Teaching:TUW - UE InfoVis WS 2005/06 - Gruppe G8 - Aufgabe 1 - Consistency: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
To give an example for the points mentioned in the list above, I want to refer to Microsoft Windows and its applications as a suite of products (list element 5). | To give an example for the points mentioned in the list above, I want to refer to Microsoft Windows and its applications as a suite of products (list element 5). | ||
'''ad 5.'''<br> | |||
In the Microsoft Windows software and in most of Microsofts products shortcut are of the same nature: <b>STRG+[underlined letter of command]</b>.<br> | In the Microsoft Windows software and in most of Microsofts products shortcut are of the same nature: <b>STRG+[underlined letter of command]</b>.<br> | ||
[[Image:Shortcuts.jpg]]<br><br> | [[Image:Shortcuts.jpg]]<br><br> | ||
Revision as of 13:28, 23 October 2005
Definition(s)
Consistency describes a harmonious uniformity or agreement among things or parts.
[Hyperdictionary.com, 2005]
Agreement or harmony of all parts of a complex thing among themselves, or of the same thing with itself at different times.
[Whatdowordsmean.com, 2005]
Key Words
Consistency, design, information visualization
Abstract
"Consistency (in Design)" is often referred to as the central criteria for successful user interaction. Any interface wants to keep its user focused, and additionally guide him to a procedure or structure. All this needs a clear and consistent framework of elements within the design of the interface. Consistency can create a distinct sense of "place" and makes parts and functions in a system memorable [Lynch and Horton, 2002].
Article
The following list tries to give a ranking, which elements of an interface are most important to be consistent [Bruce Tognazzini, 2003].
- Interpretation of user behavior, e. g., shortcut keys maintain their meanings.
- Invisible structures.
- Small visible structures.
- The overall "look" of a single application or service--splash screens, design elements.
- A suite of products.
- In-house consistency.
- Platform-consistency.
It is a common error to assume the list is should be the other way round, providing interfaces looking similar on the outside, but have a completely different behaviour on the inside. This would lead to major difficulties in usage, and thus in the success of the system. [Bruce Tognazzini, 2003]
To give an example for the points mentioned in the list above, I want to refer to Microsoft Windows and its applications as a suite of products (list element 5).
ad 5.
In the Microsoft Windows software and in most of Microsofts products shortcut are of the same nature: STRG+[underlined letter of command].
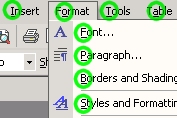
As you can see this gives the impression that the way of treating commands always swings that way. Unfortunatly it does not. The next screenshot shows that there are parts of the software where the shortcut rule is violated.
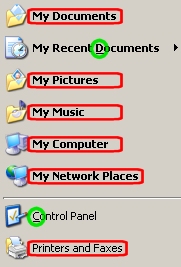
Examples
Conclusion
Bibliography
[Bruce Tognazzini, 2003]
First Principles of Interaction Design, Nielsen Norman Group
http://www.asktog.com/basics/firstPrinciples.html
[Hyperdictionary.com, 2005]
Consistency
http://www.hyperdictionary.com/dictionary/consistency
[Whatdowordsmean.com, 2005]
Consistency
http://www.whatdowordsmean.com/definition/consistency/
[Lynch and Horton, 2002]
Webstyleguide 2nd edition
http://www.webstyleguide.com/page/consistent.html
Back to G8