Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2006/07 - Gruppe 03 - Aufgabe 3 - Technique: Difference between revisions
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
====User-Interaction==== | ====User-Interaction==== | ||
The user can choose the color of his/her circle. | The user can choose the color of his/her circle. | ||
The user can move the own circle around. | The user can move the own circle around. So identity is marked by color and position. | ||
====Use of Interactions==== | ====Use of Interactions==== | ||
Revision as of 16:45, 1 December 2006
Conversation Landscape
Chat Cirles Description
- Technique for vizualising Chats.
Mainly to get an better overview of the social interactions taking place in the chat.
In text-based chats (z.B. IRC) presence is shown only when one is actively messanging thats why silence and absence can't be distinguished.
In graphical chat systems people ar presented by a figure in a pictorial space. Avatars can be pictures, drawings or icons that users choose to represent themselves. It is visible so long as one is connected to the system.
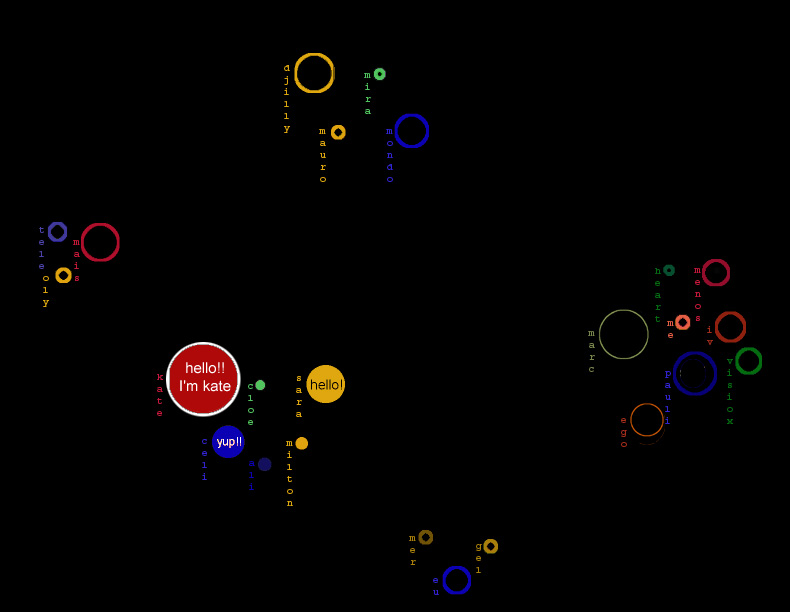
Chat Cirles is a graphical interface for synchronous communication.
Visual Mapping
- chat interface
Every person who is participating in the chat is represented with a coloured circle, the color is unique for each user. The messages of this user appears in this circle. The frequence of messages, who activ a user is, is shown this way, the circle gets bigger and brighter with every message and smaller and starts to fade within periodes of silence, but it is still visuable. The different topics are shown as groups of circles, because the user cann only "hear" others in a range around the own position.
- archive interface
Saving this movements over the time, you've got a visual communication history. In the chat archive interface of chat circles, again color is used to identify users.
Interaction
User-Interaction
The user can choose the color of his/her circle. The user can move the own circle around. So identity is marked by color and position.
Use of Interactions
- Navigation
- Zooming
- Highlighting
- Dynamic Querying
- Selection
- Brushing
Loom
Description
References
- [Donath et al., 1999] Donath, J., Karahalios, K., and Viegas, F.: Visualizing Conversation. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS) - Volume 2, page 2023. IEEE Computer Society, 1999.http://ieg.ifs.tuwien.ac.at/~aigner/teaching/infovis_ue/papers/ConversationLandscapes_VisualizeConv.pdf
- [Fernanda et al., 2002] Fernanda B. Viégas and Judith S. Donath.: Chat Circles Created at: 14, March 2000 . Retrieved at: Dezember 1, 2006. http://smg.media.mit.edu/papers/Viegas/ChatCircles/chat-circles_CHI.html.