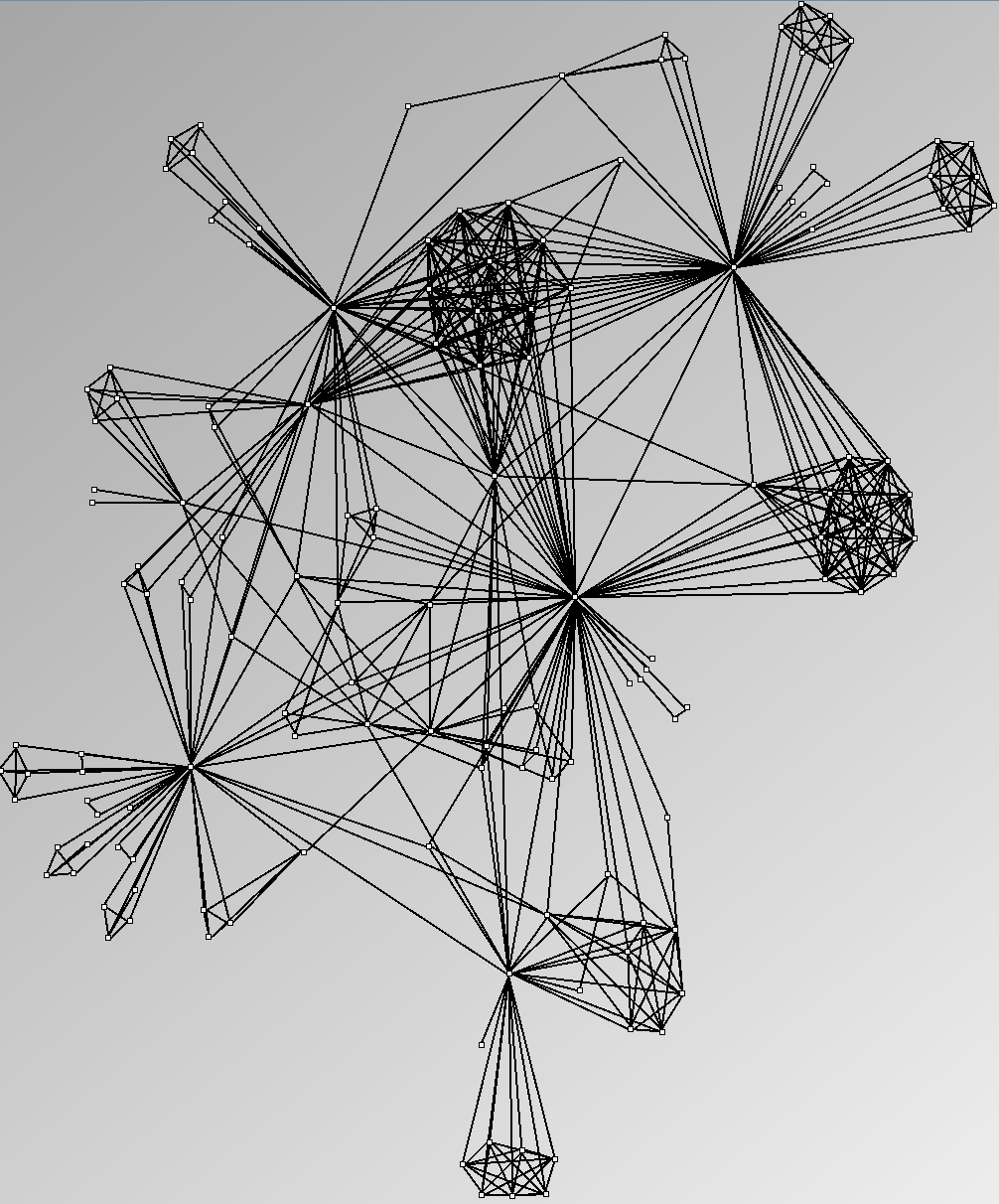
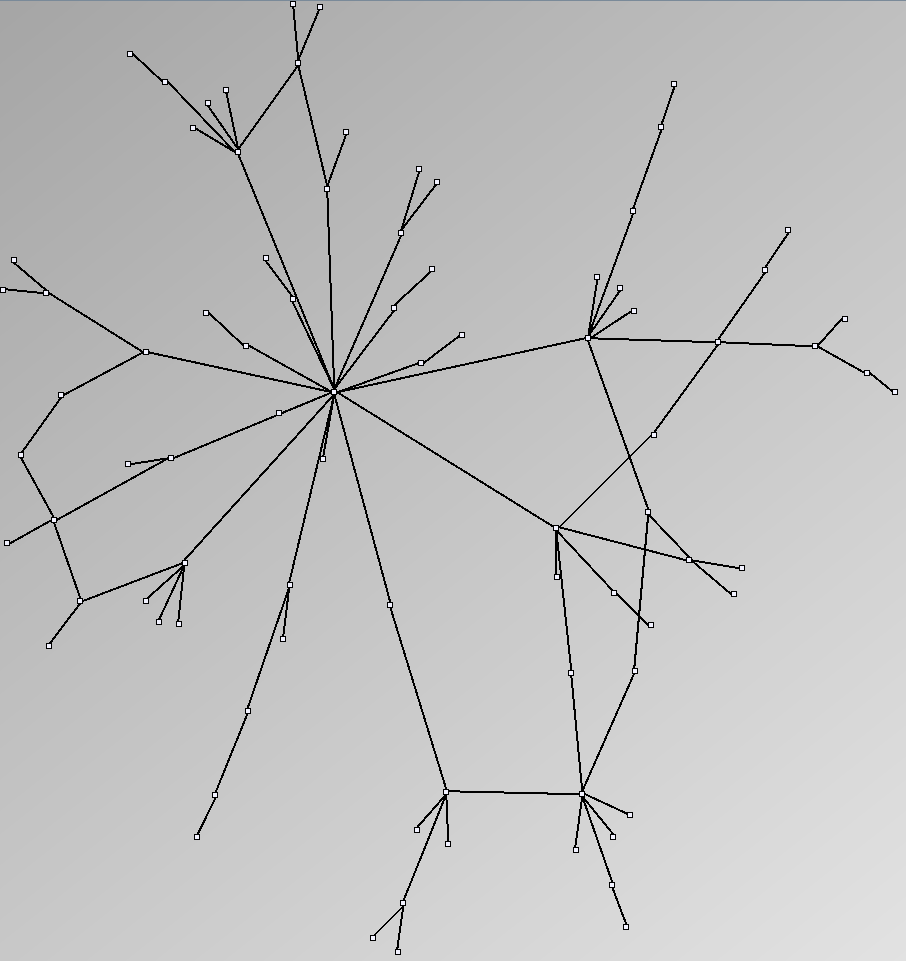
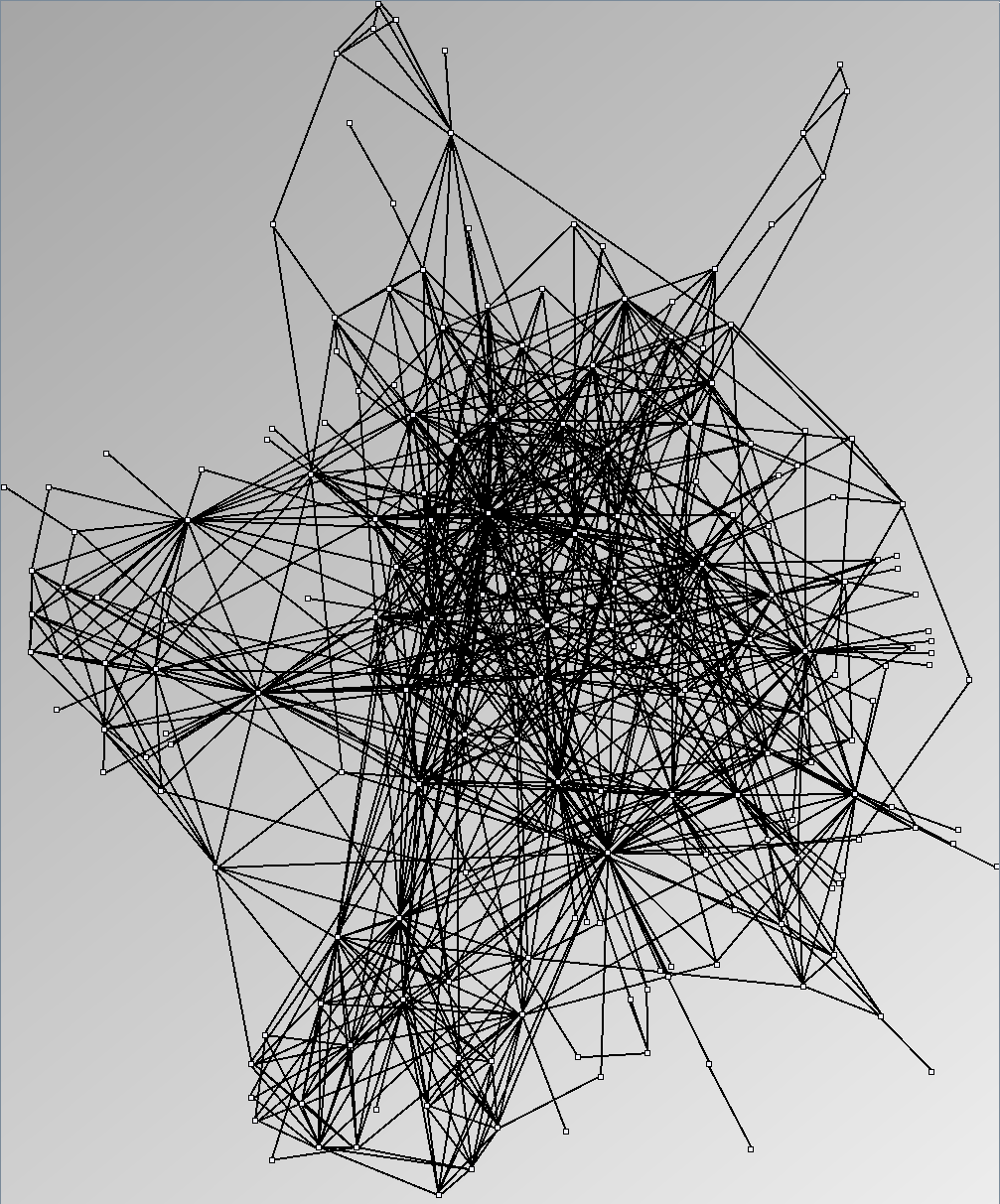
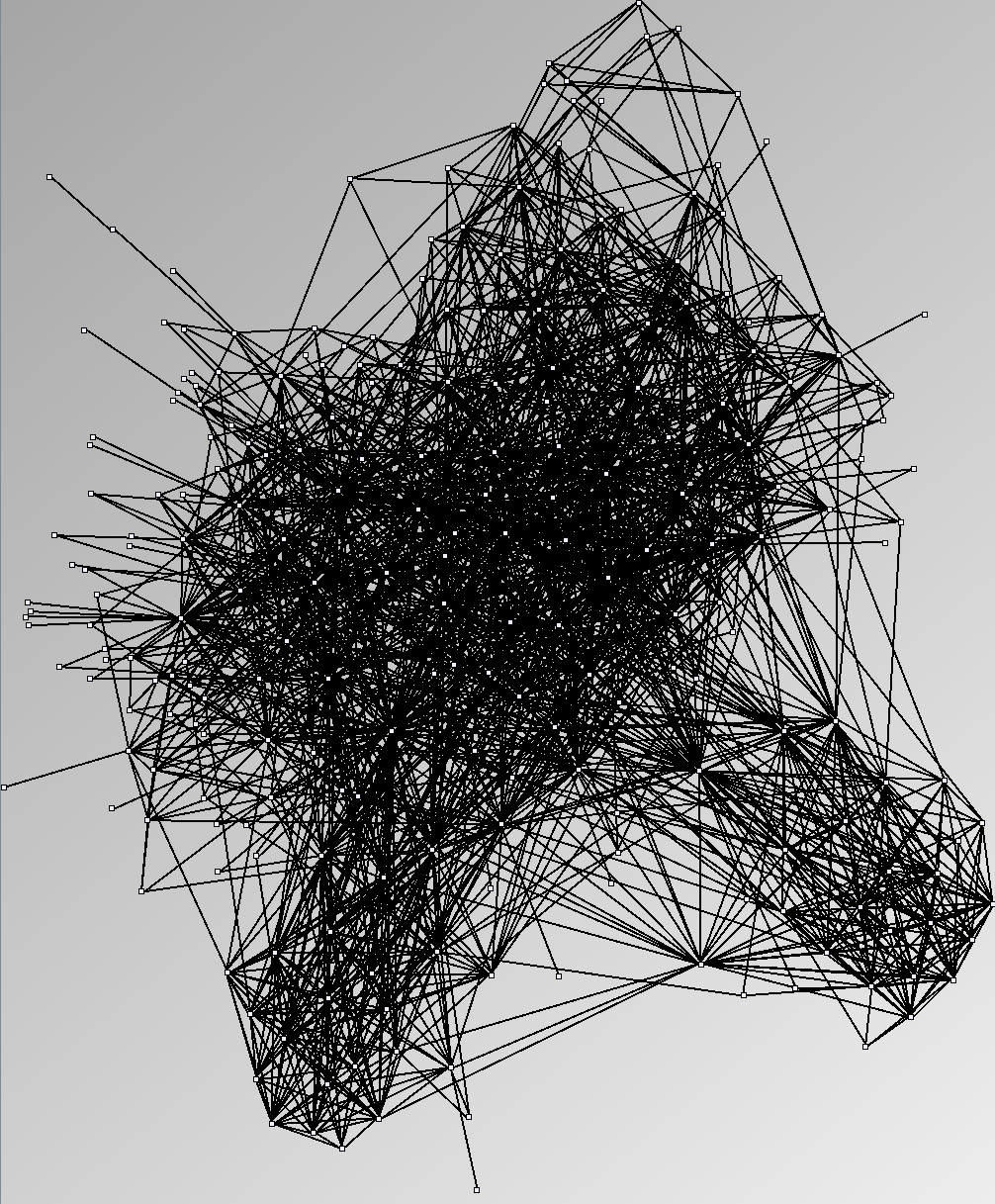
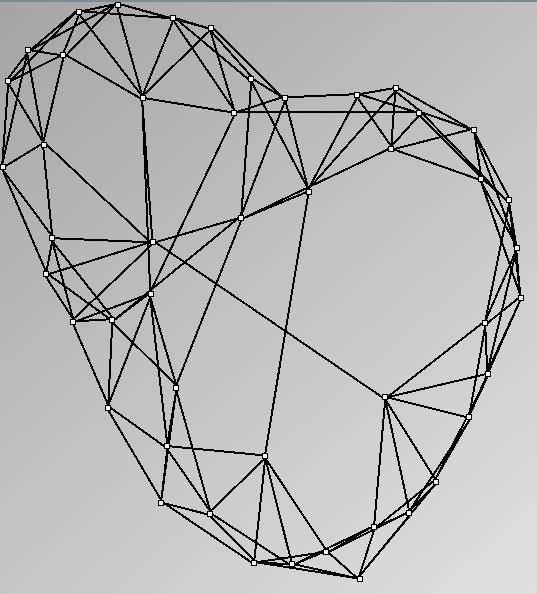
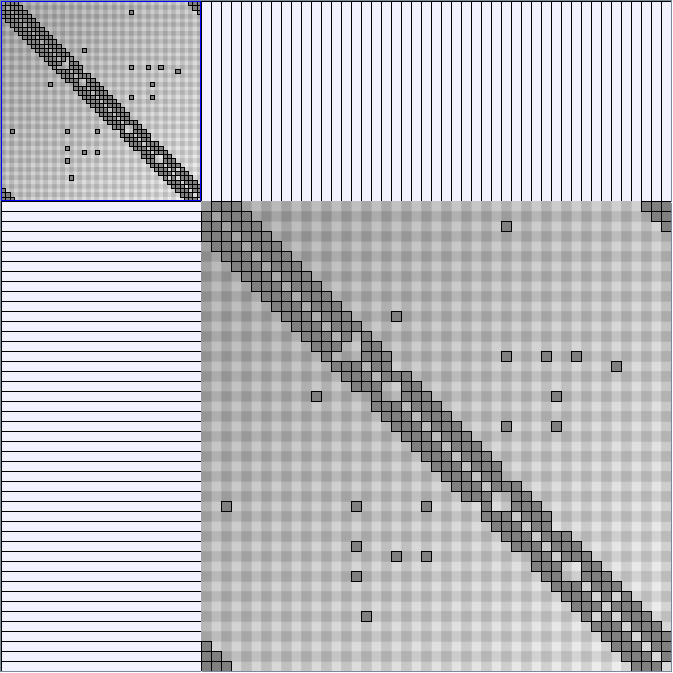
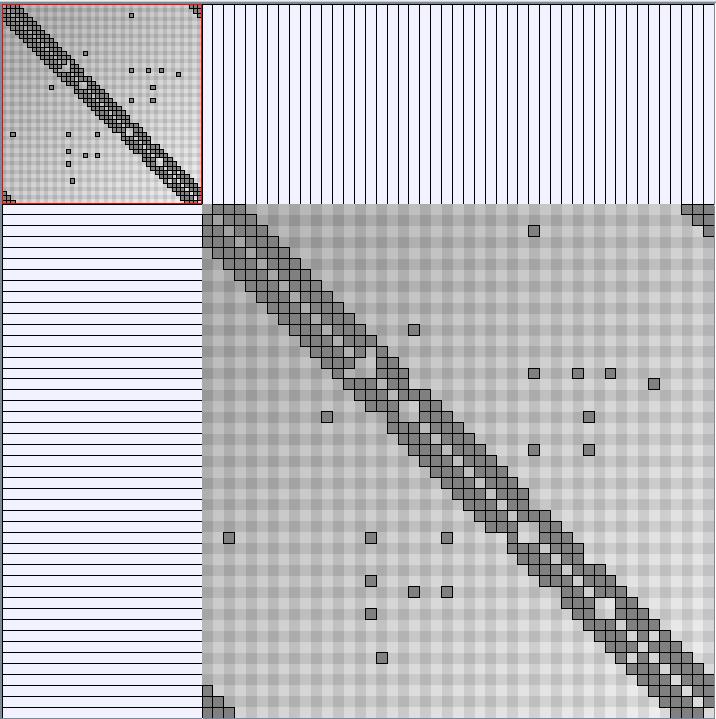
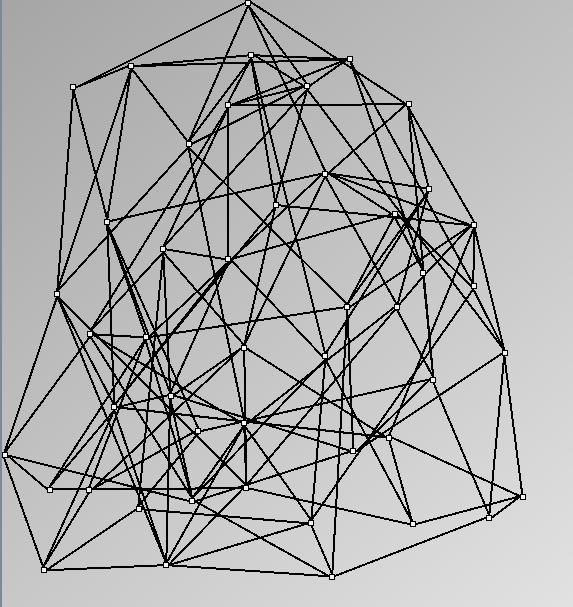
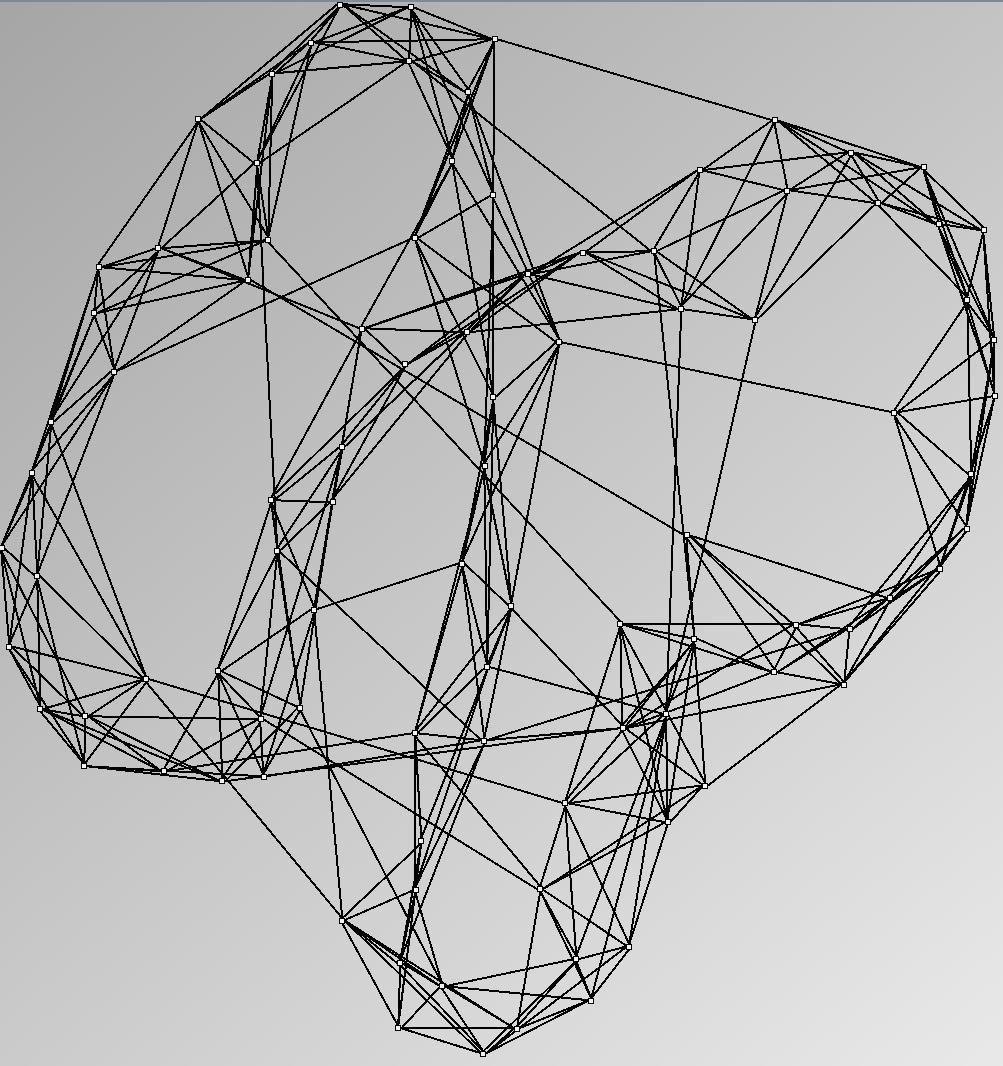
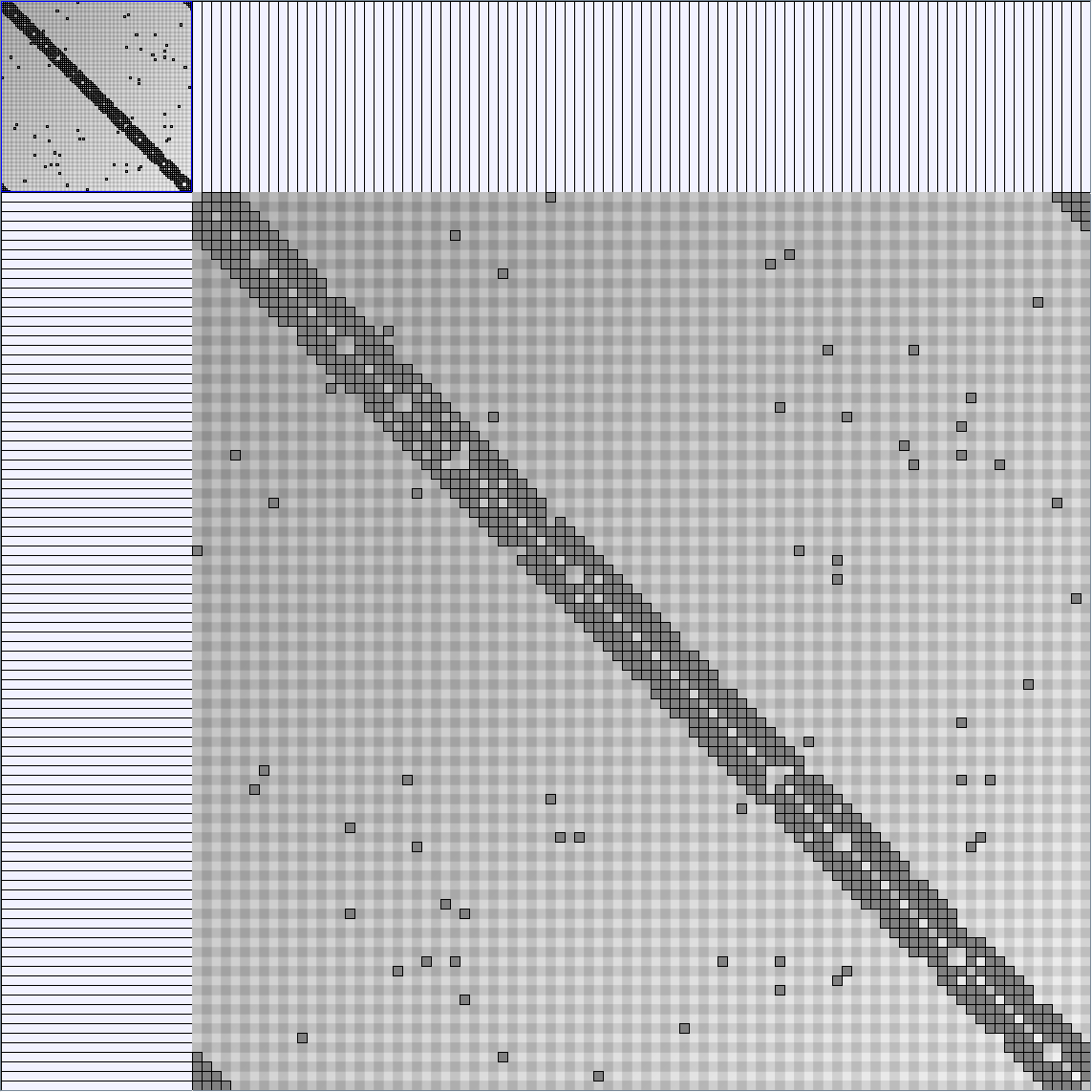
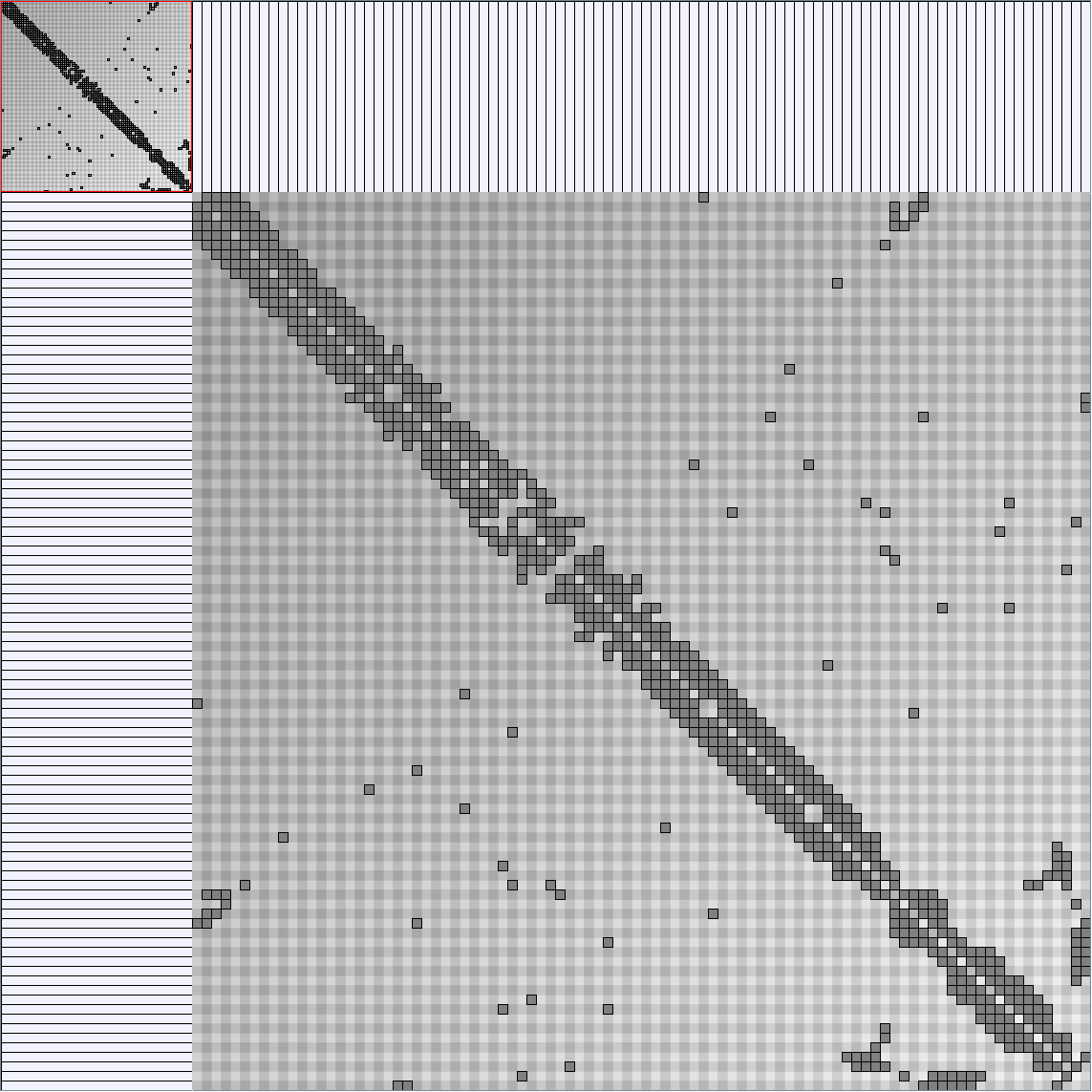
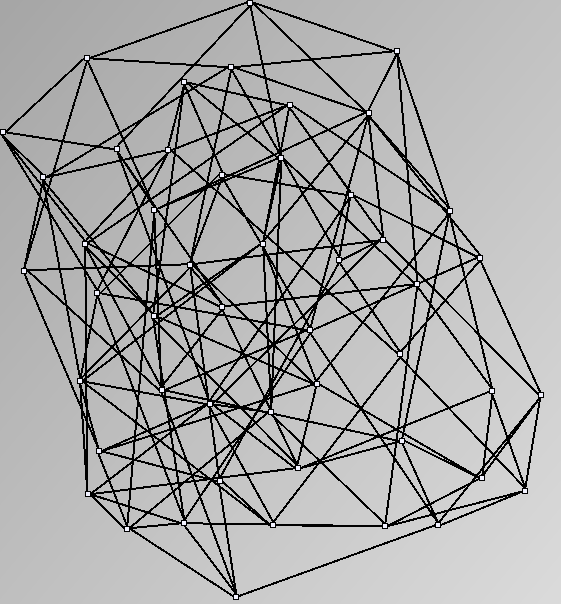
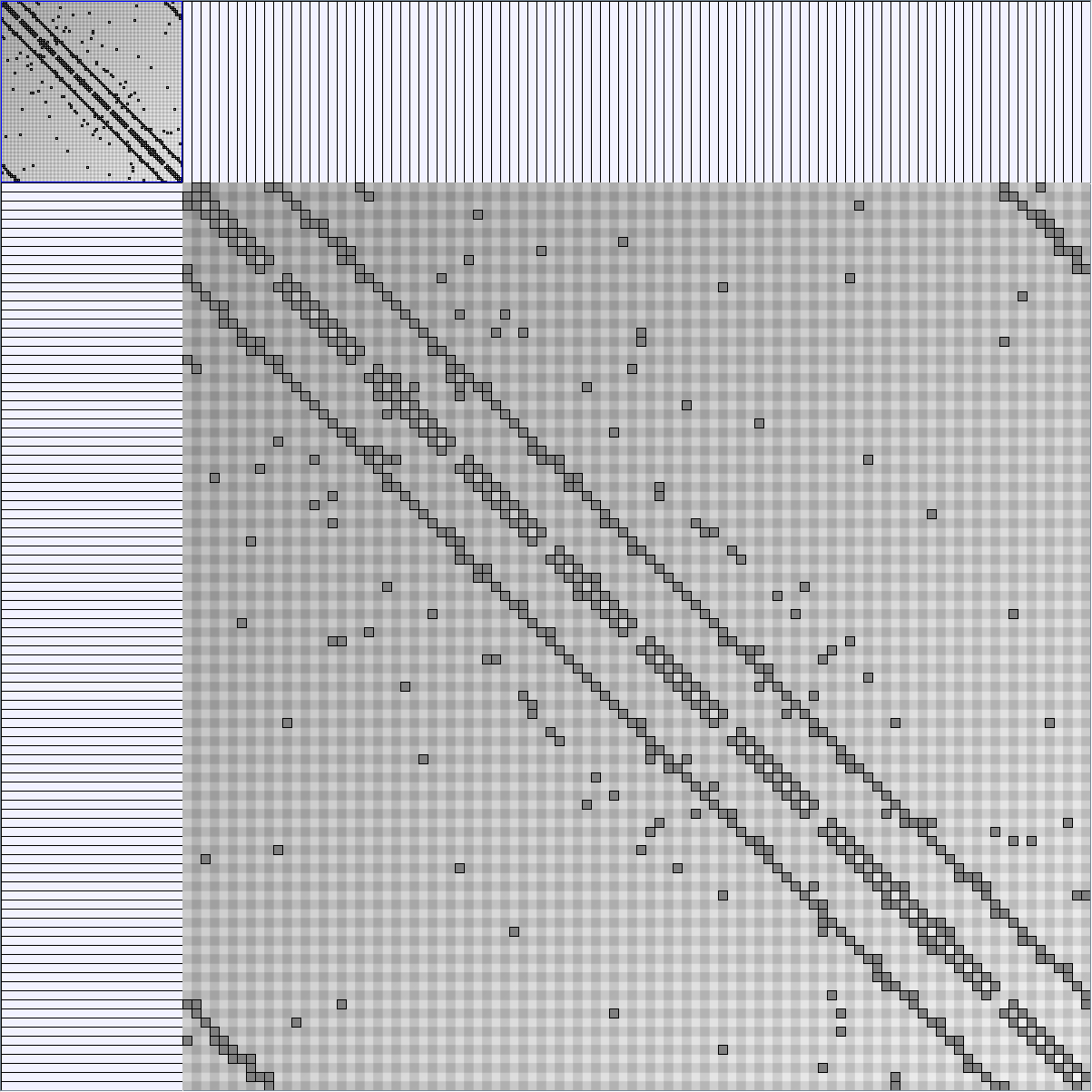
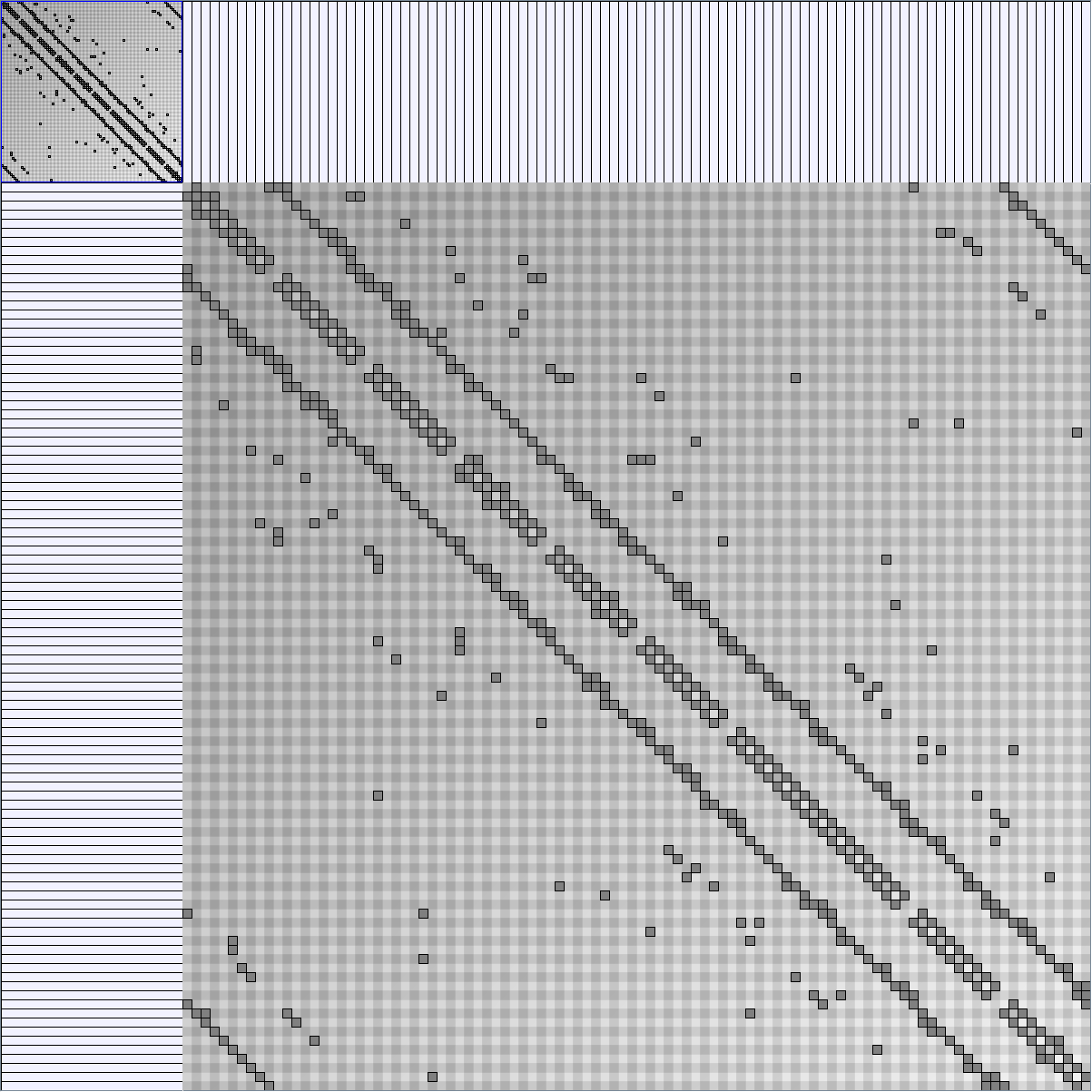
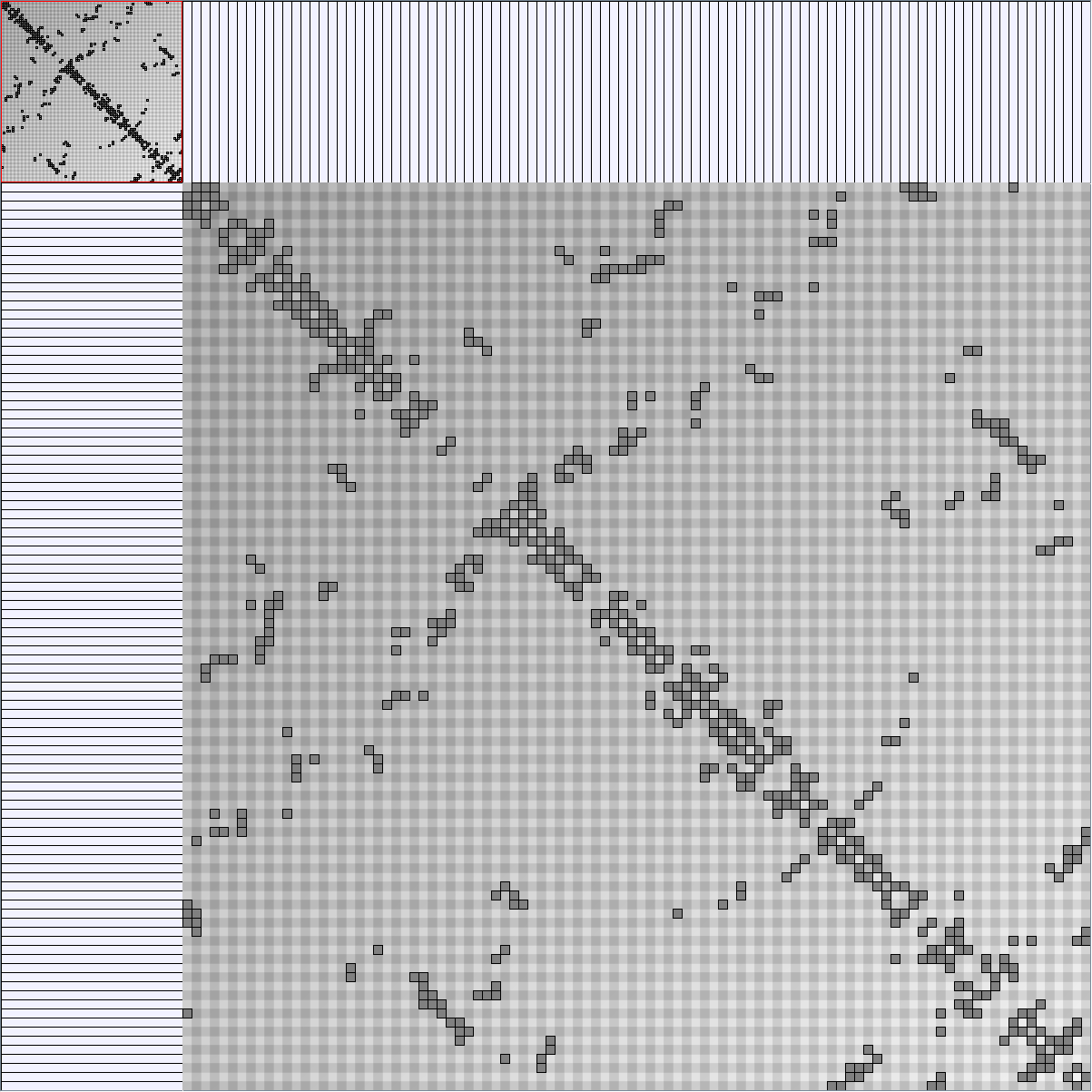
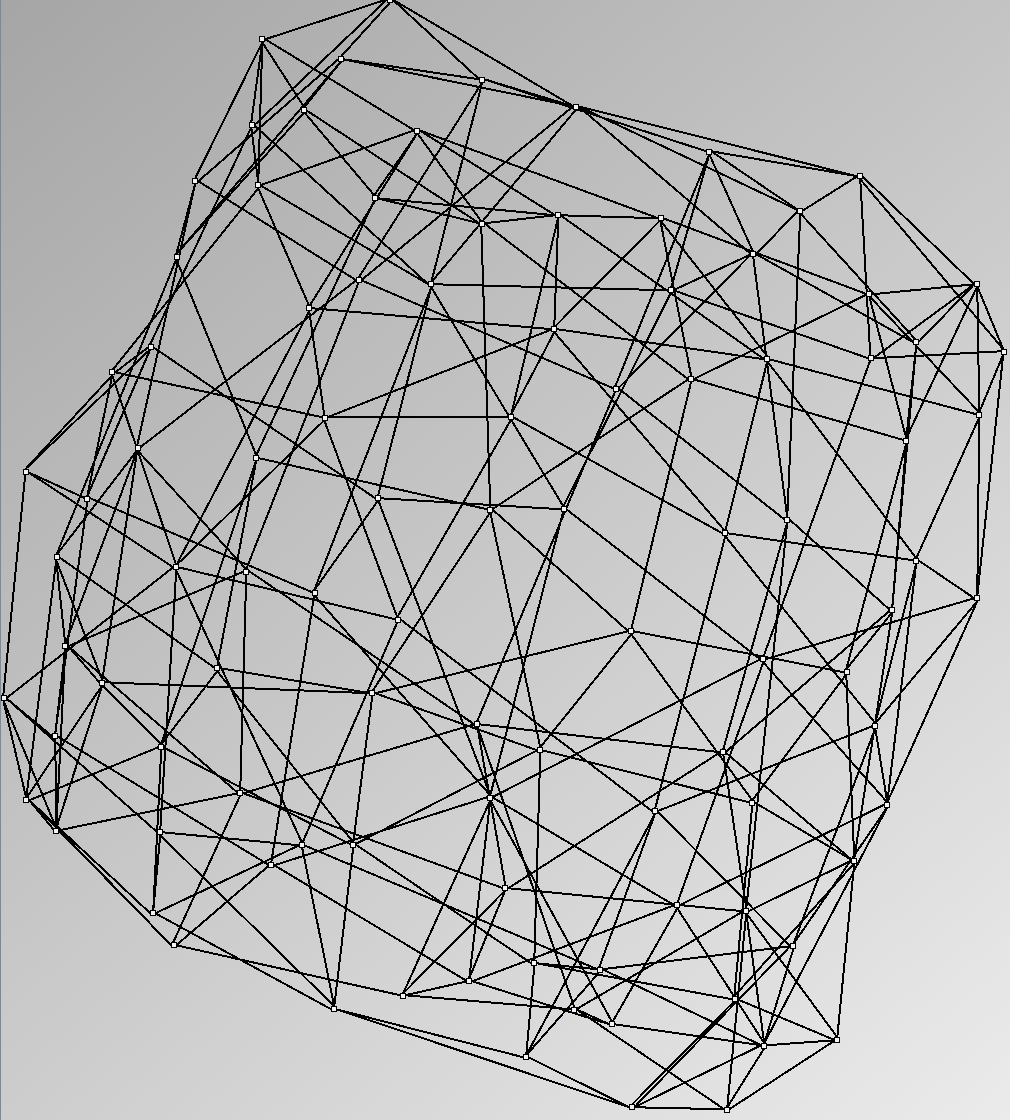
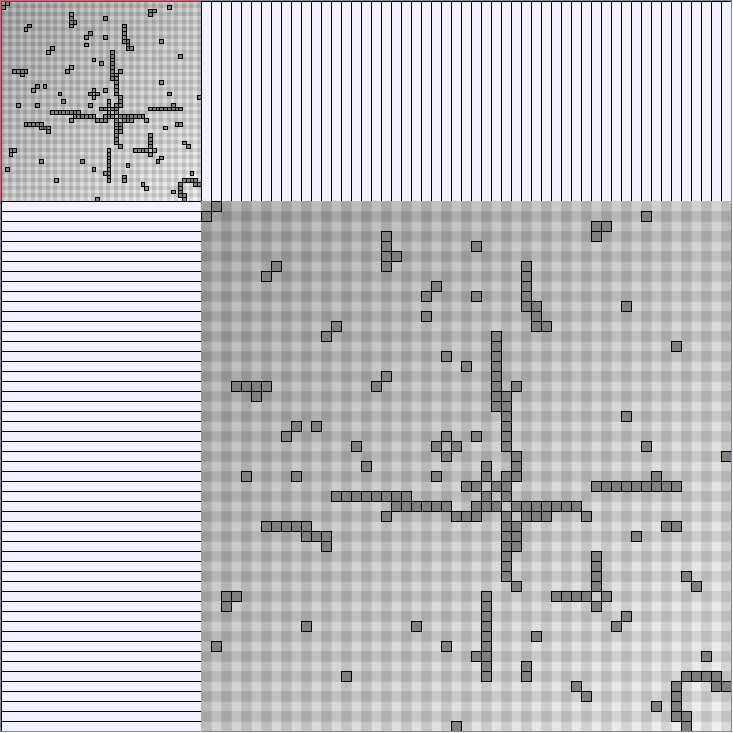
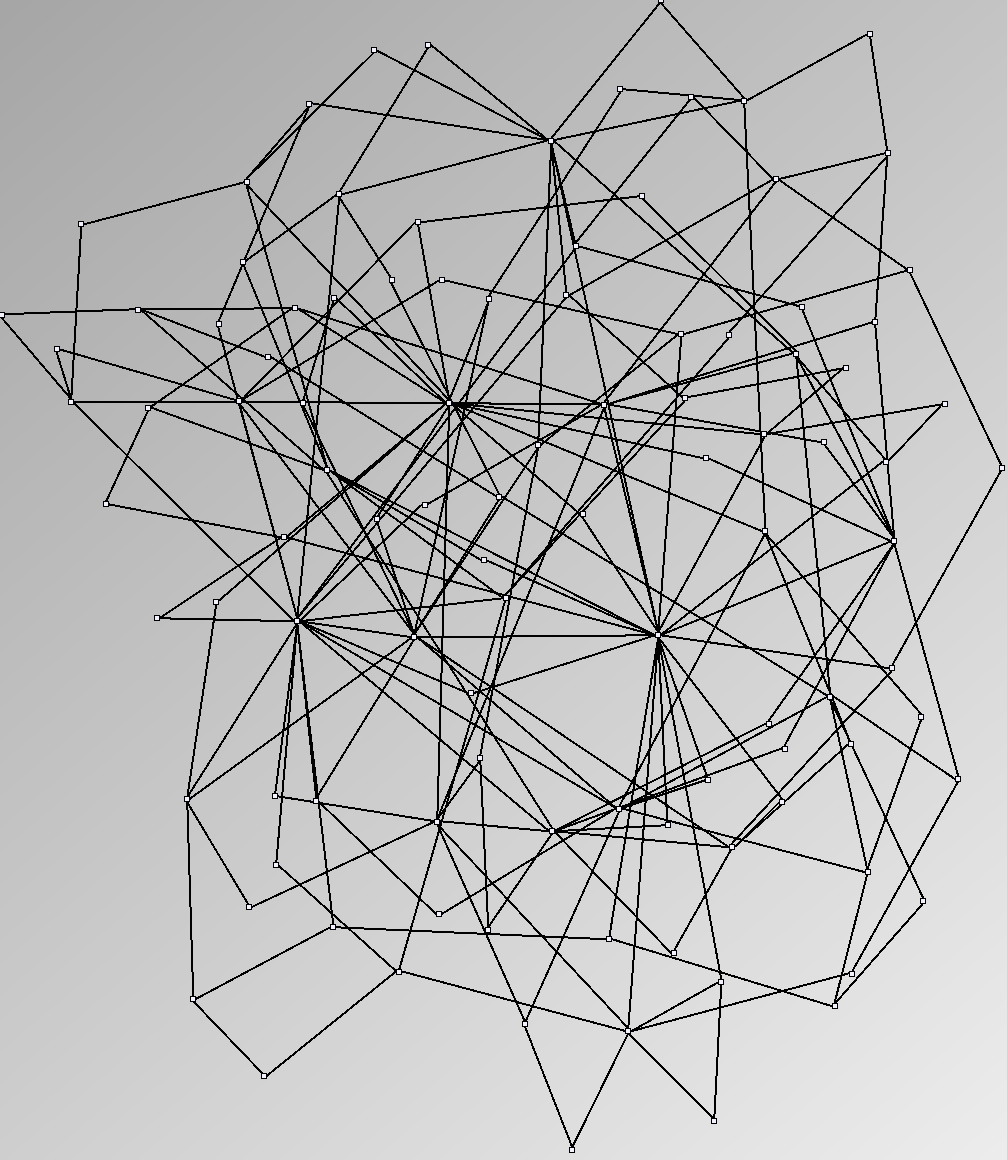
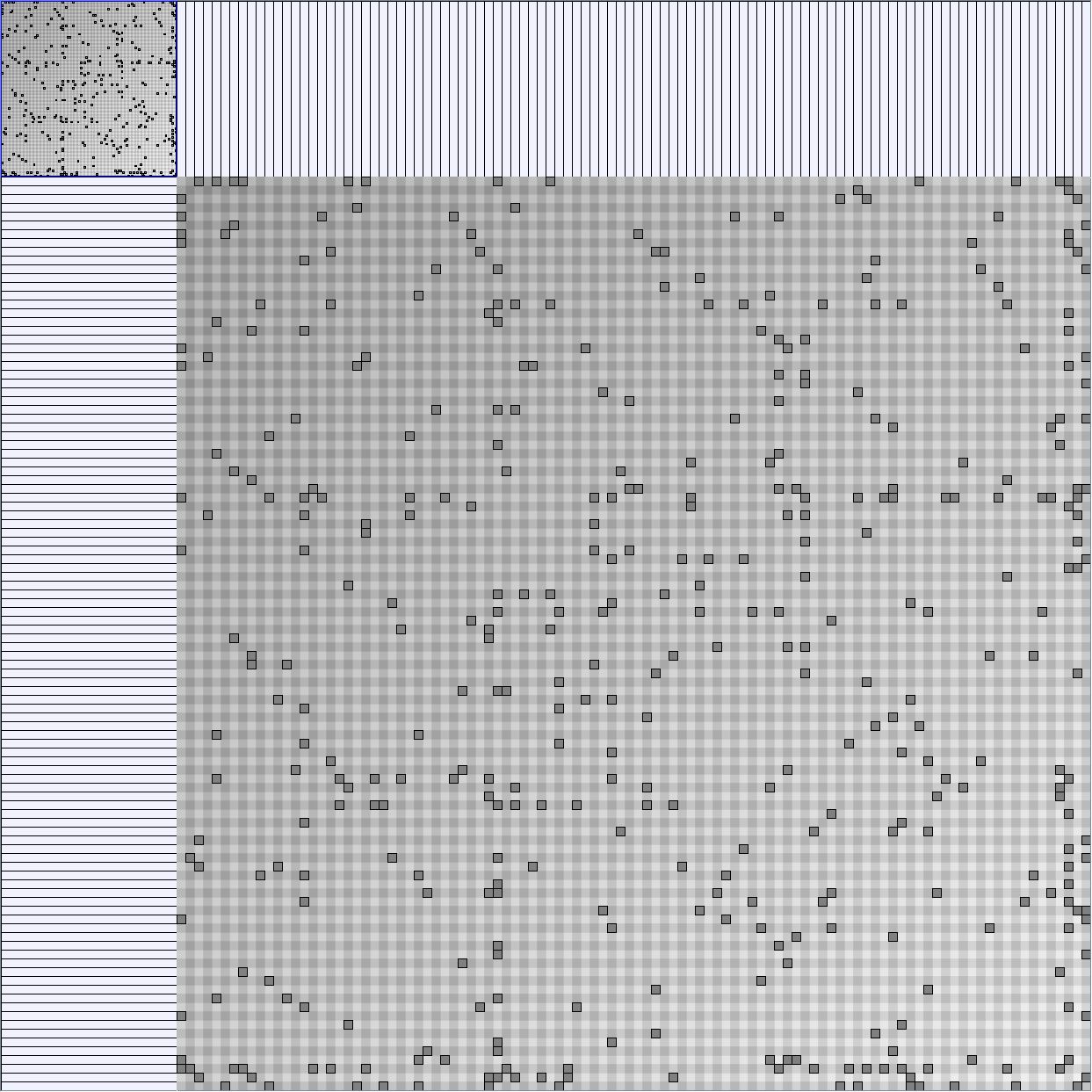
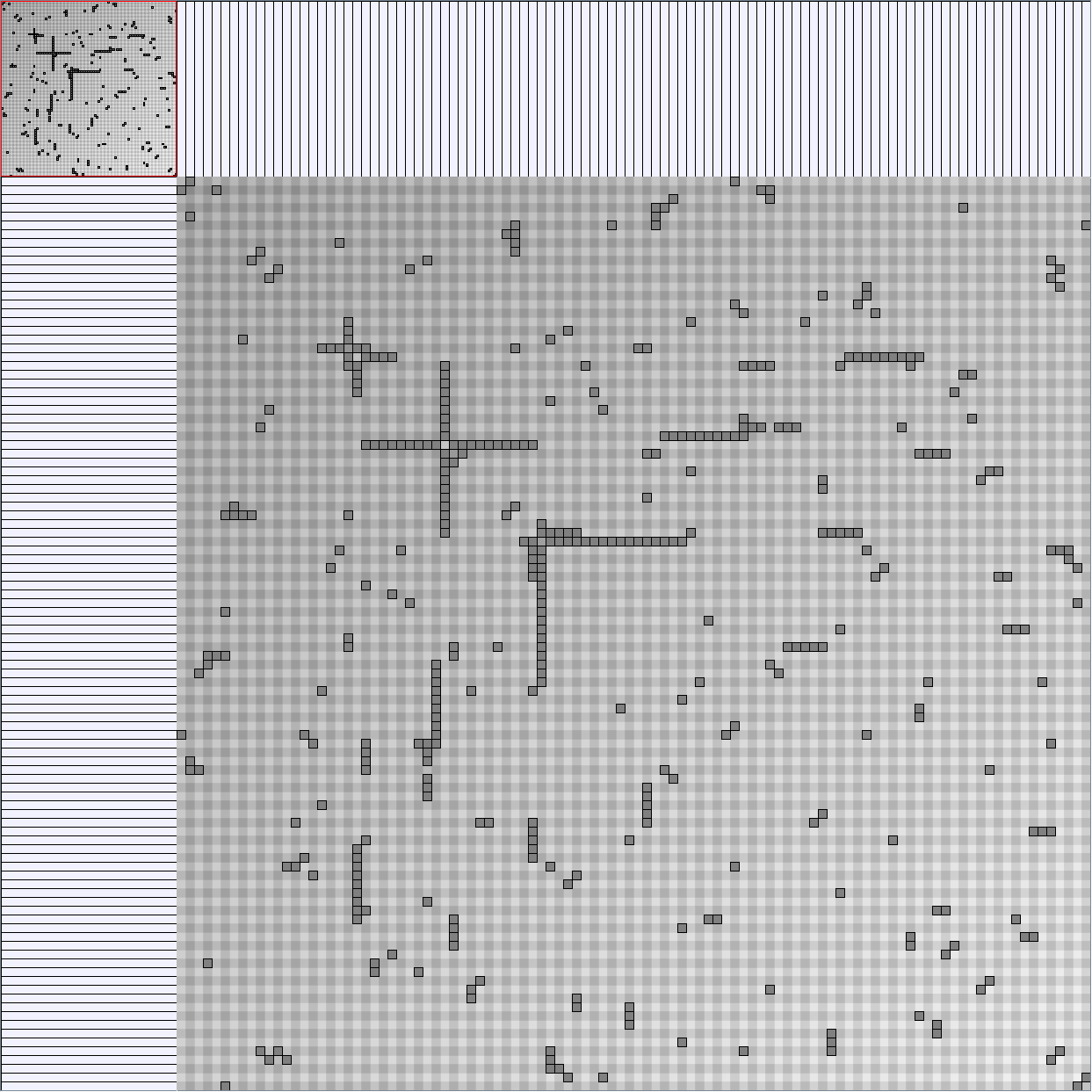
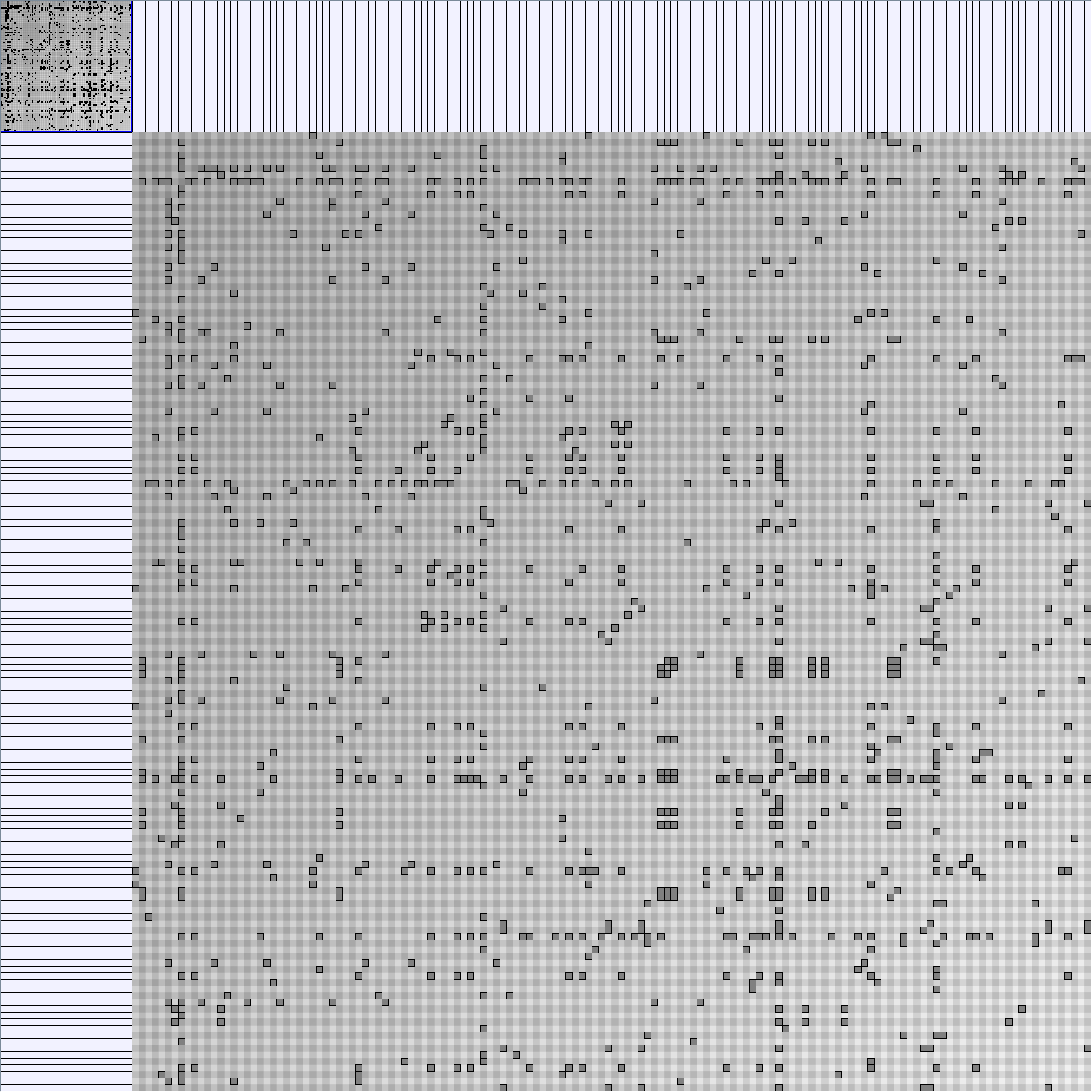
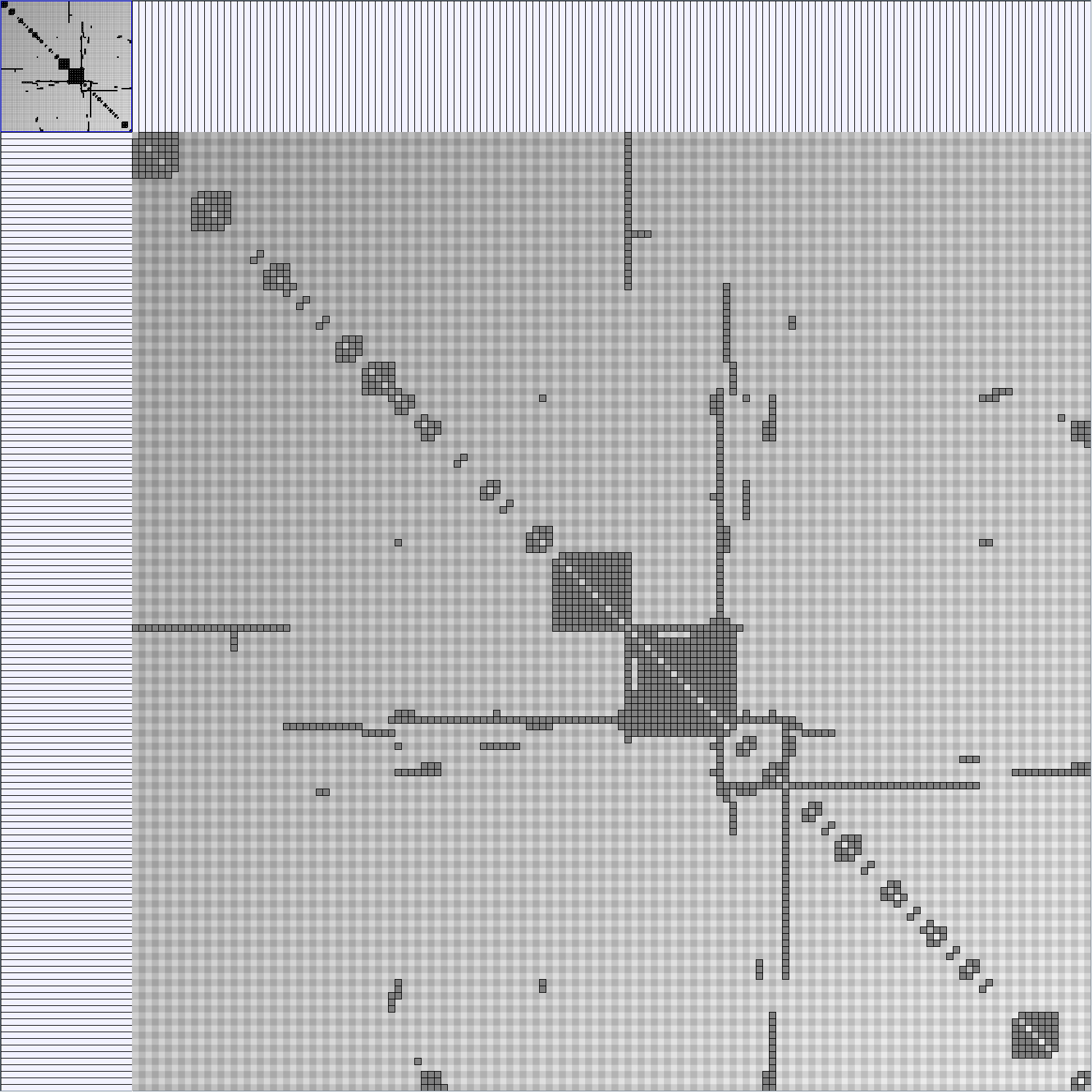
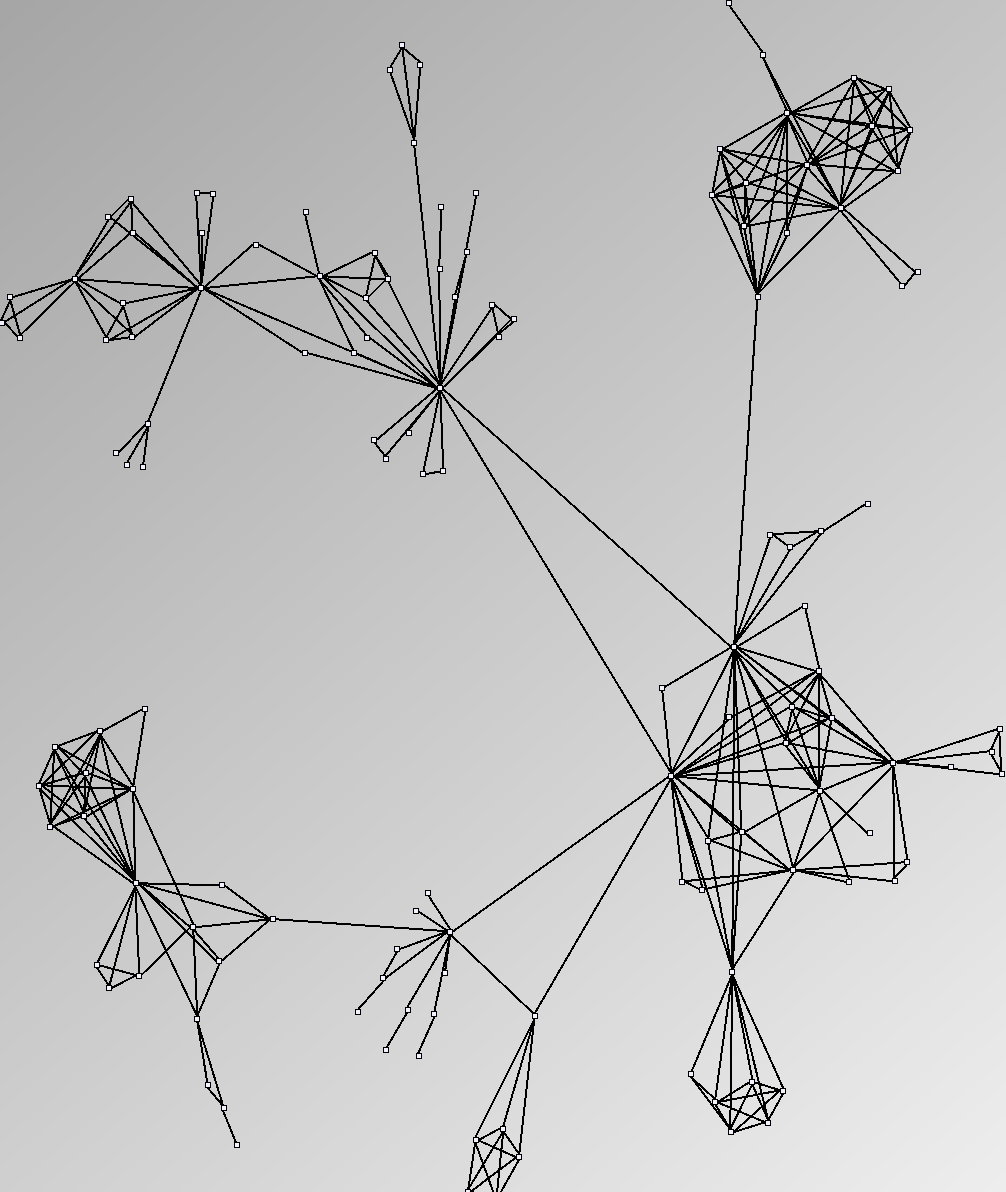
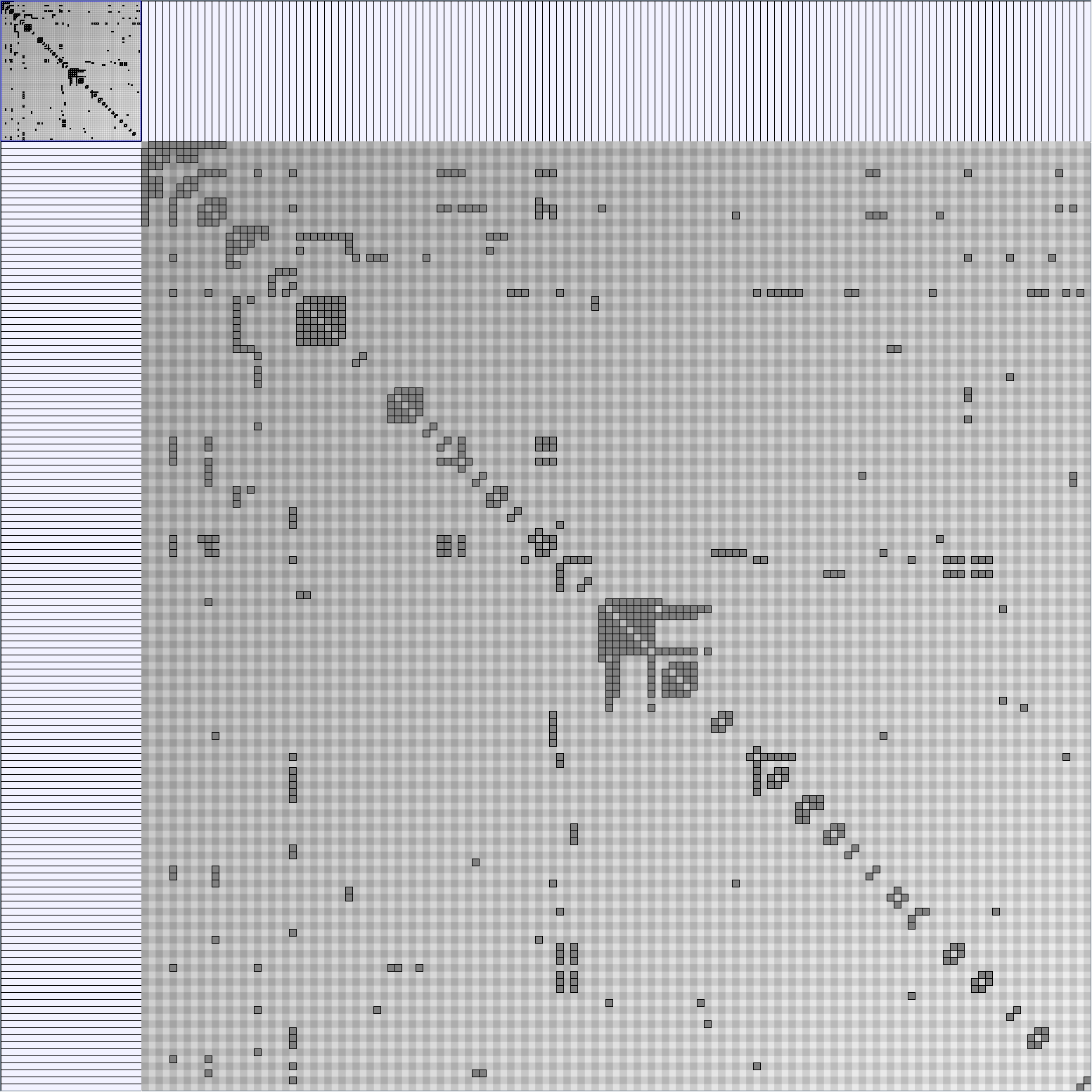
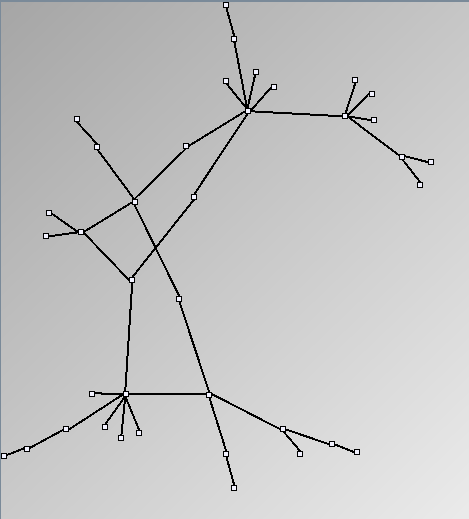
