Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2006/07 - Gruppe 08 - Aufgabe 1 - Bifocal Display: Difference between revisions
(reorganized sections) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
A '''bifocal display''' provides a detailed view of the current region of interest while providing a more compressed view of information outside that region of interest. | A '''bifocal display''' provides a detailed view of the current region of interest while providing a more compressed view of information outside that region of interest. | ||
== | == Context == | ||
The desire to present all the relevant information within its context usually results in an extremely cluttered and confusing display. If only the current region of interest is displayed, one has to arrange for a mechanism to quickly switch to relevant information before and after the region of interest. Even so, much of the surrounding context is lost as it's not as easily accessible. [Spence, 2006] | The desire to present all the relevant information within its context usually results in an extremely cluttered and confusing display. If only the current region of interest is displayed, one has to arrange for a mechanism to quickly switch to relevant information before and after the region of interest. Even so, much of the surrounding context is lost as it's not as easily accessible. [Spence, 2006] | ||
This is known as the [[Focus-plus-Context|"focus+context"]] problem. | |||
== Original concept == | |||
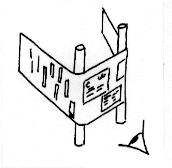
To address this problem, [[Spence, Robert|Spence]] and [[Apperley, Mark|Apperley]] proposed their "bifocal display". A bifocal display can be thought of as a continuous ribbon of data that is displayed on three seperate viewports or monitors (see image). The centre viewport is used to display the current region of interest while the left and right viewports are used to display the preceding and succeeding context respectively. The region of interest is displayed in great detail while the context in compressed, so as to allow one to identify objects at a cursory | |||
glance. | |||
Instead of simply compressing the context visually it could prove useful to choose a diffent representation for the peripherial viewports than is used for the central viewport. [Apperley et al., 1982] | Instead of simply compressing the context visually it could prove useful to choose a diffent representation for the peripherial viewports than is used for the central viewport. [Apperley et al., 1982] | ||
Most importantly, it should be easily possible to "scroll" backwards and forwards, replacing the current region of interest with content from its surrounding context, thus expanding the newly focused region of interest and relegating the former region of interest to its place in the compressed context. [Spence, 2006] | Most importantly, it should be easily possible to "scroll" backwards and forwards, replacing the current region of interest with content from its surrounding context, thus expanding the newly focused region of interest and relegating the former region of interest to its place in the compressed context. [Spence, 2006] | ||
[[Image:Bifocal_display_01.gif|frame|right||Bifocal display visualised as a continuous ribbon]] | |||
It would make sense to represent multiple documents, such as text files, using a bifocal display. The current file (region of interest) would be displayed in full on the primary (centre) display while other files would be represented by shapes on the peripherial displays. One could scroll through the documents and put individual files in and out of focus. Documents could be represented by different shape and colours, depending on characteristics such as importance, type or author. [Spence 2006] | |||
== Applications == | == Applications == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 22: | ||
Depending on how broad the metapher of bifocal display is understood, one can see all types of applications with some sort of ''navigation'' and ''detail'' pane (even Windows-Explorer) as applying this visualisation strategy. | Depending on how broad the metapher of bifocal display is understood, one can see all types of applications with some sort of ''navigation'' and ''detail'' pane (even Windows-Explorer) as applying this visualisation strategy. | ||
=== Current Examples === | === Current Examples === | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 30 October 2006
Definition
A bifocal display provides a detailed view of the current region of interest while providing a more compressed view of information outside that region of interest.
Context
The desire to present all the relevant information within its context usually results in an extremely cluttered and confusing display. If only the current region of interest is displayed, one has to arrange for a mechanism to quickly switch to relevant information before and after the region of interest. Even so, much of the surrounding context is lost as it's not as easily accessible. [Spence, 2006] This is known as the "focus+context" problem.
Original concept
To address this problem, Spence and Apperley proposed their "bifocal display". A bifocal display can be thought of as a continuous ribbon of data that is displayed on three seperate viewports or monitors (see image). The centre viewport is used to display the current region of interest while the left and right viewports are used to display the preceding and succeeding context respectively. The region of interest is displayed in great detail while the context in compressed, so as to allow one to identify objects at a cursory glance.
Instead of simply compressing the context visually it could prove useful to choose a diffent representation for the peripherial viewports than is used for the central viewport. [Apperley et al., 1982]
Most importantly, it should be easily possible to "scroll" backwards and forwards, replacing the current region of interest with content from its surrounding context, thus expanding the newly focused region of interest and relegating the former region of interest to its place in the compressed context. [Spence, 2006]
It would make sense to represent multiple documents, such as text files, using a bifocal display. The current file (region of interest) would be displayed in full on the primary (centre) display while other files would be represented by shapes on the peripherial displays. One could scroll through the documents and put individual files in and out of focus. Documents could be represented by different shape and colours, depending on characteristics such as importance, type or author. [Spence 2006]
Applications
Depending on how broad the metapher of bifocal display is understood, one can see all types of applications with some sort of navigation and detail pane (even Windows-Explorer) as applying this visualisation strategy.
Current Examples
[[Image:http://www.inxight.com/images/chart_timewall3.jpg%7Cframe%7Cright%7Cthumb%7C175px%7C%7CTimeWall(TM) - Employment of the metapher of continuous ribbon in a commercial application]
References
- [Spence, 2006] Bob Spence, The Acquisition of Insight. Accessed at: Oct 29, 2006, http://www.ee.ic.ac.uk/research/information/www/Bobs.html#Context
- [Apperley et al., 1982] M.D. Apperley, I. Tzavaras, R. Spence. A bifocal display technique for data presentation. Eurographics '82, p. 27. Abstract: http://diglib.eg.org/EG/DL/Conf/EG82/papers/EUROGRAPHICS_82pp027-043.pdf.abstract.pdf
Current Applications - bifocal display in practice/business:
- [InxightVizServer] Inxight VizServer - corporate web-site, product section. Accessed at: Oct 30, 2006. http://www.inxight.com/products/vizserver/
- [BrainEKP] TheBrainEKP: Enterprise Knowledge Platform - corporate web-site, product section. Accessed at: Oct 30, 2006.