Social Network Generation
Issues on Social Network Generation for Evaluating Visualizations
Watts and Strogatz first described in (Watts, D. J. and S. H. Strogatz (1998). "Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks." Nature 393: 440 - 442) the concept of small-world networks. They formalized these networks as graphs with three properties: power-law degree distribution, high clustering coefficient and small average shortest path. In the same paper they propose a basic model fitting these properties consisting in a grid (fixed local neighborhood) with additional links simulating some unexpected relations support to the six degrees of separation discovered by Milgram (Milgram, S. (1967). "The small world problem." Psychology Today: 60-67). Barabási and Albert proposed an incremental model to improve it (Barabási, A.-L. and R. Albert (1999). "Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks." Science 286(5439): 509 - 512. ). Since Watts and Strogatz’ model, several have been proposed each generating networks with one or two of the described properties (power-law) but none combine the three of them.
Here are some results of available generators present in the JUNG package.
Small-World Generator
WattsBetaSmallWorldGenerator
Parameters: numNodes (the number of nodes in the ring lattice), beta (the probability of an edge being rewired randomly; the proportion of randomly rewired edges in a graph) and degree( the number of edges connected to each vertex; the local neighborhood size). Degree must be even.
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 | W9 | W10 | W11 | W12 |
| numNodes | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 94 |
| beta | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| degree | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| numNodes | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 94 |