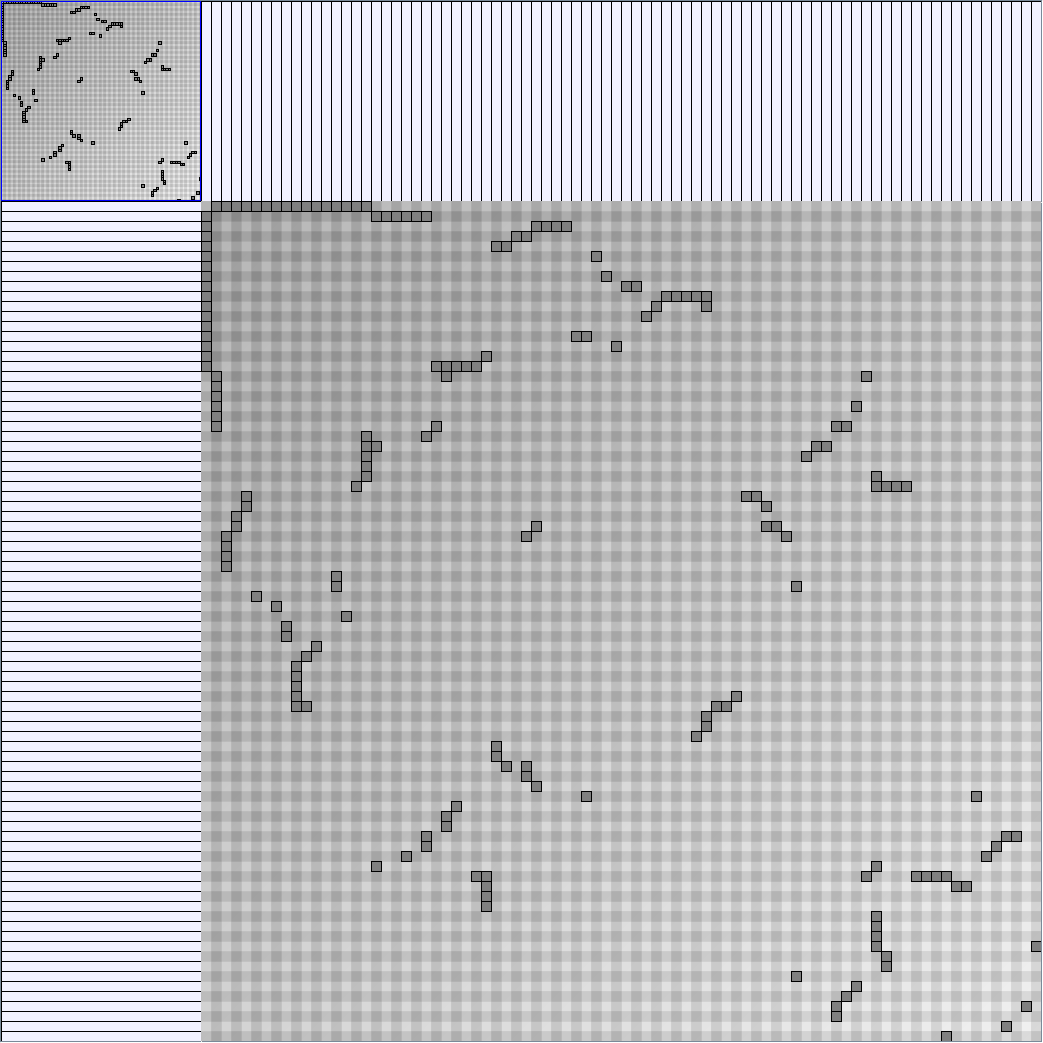
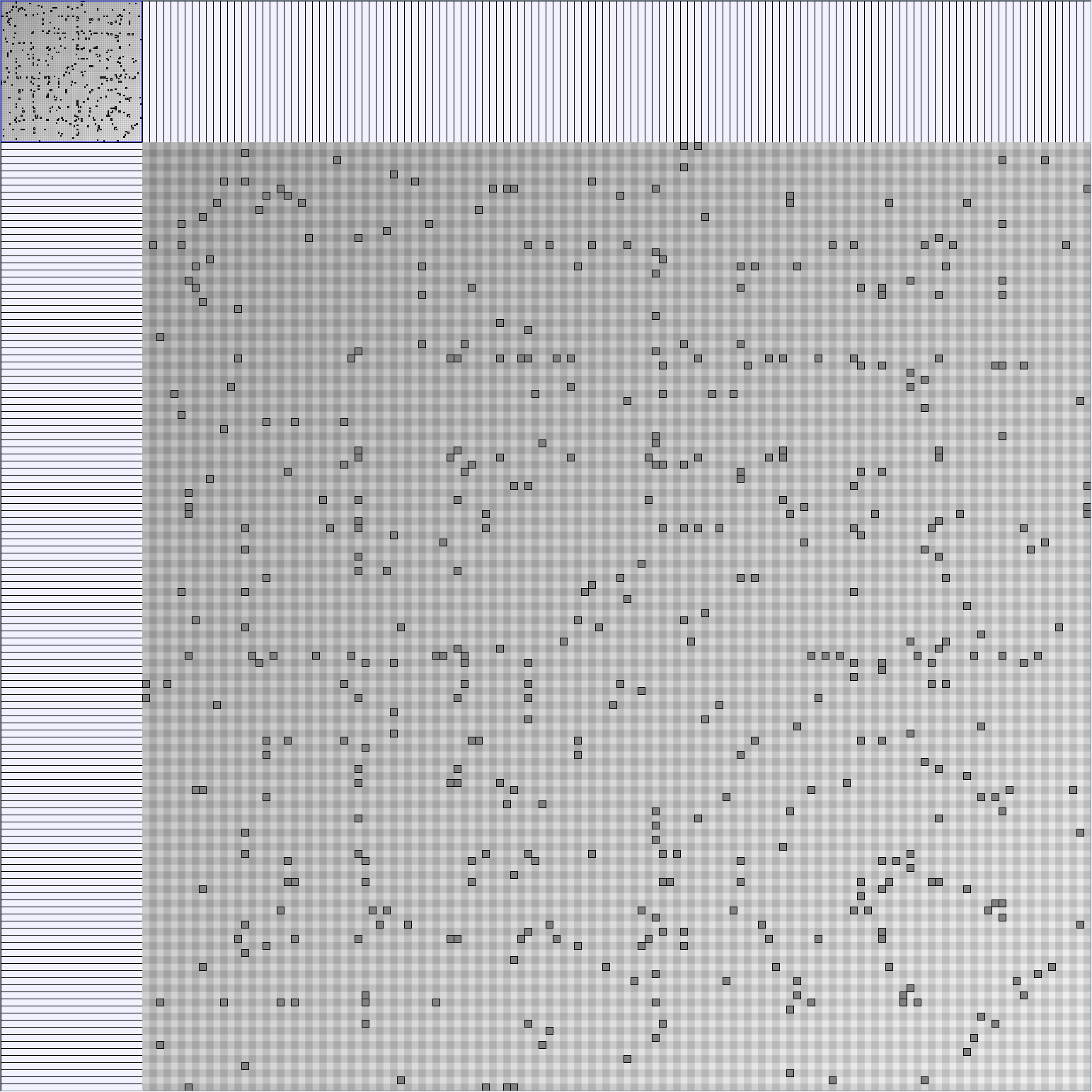
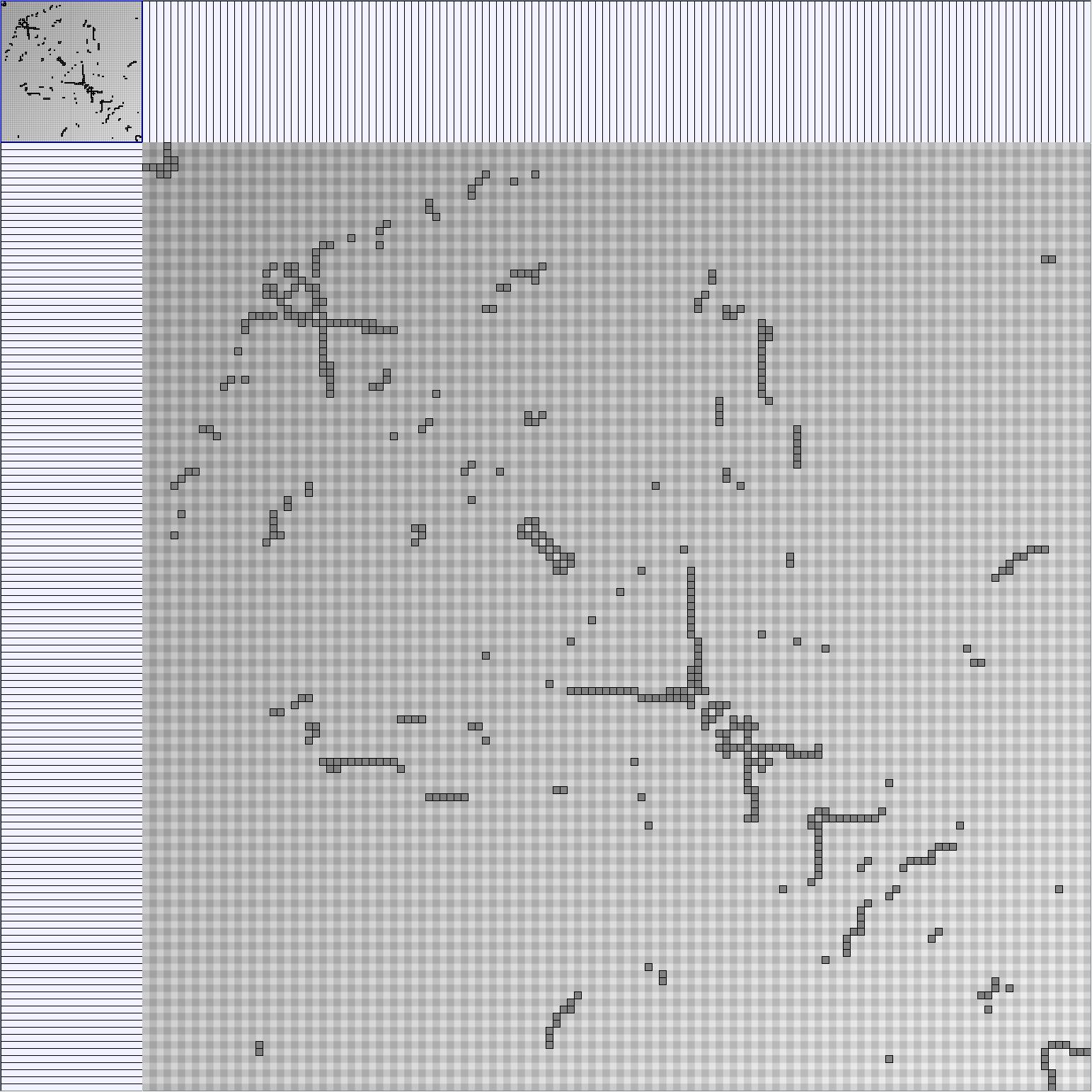
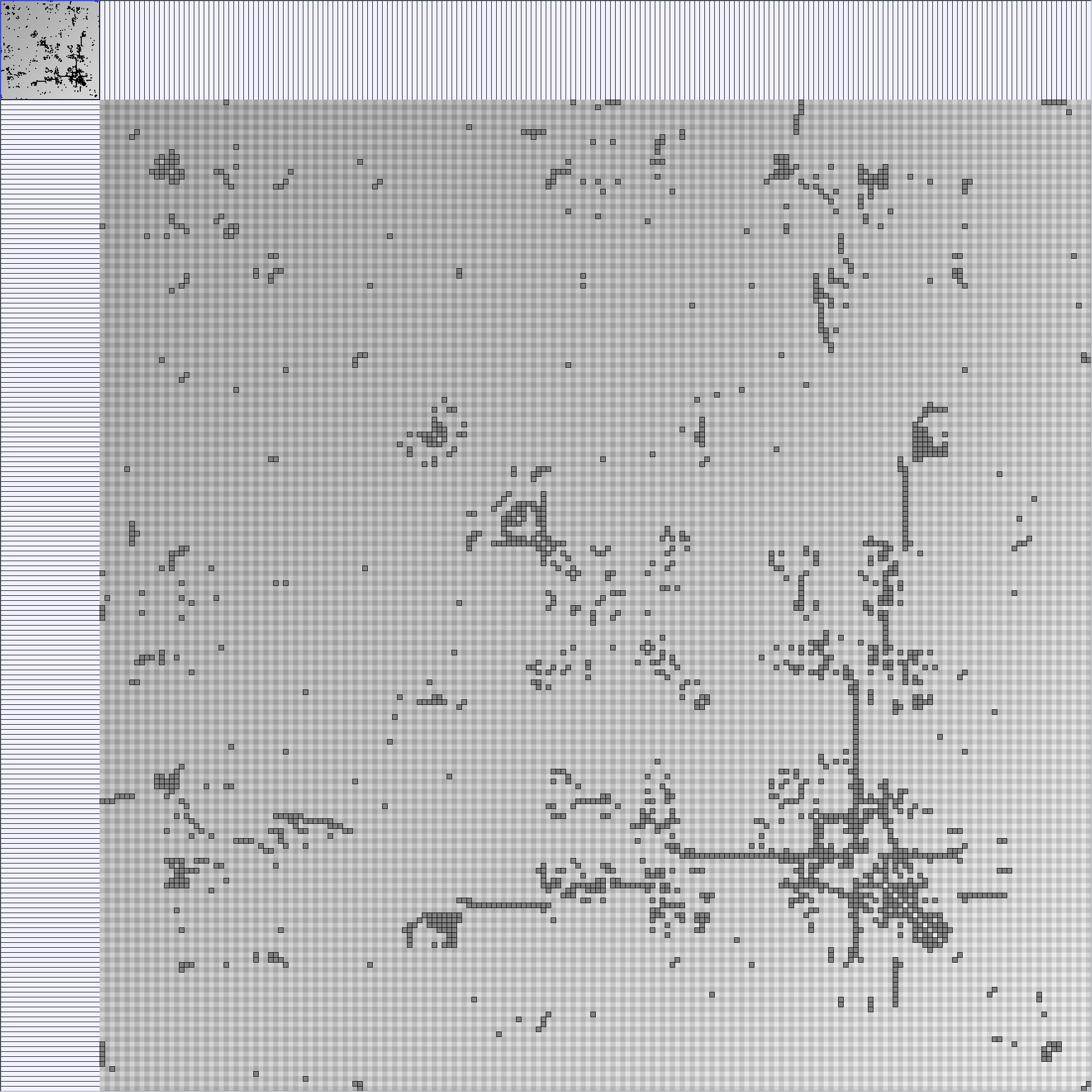
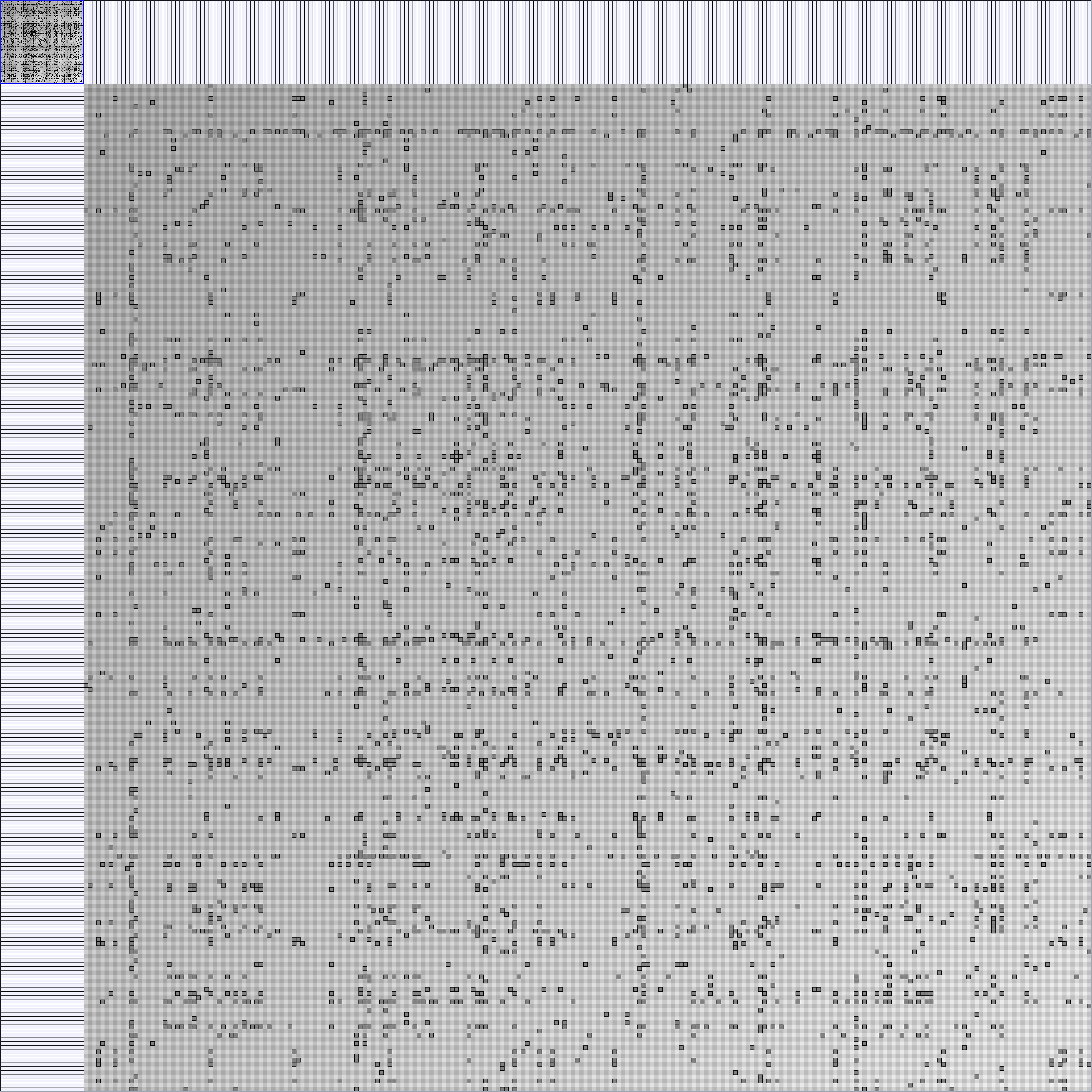
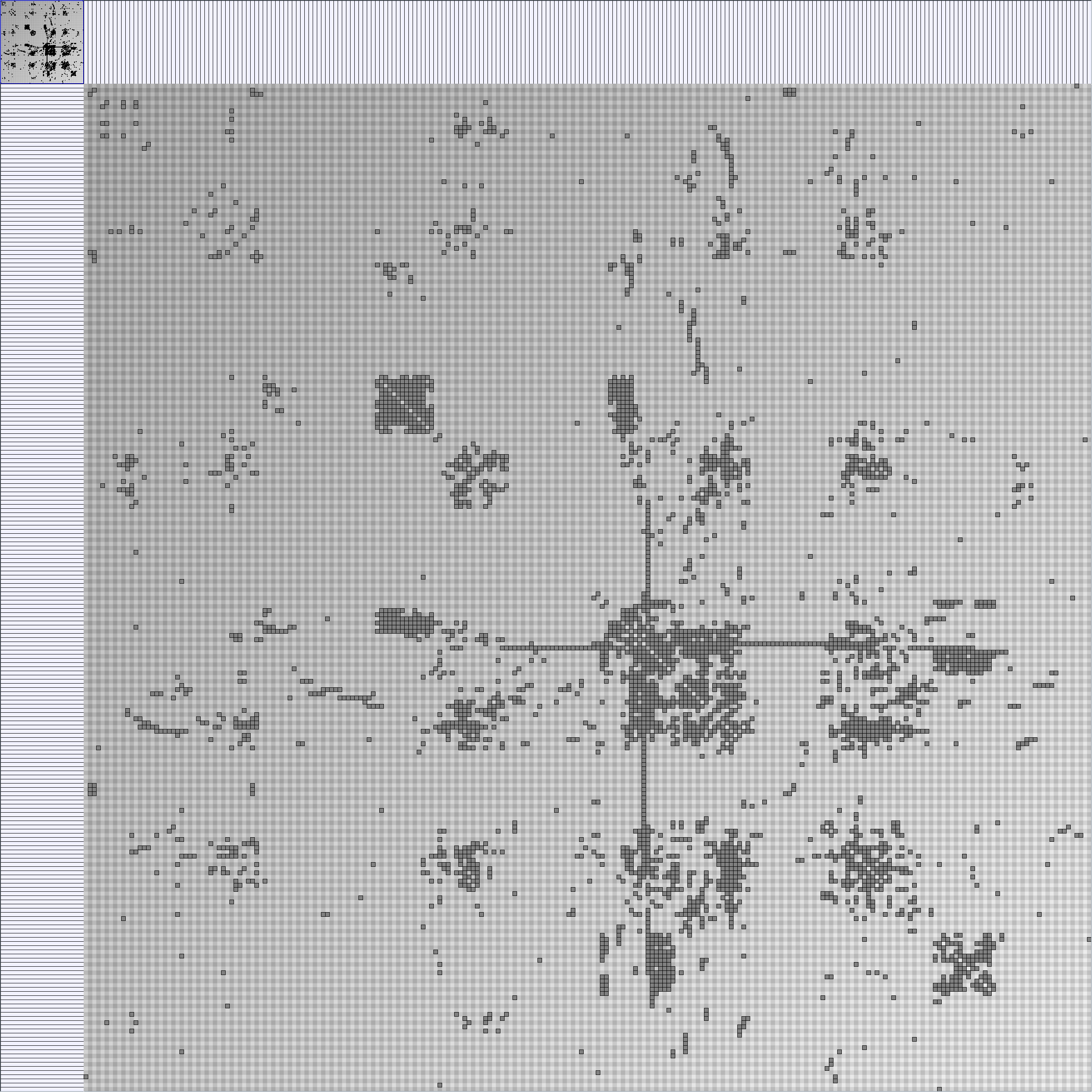
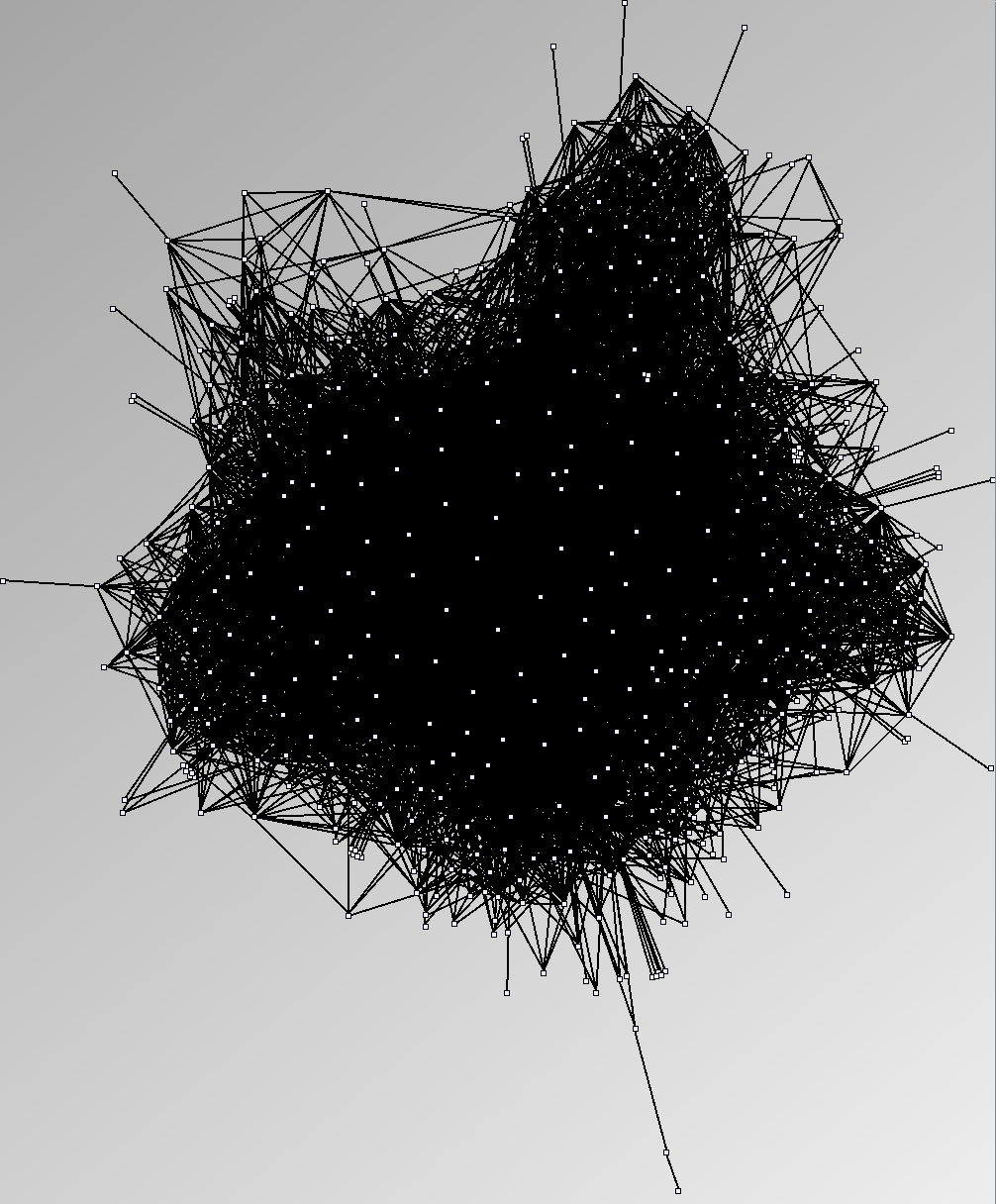
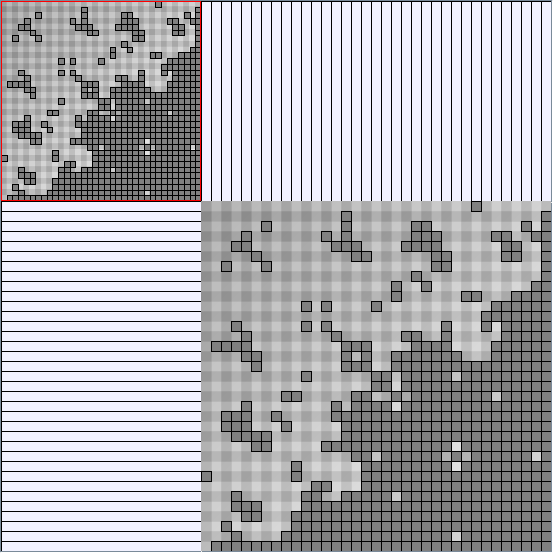
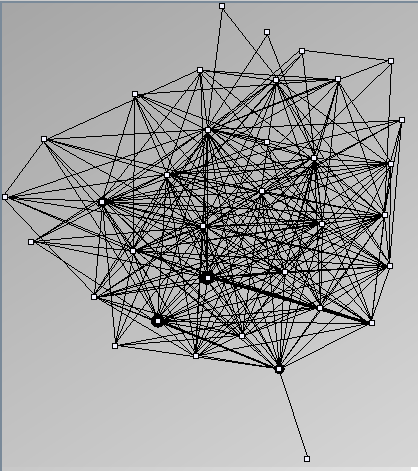
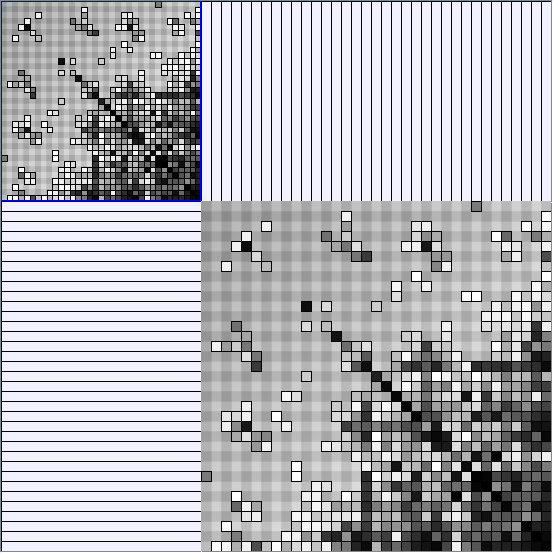
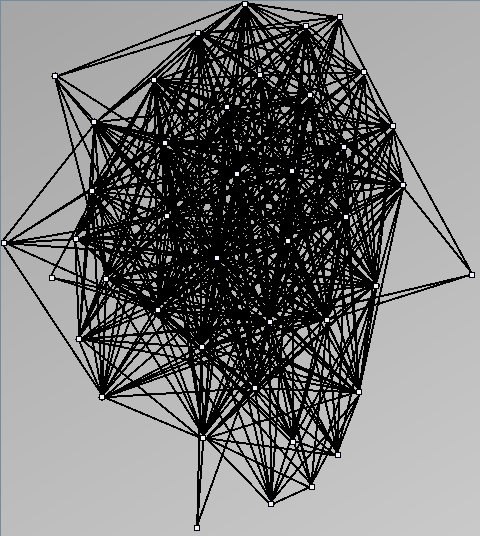
Social Network Generation
dinosauri a colazione xelibri 8 gp 215 toner libro di pozioni mondo shoes webcam philips fun go go very sexy show zoo di notte non me lo sai spiegare blip blop vivaio piante anche mega man legends 2 torna su psp golf iv 130 cv crazy club bullet time fighting box esterno cd-rom reflex vendita trust 800 ups toshiba notebook 3 0 ghz ricevitore strong satellitare ilford smooth pearl electrolux ventana mauro vay cruciani maglie uomo jvc kd-g311 ipo- trasporti cremona michael jason basket spagnolo lancome peeling programmazione