Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2007/08 - Gruppe 09 - Aufgabe 1 - Computer Graphics
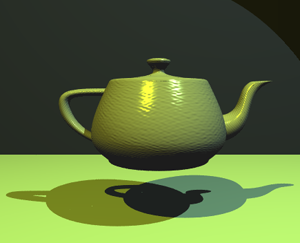
Perhaps the best way to define computer graphics is to find out what it is not. It is not a machine. It is not a computer, nor a group of computer programs. It is not the know-how of a graphic designer, a programmer, a writer, a motion picture specialist, or a reproduction specialist.
Computer graphics is all these – a consciously managed and documented technology directed toward communicating information accurately and descriptively.
[Fetter, 1965]
Definition
Computer graphics broadly studies the manipulation of visual and geometric information using computational techniques. Computer graphics as an academic discipline focuses on the mathematical and computational foundations of image generation and processing rather than purely aesthetic issues.
[Wikipedia, 2007]
Subfields
Computer Graphics may be divided into four major categories:
- Geometry: studies ways to represent and process surfaces
- Animation: studies with ways to represent and manipulate motion
- Rendering: studies algorithms to reproduce light transport
- Imaging: studies image acquisition or image editing

History
Application
- graphs and charts
- computer-aided design
- virtual-reality environment
- data visualisation
- education and training
- computer art
- entertainment
- image processing
- graphical user interfaces
References
[Fetter, 1966] W. A. Fetter, Computer Graphics in Communication, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, 1965.
[Wikipedia, 2007] Wikipedia, Computer Graphics. Retrieved at: November 8, 2007. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_graphics.