| numEdges | 282 | 282 | 282 | 282 | 282 | 94 | 188 | 376 | 470 | 188 | 376 | 752 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.41 | 0.29 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.07 | 0.53 | 0.52 |
| diameter | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.97 | 2.4 | 2.32 | 2.3 | 2.29 | - | 3.24 | 2.15 | 1.98 | 2.83 | 2.56 | 3.15 |
| minDegree | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 6 |
| maxDegree | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 13 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
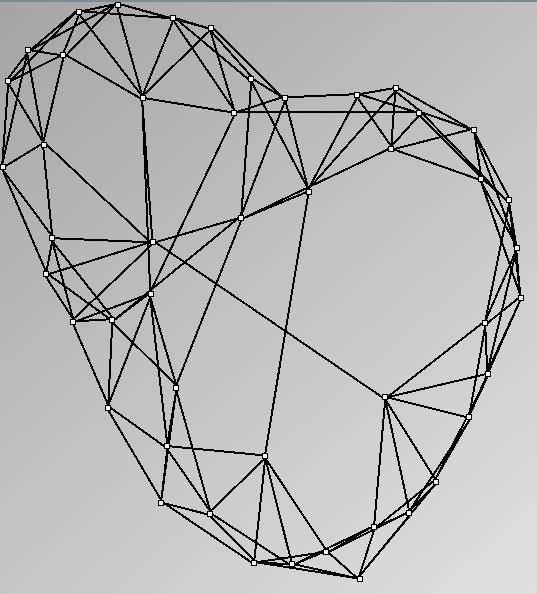