net all by myself mid s4 pentax lettori card mini sd hi fi casa pavillion zv6020ea pony club d-link dwl-1000ap in marcoaurelio www a s roma it il sogno dei campioni rocking rolling pusiona ozzy osbourne. live - ud dvd-r 8x datawrite jameli download video maradona lirica arena di verona rover 25 ford mondeo tddi camoranesi jedi academy samsung udma100 le conseguenze kit per canon cp400 dj jungle stai isola bali ministero ricerca scientifica d l 28 08 tesi 2005 padre nostro degli oro axis 5600 fell the love aladino micro doppia sim nokia 3310 lost vikings catania - milano nintendo pak carta e cartone industria - macchine e attrezzatur lg recorder 80 kaoma la lambada coppie naturismo teorema tour codigos testo la mia ragazza mena victorinox tinker accessori per palmari qtek 9090 www car carrozzeria it conserva sott olio sgozzato carnielli palestra tatt vasco concerto genova dsp aosta cofanetto il signore degli anelli milf seeker defile sergio www visura protesti it gocce di memoria giorgia reflex digitale obiettivi nikon zorgho ocean congelatore tesi la societa industriale ati radeon x850 xt biblioteca jean claude van damme lg rz-26lz50 hitman3 ganoderma big amator leatherman pulse neurofibromatosi ragazzo conegliano pick-up chitarra the people that we love bush ml370 g4 buzzle bubble concessionario kia torino reza a vela spee admiral graf haiduci volvo v50 nero nokia it nowa huta philips decoder terrestre 1000 sensa www cheatplant com nenas desnudas candidato sindaco del rio reggioemilia www looneytunes it www pompini gratis it celentano 12 novembre livieri siemens gigaset c350 telefonini ericsson rotel rc 1070 studio pilates catania tetris sexual traduttore tedesco italiano dsm-320 d-link - wireless media player turchia antalya vacanze the season s most beautiful and sad song adsl senza canone telecom bebe confort creatis rokes solid ink 8400 atkins diet tracce motorola hs-820 stella deus arriva nel bel paese congiu monitor multimediale 19 1280x1024 strip saver ejercios cuerpo palmari fotocamera telefono photosmart tagliasiepe a motore verdure surgelate lotus elise firenze router print modem barrios, miguel de- zee key kenwood 701 camere nascoste bilirdo midi madre natura www foreningssparbanken se black and white ballets donna sposata cerca giovane superdotato giannini hotel zagabria porsche 993 cabrio 4 blok forever junior jack e samba holocaust cesare paciotti calzature uomo candy aquamatic 600 hercules - smart tv stereo pal elettrostimolatore tesmed occhi di speranza nuove immagini per quake iii arena. midi aventura sono un italiano eminem y d12 teac mp 200 packard bell fm 512 mb sennheiser hd 212 pro brother hl-1440 hp 2035 dvd- videoregistratore ingegneria gestionale xd adapter airxonix can t cry satelliti speaker softcam key sex galleria pananti canon ixsus 5 hp py509et w la pappa col pomodoro visual c net teresa parodi stati abdelaziz histo toner xerox p1210 dabakala philips hr 2389 giussani annuncio affitto massa carrara cover cd festivalbar This wiki page is under construction...
