- | |||
===different opinions...=== | |||
{{Quotation | All research ultimately has a qualitative grounding | [Donald Campbell] }}{{Quotation | There's no such thing as qualitative data. Everything is either 1 or 0 | [Fred Kerlinger] }} | {{Quotation | All research ultimately has a qualitative grounding | [Donald Campbell] }}{{Quotation | There's no such thing as qualitative data. Everything is either 1 or 0 | [Fred Kerlinger] }} | ||
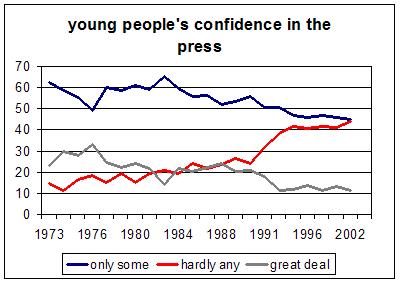
===Example for quantitative data:=== | ===Example for quantitative data:=== | ||
Revision as of 01:39, 26 November 2008
Definition
Qualitative data
Quantitative data
Field of Application
Quantitative research
Quantitative research is done by systematically collecting and analyzing numerical data concerning the subject. The researcher knows clearly in advance what he/she is looking for, i.e. all aspects of the study have to be carefully designed before the data is collected. One advantage of quantitative research is, that it tends to stay more objective than qualitative research. Furthermore statistical models can be constructed or hypotheses can be developed based on the collected quantitative data.
Quantitative research is widely used in both, natural and social sciences. Because quantitative methods are only supplied with numerical data, the results most of the times lack contextual details.
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is used when the goal is a complete and detailed description of the subject. The data is not presented in form of numbers an statistics as in quantitative data, but in the form of words, pictures and objects. Contrary to quantitative methods it is much more subjective, because the observations which are made during a research a strongly dependent on the researcher's interpretation.
In most cases qualitative methods aim to gather an in-depth understanding of human behavior and the causes that affect human behavior. There are many different ways of doing qualitative research. Qualitative data can be gained through in-depth interviews with persons or groups, direct observation or even through referring to existing written papers.
Example: Qualitative data vs. quantitative data
Oil Painting
|
Qualitative data:
|
Quantitative data:
|
different opinions...
Example for quantitative data:
References
[James Neill] Qualitative versus Quantitative Research:
Key Points in a Classic Debate, http://wilderdom.com/research/QualitativeVersusQuantitativeResearch.html
[Donna Roberts] Qualitative vs Quantitative Data, http://www.regentsprep.org/Regents/math/ALGEBRA/AD1/qualquant.htm
[Peter Levine] http://www.peterlevine.ws/mt/archives/cat_press_criticism.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantitative_data
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Qualitative_data