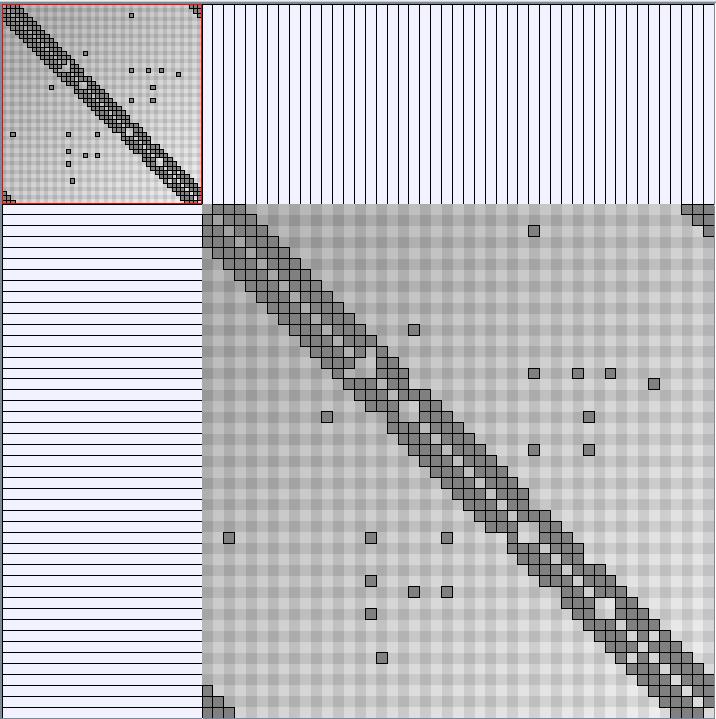
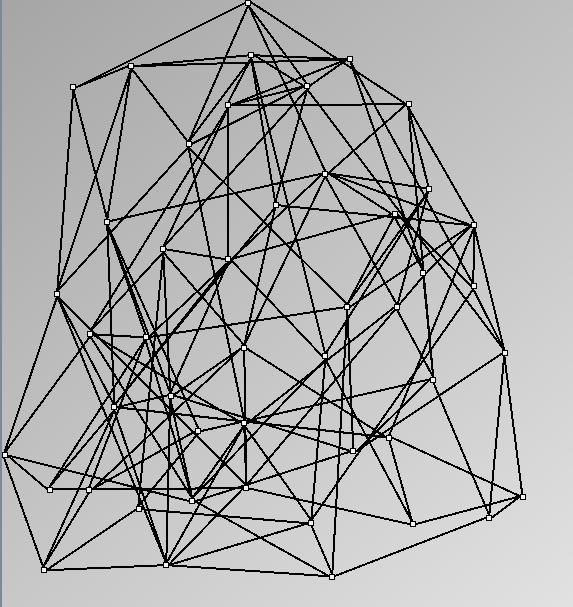
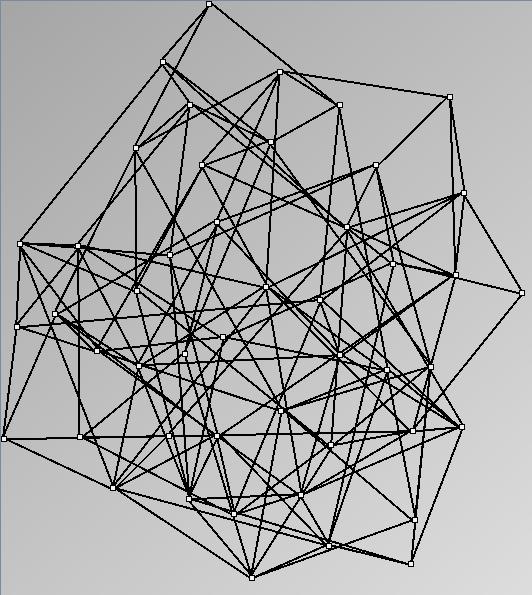
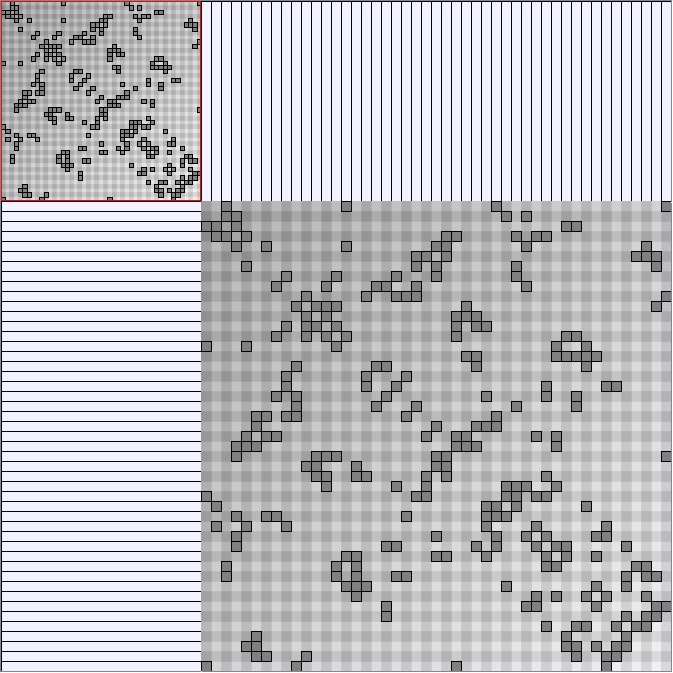
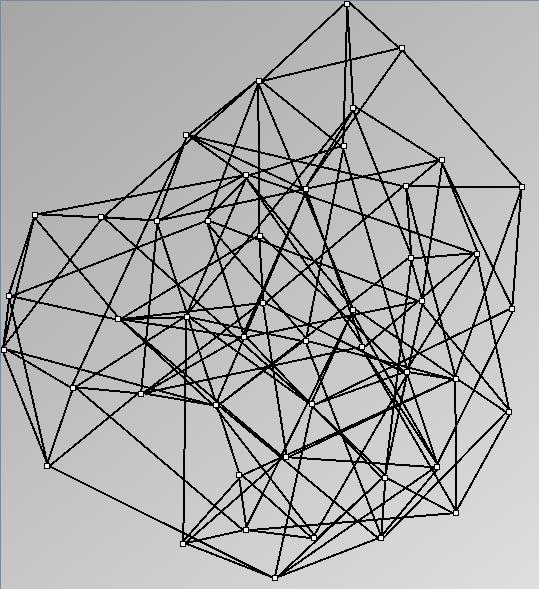
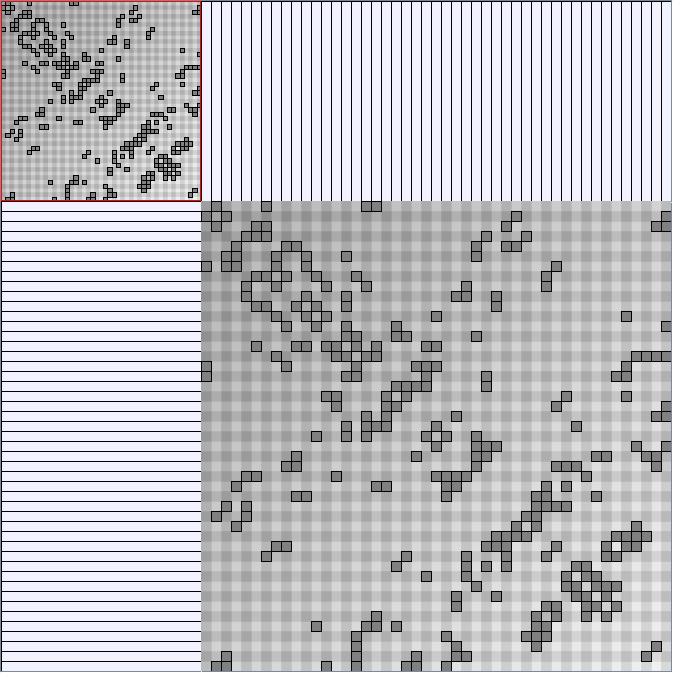
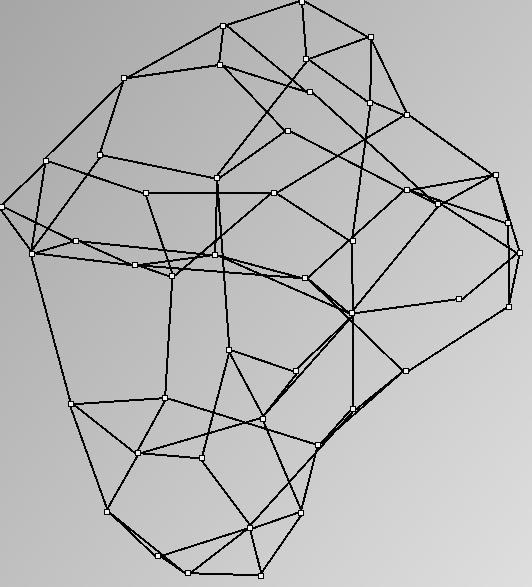
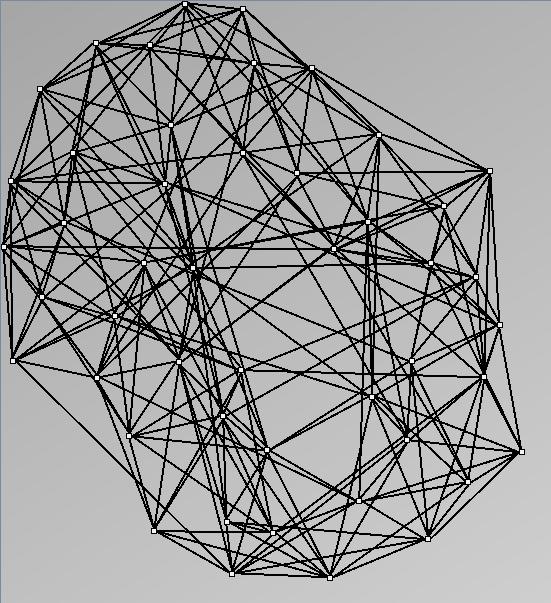
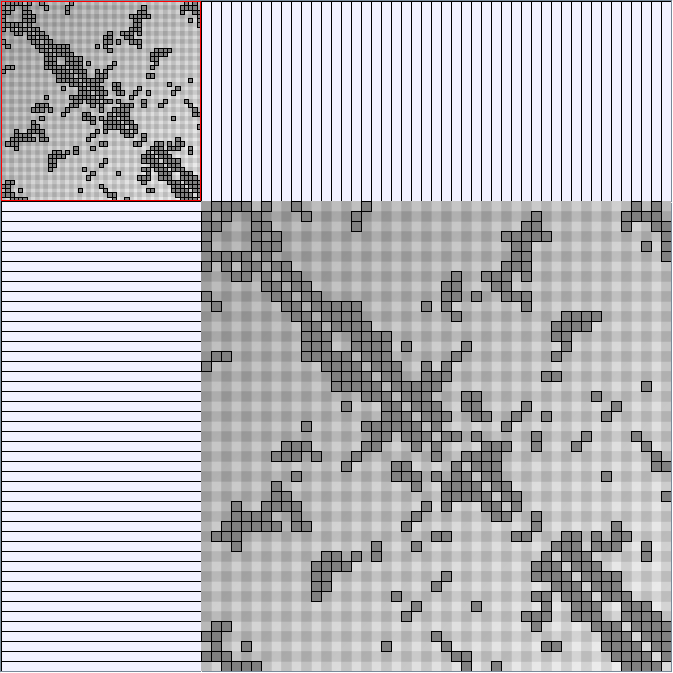
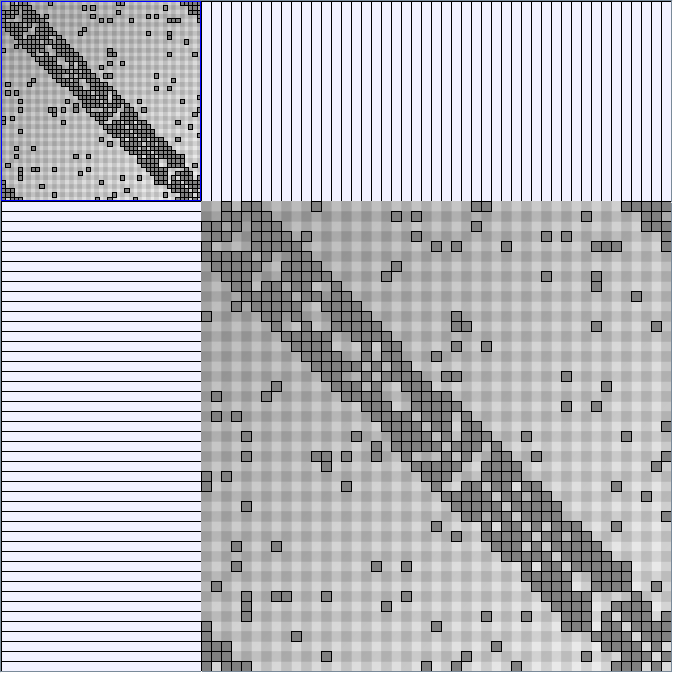
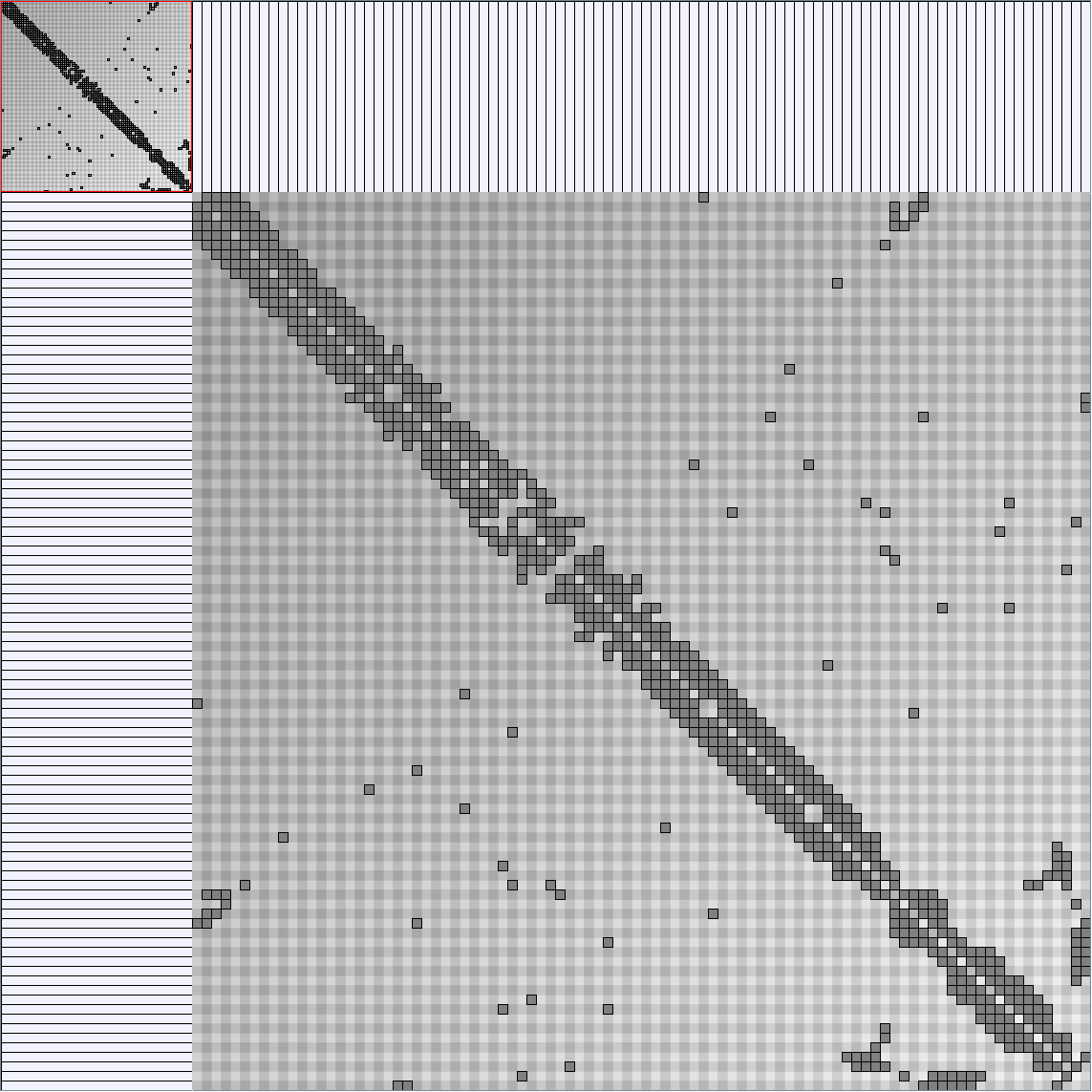
GraphMl files and Pictures:
- Node-Link diagrams are ordered with the linLog algorithm of Andreas Noack [Graph Drawing 2005] (with edge-repulsion coefficient of 2.5f).