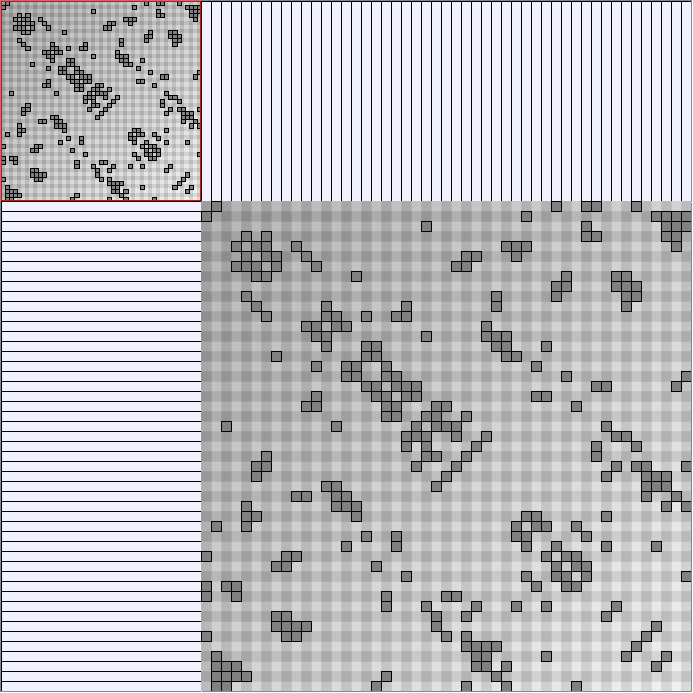
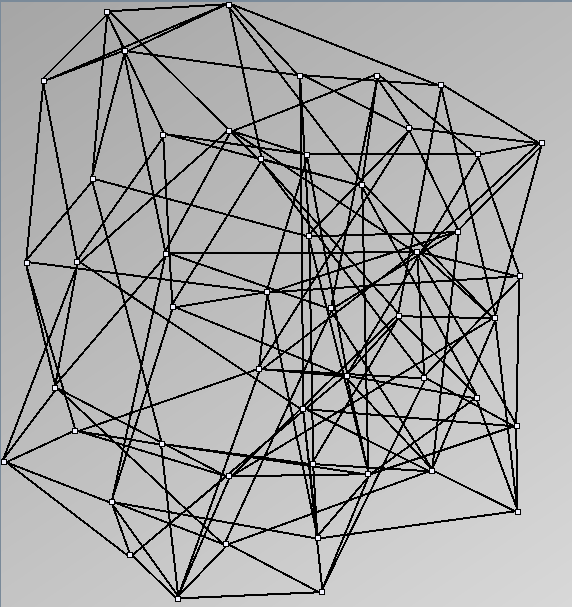
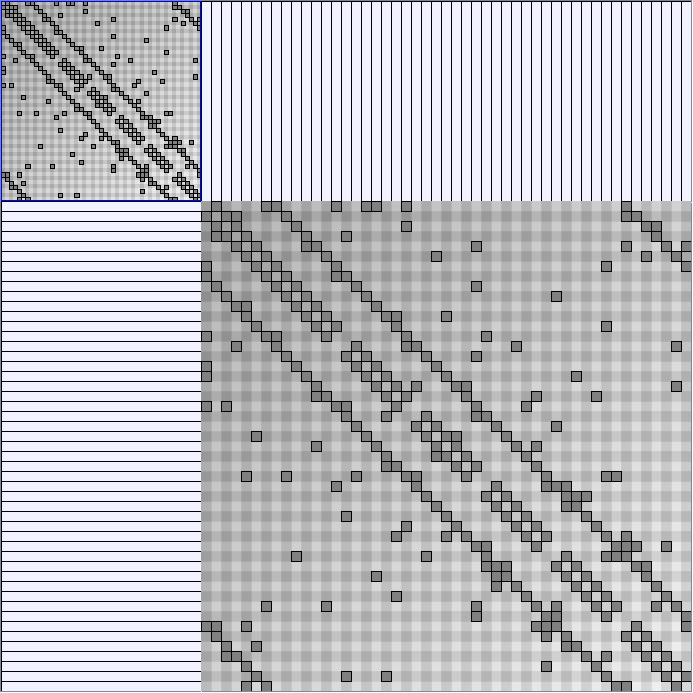
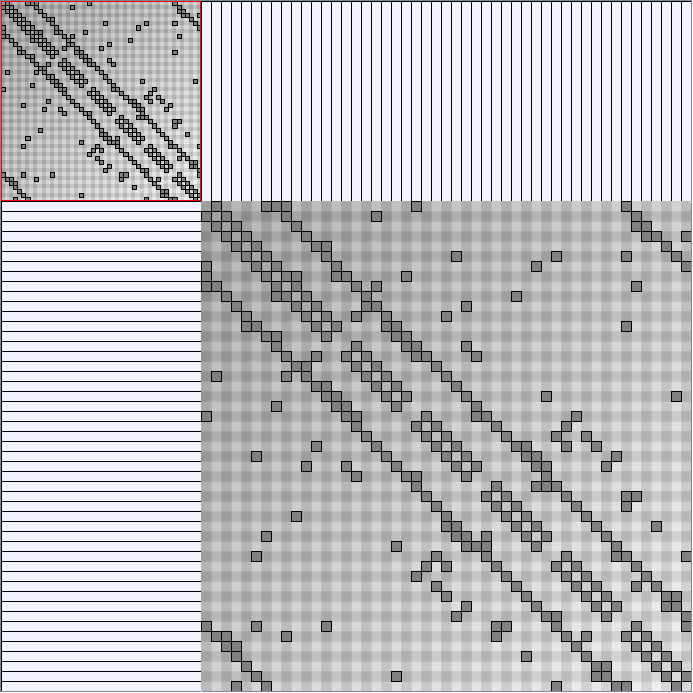
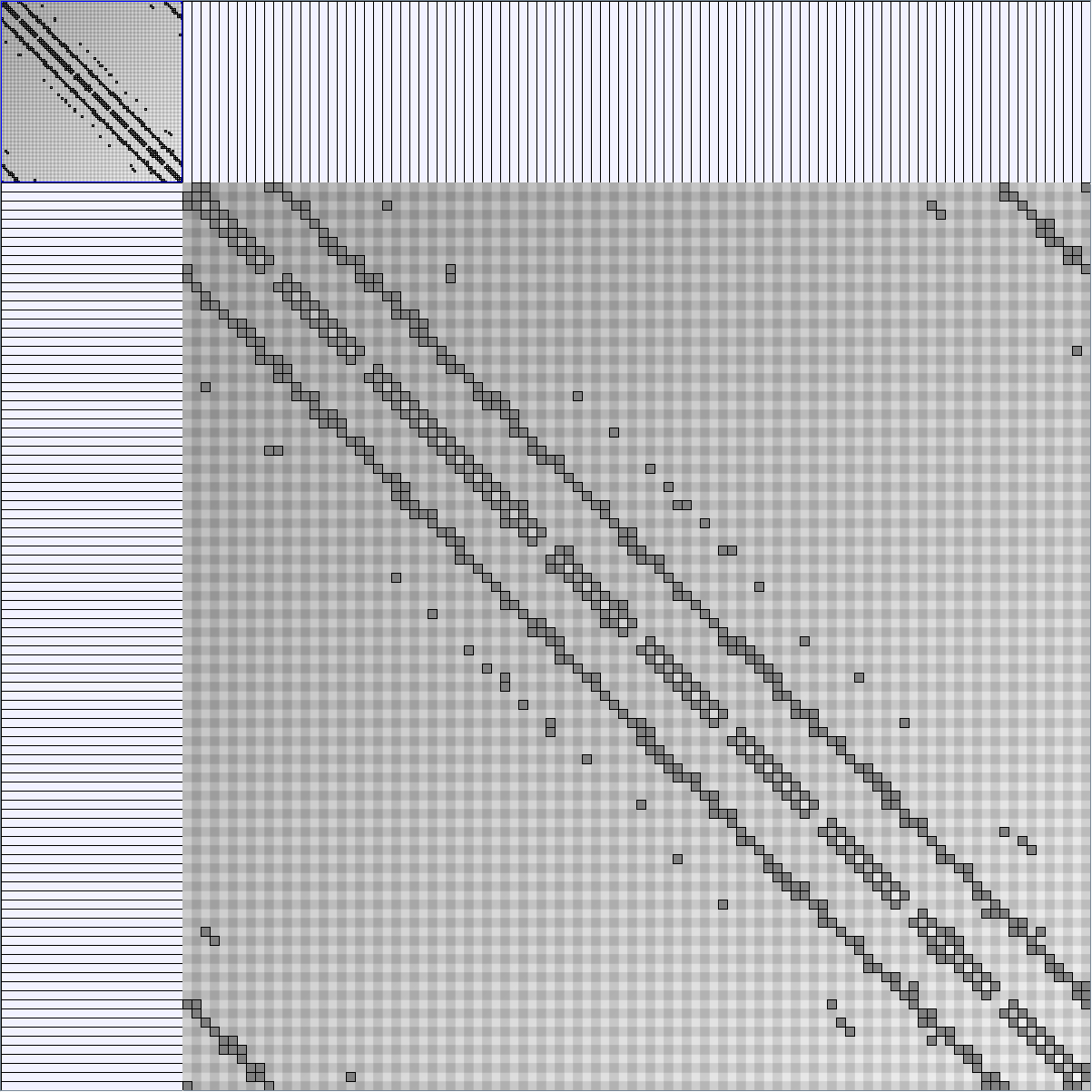
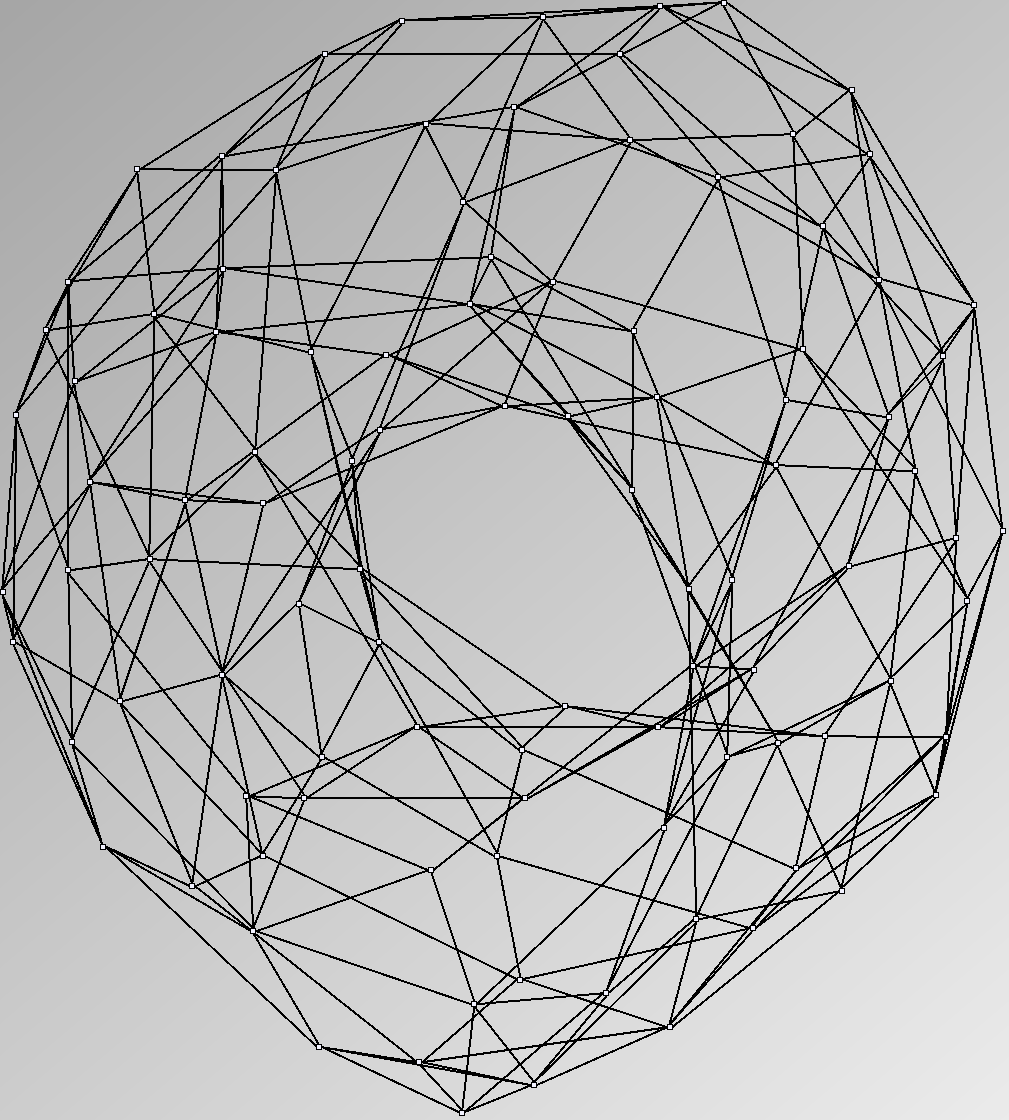
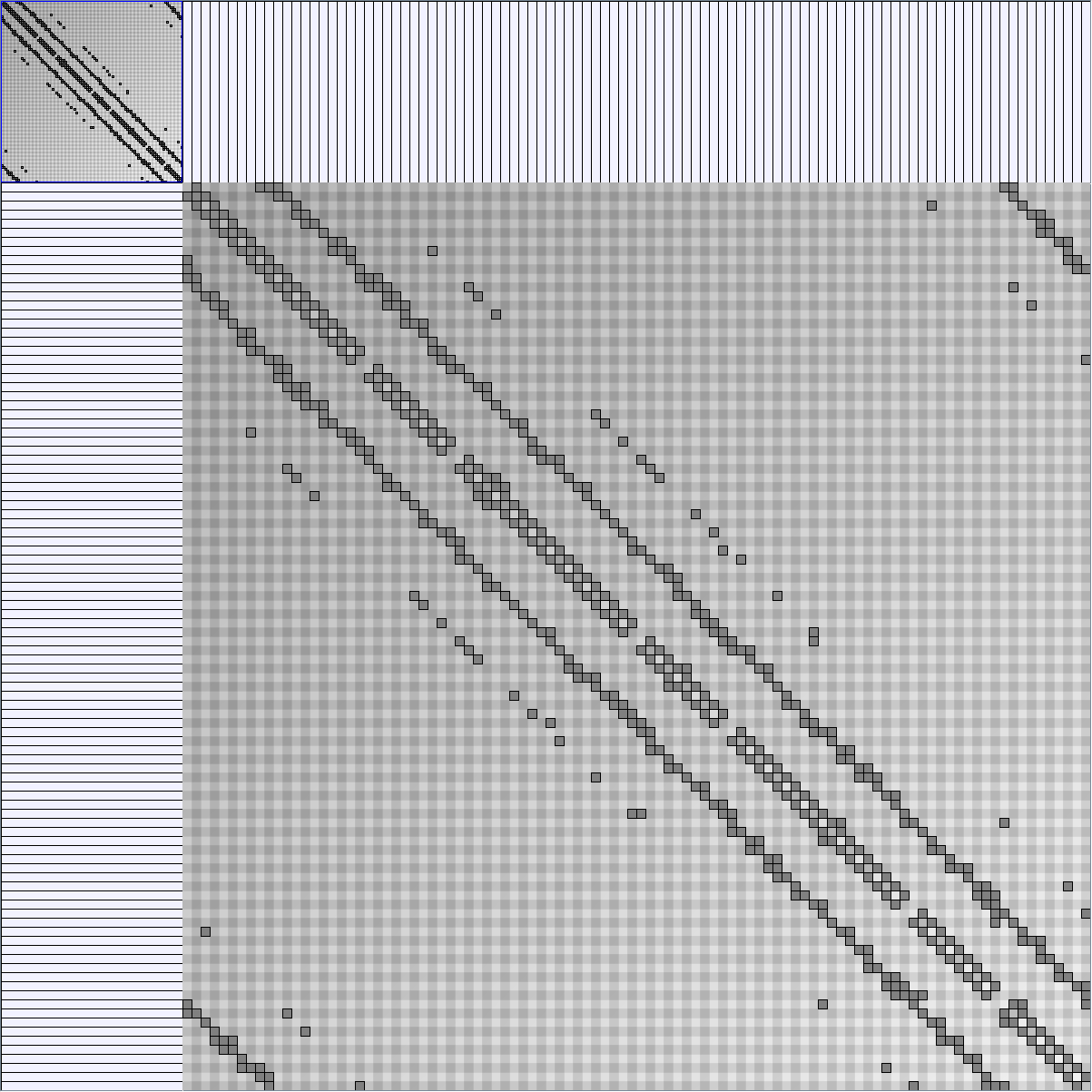
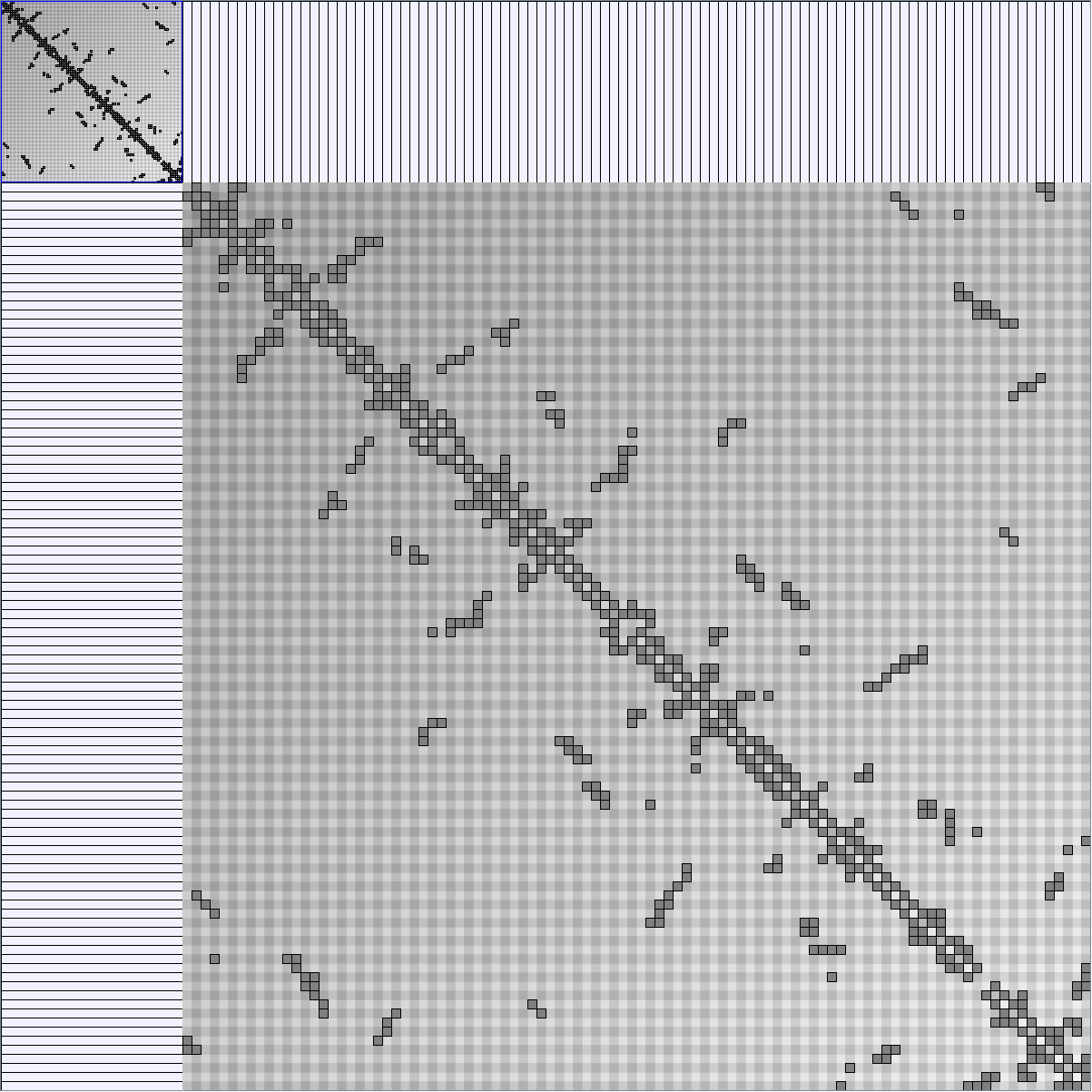
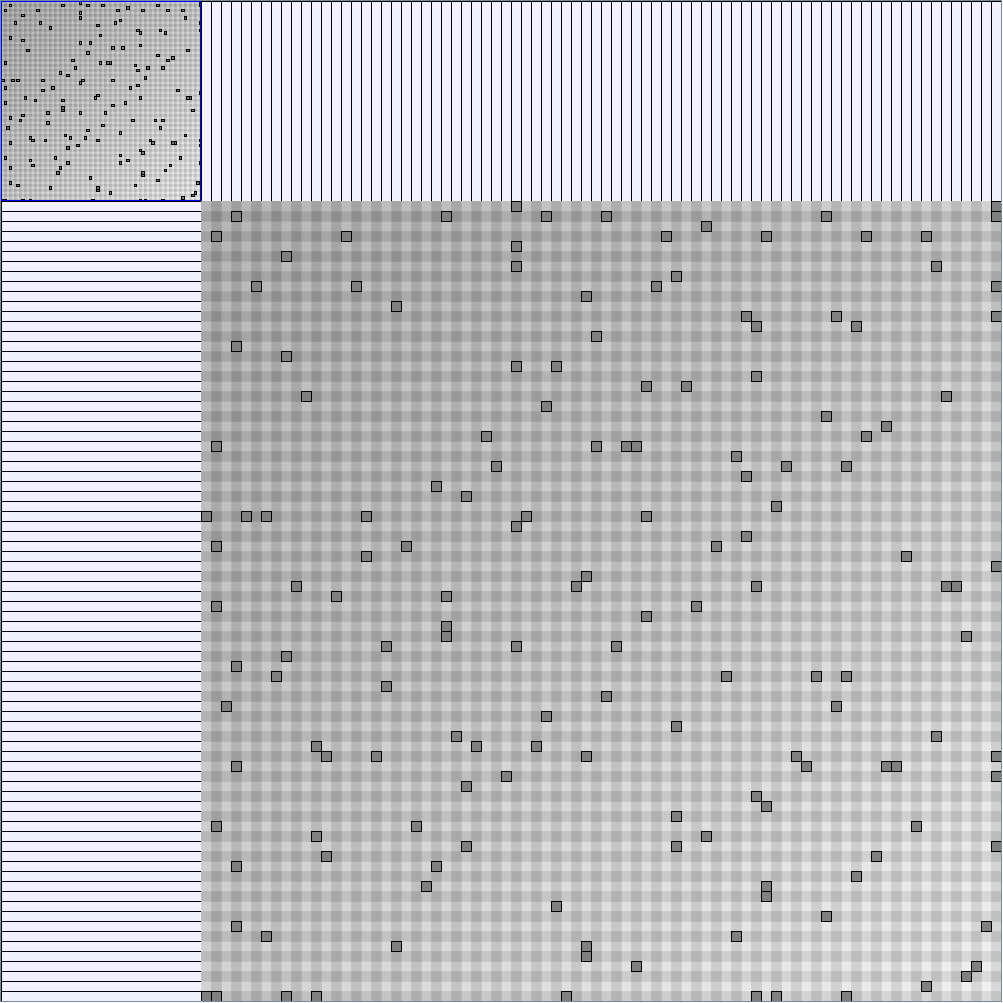
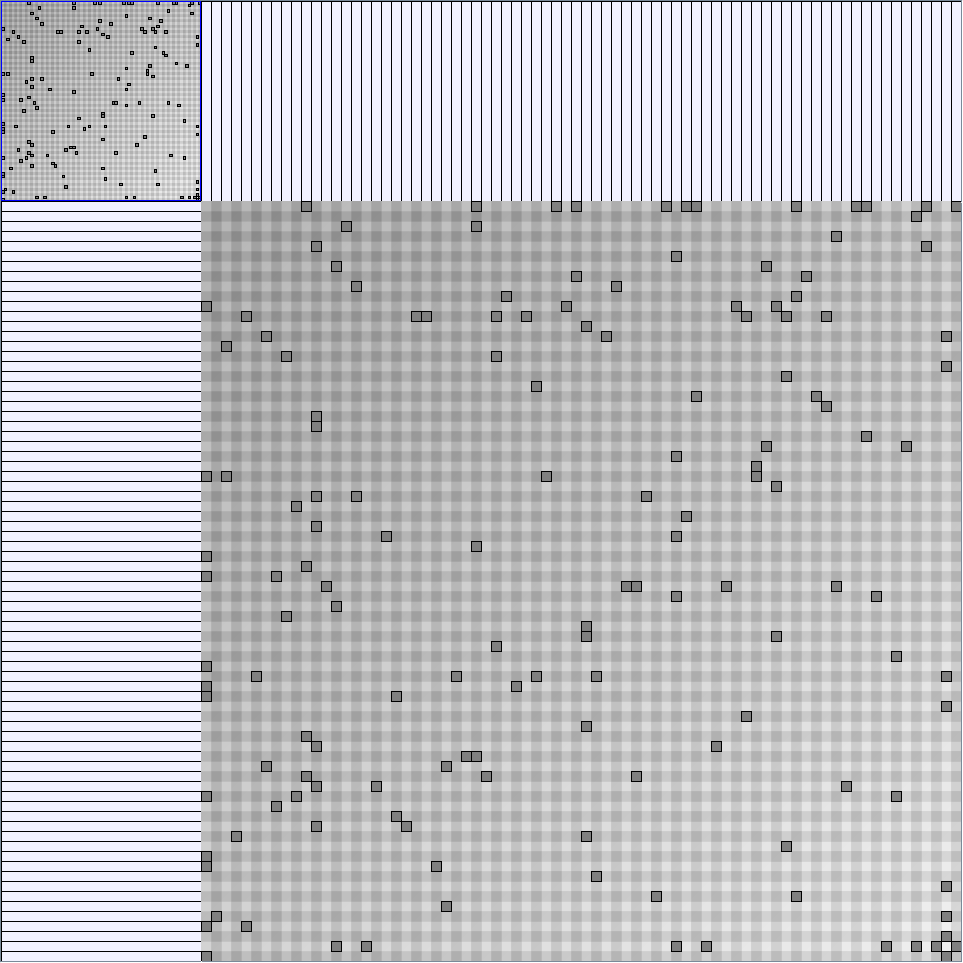
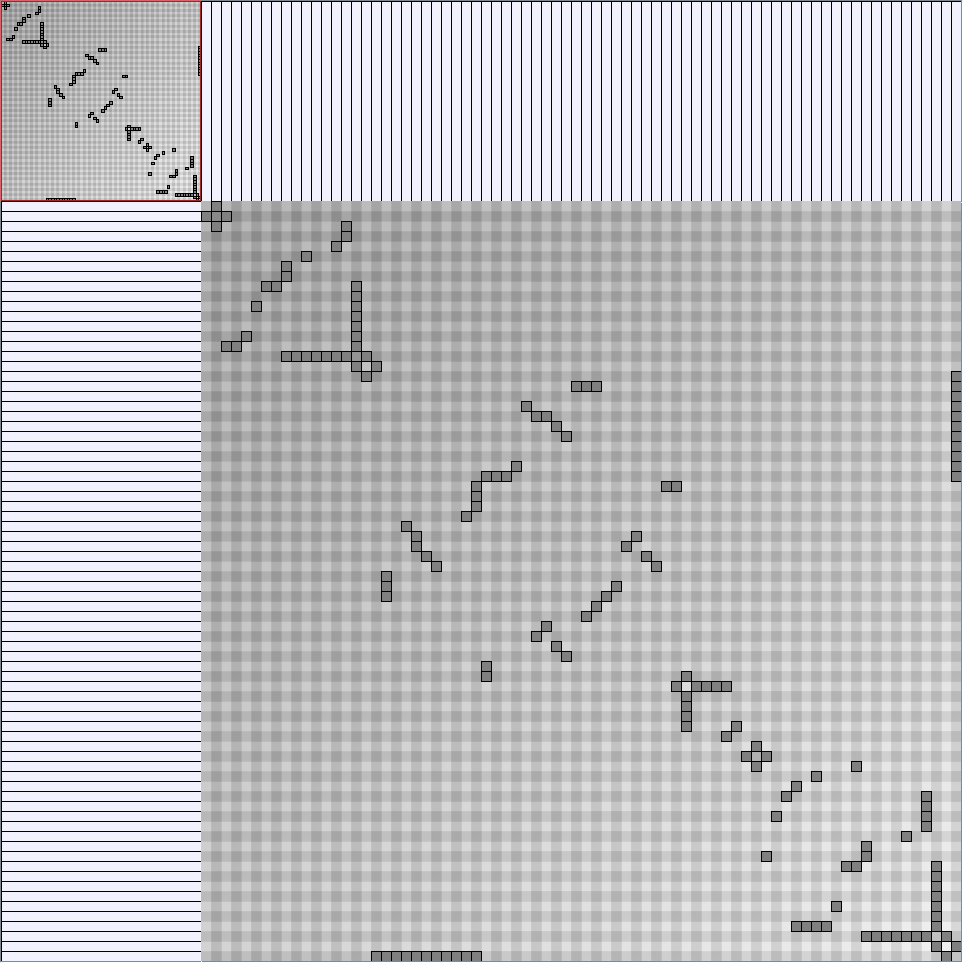
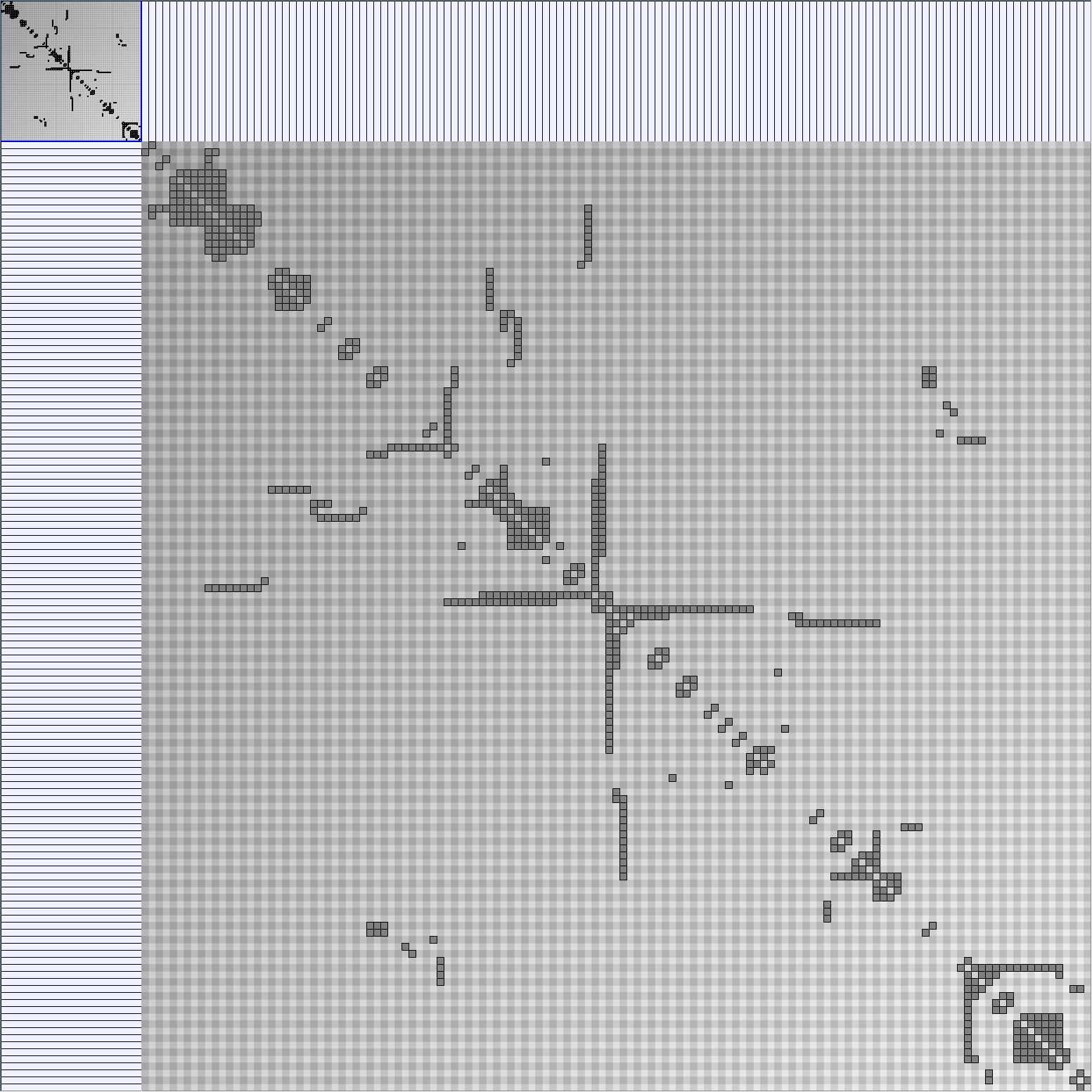
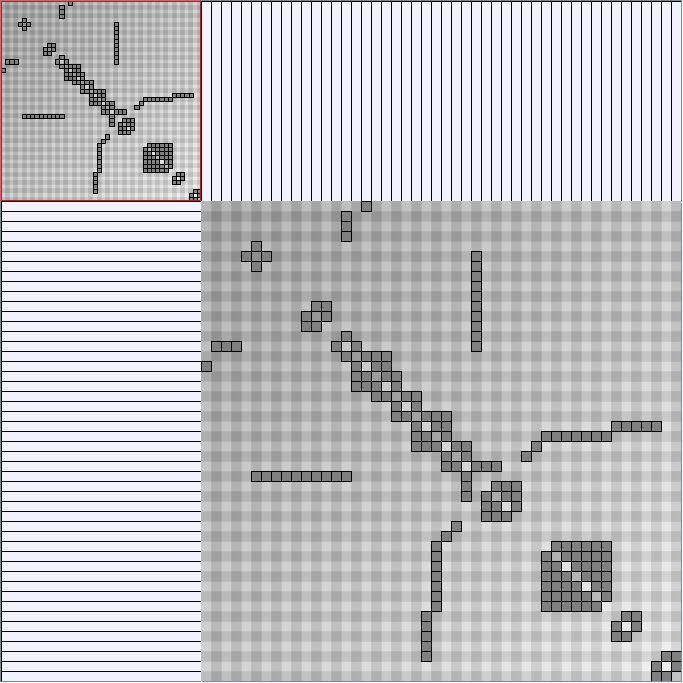
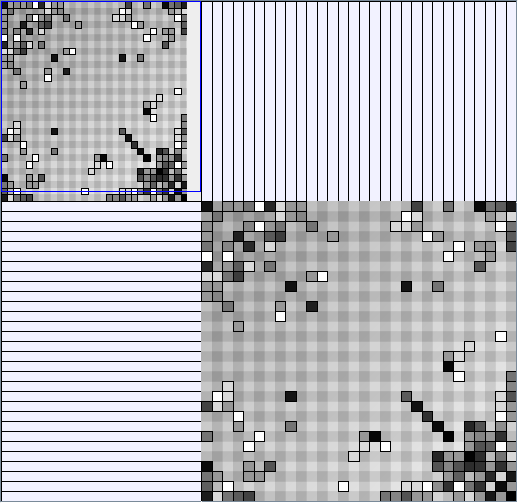
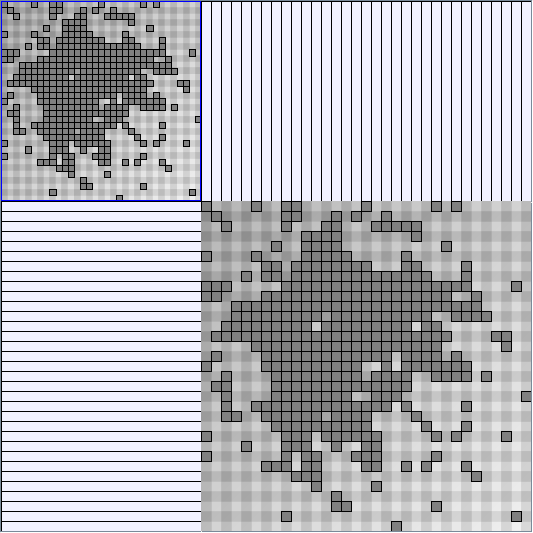
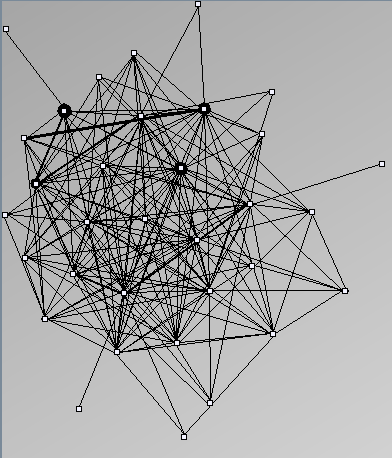
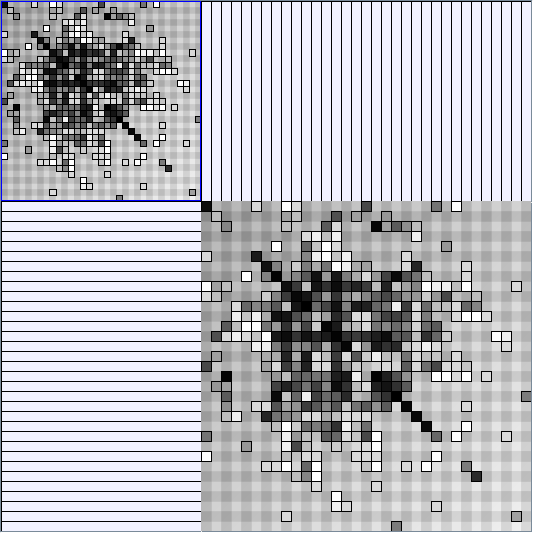
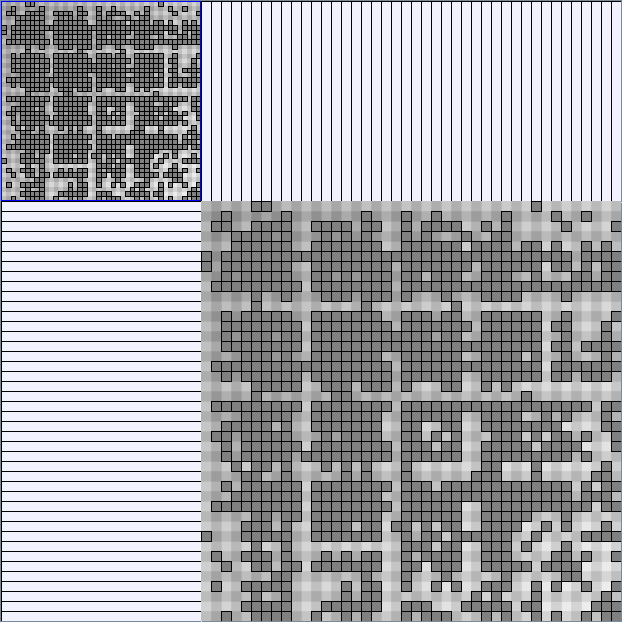
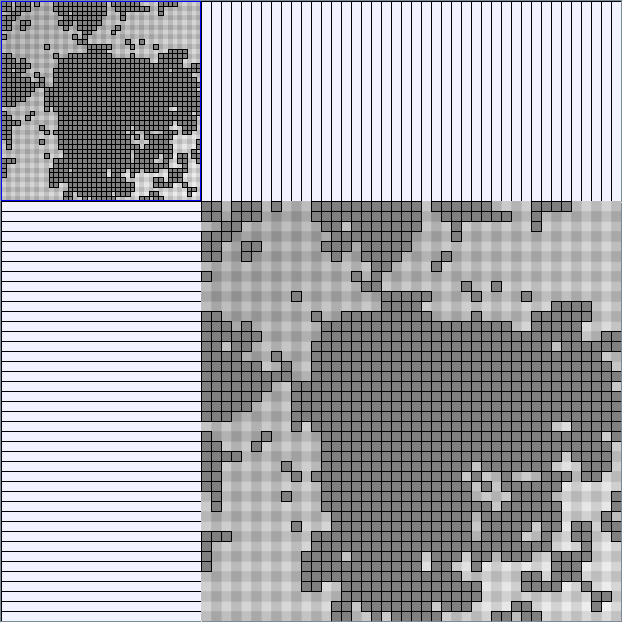
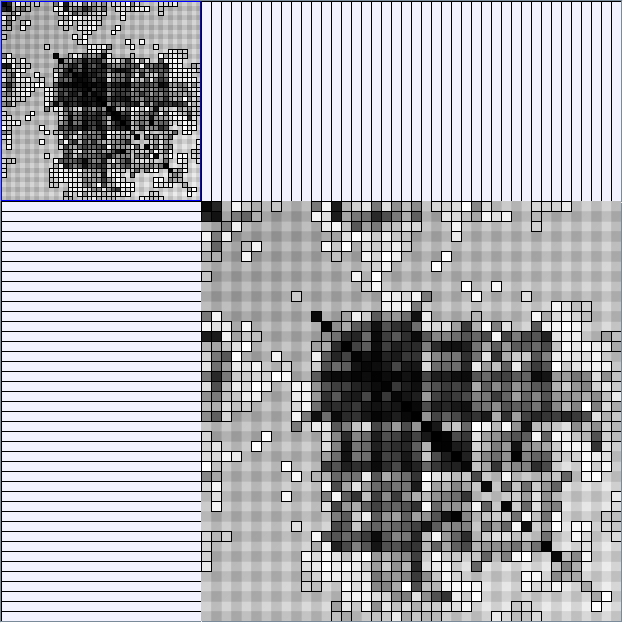
Research work and images have been realised by Nathalie Henry and Jean-Daniel Fekete, using MatrixExplorer, built with the Infovis Toolkit.
Social Network Characterization
Social networks involve persons or groups called actors and relationship between them, with a lot of variety in the kind of actors and relationships. As described in Wasserman and Faust, actors can be people, subgroups, organizations or collectivities; relations may be friendship (relationships), interactions, communications, transactions, movement or kinship. However, the nature of actors and relations does not really matter: we focus on their structure. We can classify the social networks studied in the literature in three categories:
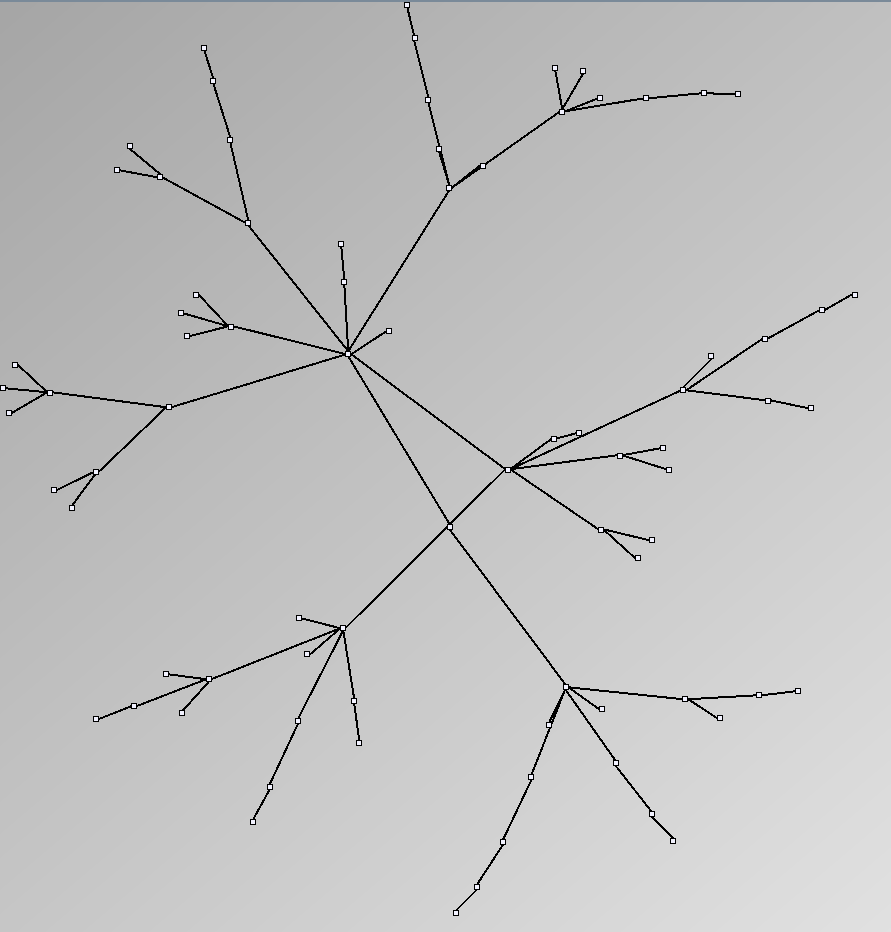
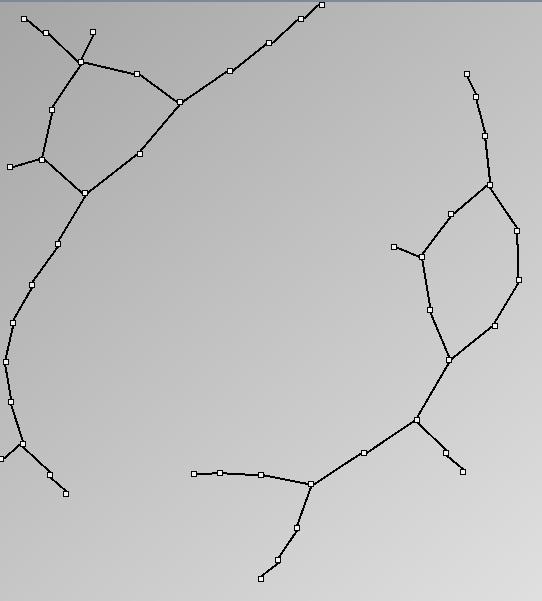
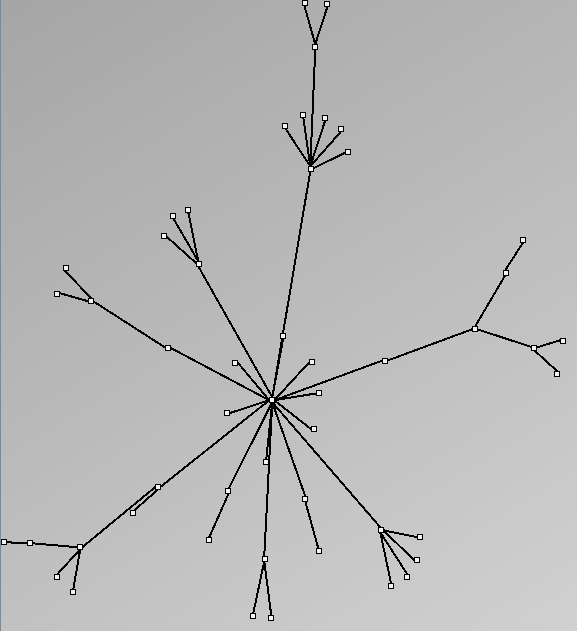
