Social Network Generation
Issues on Social Network Generation for Evaluating Visualizations
Watts and Strogatz first described in (Watts, D. J. and S. H. Strogatz (1998). "Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks." Nature 393: 440 - 442) the concept of small-world networks. They formalized these networks as graphs with three properties: power-law degree distribution, high clustering coefficient and small average shortest path. In the same paper they propose a basic model fitting these properties consisting in a grid (fixed local neighborhood) with additional links simulating some unexpected relations support to the six degrees of separation discovered by Milgram (Milgram, S. (1967). "The small world problem." Psychology Today: 60-67). Barabási and Albert proposed an incremental model to improve it (Barabási, A.-L. and R. Albert (1999). "Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks." Science 286(5439): 509 - 512. ). Since Watts and Strogatz’ model, several have been proposed each generating networks with one or two of the described properties (power-law) but none combine the three of them.
Here are some results of available generators present in the JUNG package.
Issues on Social Network Generation for Evaluating Visualizations
Watts and Strogatz first described in (Watts, D. J. and S. H. Strogatz (1998). "Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks." Nature 393: 440 - 442) the concept of small-world networks. They formalized these networks as graphs with three properties: power-law degree distribution, high clustering coefficient and small average shortest path. In the same paper they propose a basic model fitting these properties consisting in a grid (fixed local neighborhood) with additional links simulating some unexpected relations support to the six degrees of separation discovered by Milgram (Milgram, S. (1967). "The small world problem." Psychology Today: 60-67). Barabási and Albert proposed an incremental model to improve it (Barabási, A.-L. and R. Albert (1999). "Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks." Science 286(5439): 509 - 512. ). Since Watts and Strogatz’ model, several have been proposed each generating networks with one or two of the described properties (power-law) but none combine the three of them.
Here are some results of available generators present in the JUNG package.
Small-World Generator
WattsBetaSmallWorldGenerator
Parameters: numNodes (the number of nodes in the ring lattice), beta (the probability of an edge being rewired randomly; the proportion of randomly rewired edges in a graph) and degree( the number of edges connected to each vertex; the local neighborhood size). Degree must be even.
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 | W9 | W10 | W11 | W12 |
| numNodes | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 94 |
| beta | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| degree | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| numNodes | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 94 |
| numEdges | 282 | 282 | 282 | 282 | 282 | 94 | 188 | 376 | 470 | 188 | 376 | 752 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.41 | 0.29 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.07 | 0.53 | 0.52 |
| diameter | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.97 | 2.4 | 2.32 | 2.3 | 2.29 | - | 3.24 | 2.15 | 1.98 | 2.83 | 2.56 | 3.15 |
| minDegree | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 6 |
| maxDegree | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 13 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
GraphMl files and Pictures
W1 SmallWorld_47_0.1_6
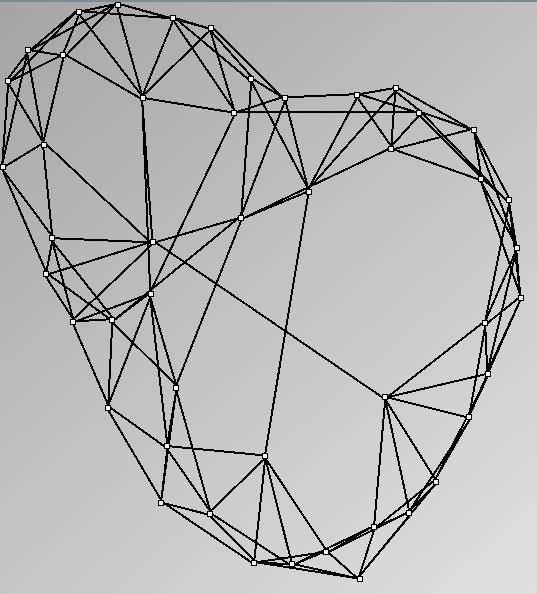
W2 SmallWorld_47_0.3_6


W3 SmallWorld_47_0.5_6


KleinbergSmallWorldGenerator
Parameters:latticeSize (the lattice size (length of row or column dimension)) and clusteringExponent (the clustering exponent parameter).
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 | W9 | W10 | W11 |
| numNodes (sqrt) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| clustering exponent | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 2.5 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| numNodes | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| numEdges | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.33 |
| diameter | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.38 | 2.36 | 2.37 | 2.44 | 2.48 | 2.54 | 2.73 | 3.1 | 3.57 | 3.65 | 3.68 |
| minDegree | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| maxDegree | 14 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 12 |