- Matrices are reordered with the TSP-Based algorithm described by Henry and Fekete [Infovis 2006].
W1 SmallWorld_47_0.1_6
W2 SmallWorld_47_0.3_6
W3 SmallWorld_47_0.5_6
W4 SmallWorld_47_0.7_6
W5 SmallWorld_47_0.9_6
W6 SmallWorld_47_0.3_2
W7 SmallWorld_47_0.3_4
W8 SmallWorld_47_0.3_8 (Second matrix not reordered)
W9 SmallWorld_47_0.3_10 (Second matrix not reordered)
W10 SmallWorld_47_0.7_4
W11 SmallWorld_47_0.1_8
W12 SmallWorld_94_0.1_8
KleinbergSmallWorldGenerator
Parameters:latticeSize (the lattice size (length of row or column dimension)) and clusteringExponent (the clustering exponent parameter).
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 | W9 | W10 | W11 |
| numNodes (sqrt) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| clustering exponent | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 2.5 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| numNodes | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| numEdges | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.33 |
| diameter | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.38 | 2.36 | 2.37 | 2.44 | 2.48 | 2.54 | 2.73 | 3.1 | 3.57 | 3.65 | 3.68 |
| minDegree | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| maxDegree | 14 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 12 |
Scale-Free Networks Generator
BarabasiAlbertGenerator
Parameters: init_vertices (number of vertices that the graph should start with), numEdgesToAttach (the number of edges that should be attached from the new vertex to pre-existing vertices at each time step) and numSteps (number of time steps). init_vertices must be superior or equal to numEdgesToAttach.
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 |
| numStartingNodes | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| numAdditionnalEdges | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| numSteps | 10 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| numNodes | 14 | 53 | 104 | 80 | 76 | 51 | 52 | 54 |
| numEdges | 40 | 200 | 400 | 158 | 150 | 100 | 200 | 400 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.27 | 0.37 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.07 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 0.16 | 0.23 |
| diameter | 4 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 14 | 8 | 5 | 4 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.24 | 2.81 | 3.18 | 5.26 | 5.7 | 3.74 | 2.8 | 2.15 |
| minDegree | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| maxDegree | 5 | 16 | 19 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 17 | 26 |
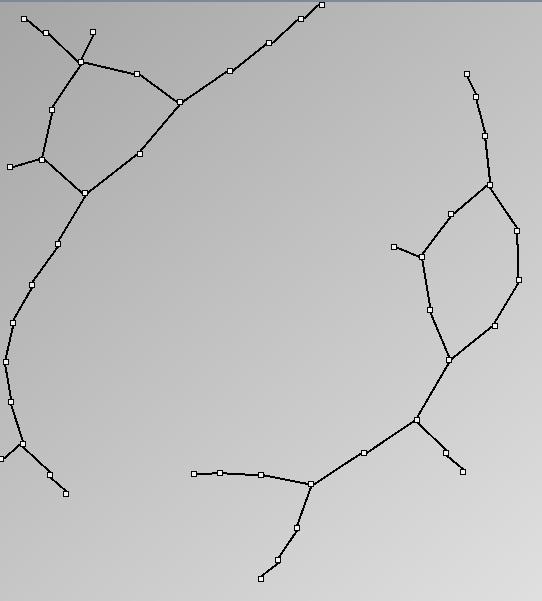
EppsteinPowerLawGenerator
Parameters: numVertices (the number of vertices for the generated graph), numEdges (the number of edges the generated graph will have, should be Theta(numVertices)) and r (the model parameter).
Issues on using real Social Networks for Evaluating Visualizations
Here is a panel of undirected networks issued from scientific articles, benchmarks or contests. Social network visualization or analysis tools provide also some real datasets: Pajek [1] and UCINet [2].
| Name | Infovis Comp4 |
| Type | Co-authoring network |
| File | |
| numNodes | 32 |
| numEdges | 109 |
| components | 1 |
| density | 0.33 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.81 |
| diameter | 6 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.60 |
| minDegree | |
| maxDegree |