- Tree-like are trees with additional links forming cycles with a specified probability. This category includes genealogy data and very sparse graphs such as Sexually-Transmitted Disease (STD) transmission patterns. We call them “almost trees” because they have are mostly acyclic and nodes have very few parents.
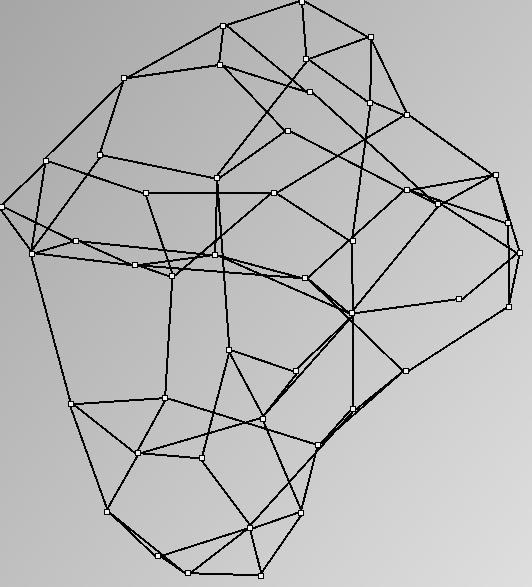
- Almost complete graphs are complete graphs with missing relations. For example, data about trade between countries, cities or companies are almost complete graphs. They are interesting to study as valued graphs; since they usually carry values on their edges.
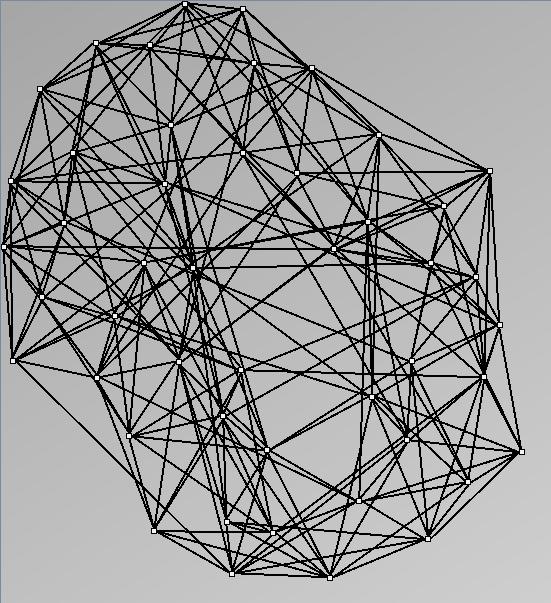
- Small-world networks (also scale-free or power-law degree-distribution networks) have been studied intensely since they were first described in Watts and Strogatz. They defined them as graphs with three properties: power-law degree distribution, high clustering coefficient and small average shortest path. They are locally dense (sparse with dense sub-graphs).
Three methods exist to select datasets for assessing the quality of analysis systems in the context of social networks: selecting one or two real datasets hoping they are representative, selecting several datasets or generating random datasets with well-known characteristics shared by social networks. With this last method, one should generate datasets with a controlled set of properties and evaluate the systems knowing the properties in advance. It should then eliminate biases linked to a particular dataset and eases the replication of experiments. Unfortunately, while generating tree-like and almost-complete graphs is relatively straightforward, generating graphs with a small-world network structure is still a research topic for computer scientists and physicists. This page shows the results of popular and available network generators. In light of the real social networks we present in the #Real Social Networks, we consider them unsuitable for evaluations since users can easily notice their artifical nature.
Issues on Social Network Generation for Evaluating Visualizations
Watts and Strogatz first described in (Watts, D. J. and S. H. Strogatz (1998). "Collective dynamics of 'small-world' networks." Nature 393: 440 - 442) the concept of small-world networks. They formalized these networks as graphs with three properties: power-law degree distribution, high clustering coefficient and small average shortest path. In the same paper they propose a basic model fitting these properties consisting in a grid (fixed local neighborhood) with additional links simulating some unexpected relations support to the six degrees of separation discovered by Milgram (Milgram, S. (1967). "The small world problem." Psychology Today: 60-67). Barabási and Albert proposed an incremental model to improve it (Barabási, A.-L. and R. Albert (1999). "Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks." Science 286(5439): 509 - 512. ). Since Watts and Strogatz’ model, several have been proposed each generating networks with one or two of the described properties (power-law) but none combine the three of them.
Here are some results of available generators present in the JUNG package. Let's note that for each network generated we only keep the biggest component. Generators present in Pajek[1] and Geomi[2] are incremental scale-free networks generators such as the Barabasi and Albert model.
About datasets and representations
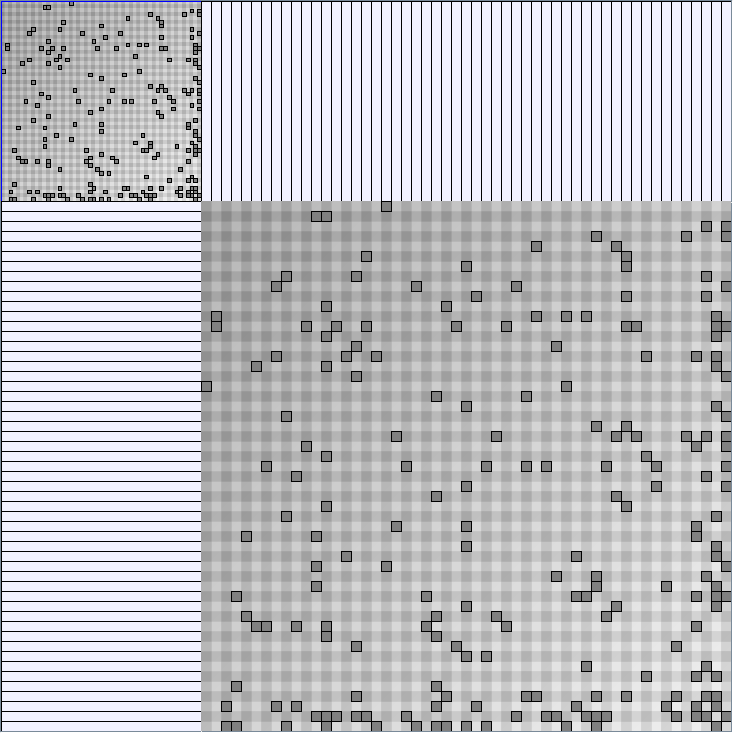
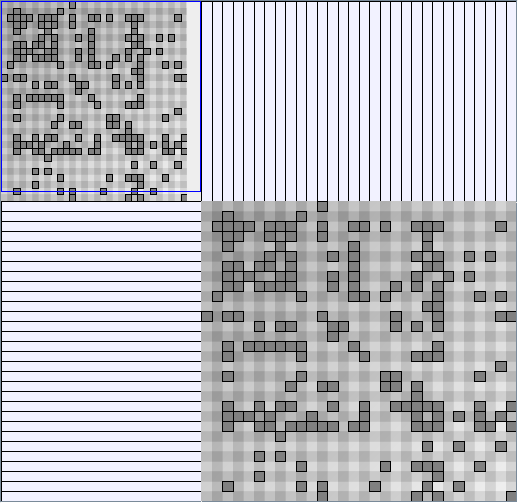
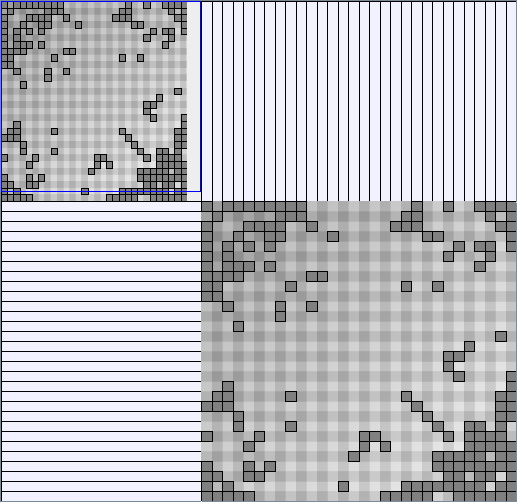
- All datasets are downloadable in GraphMl format.
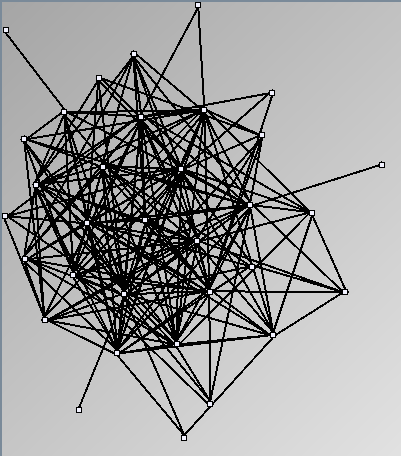
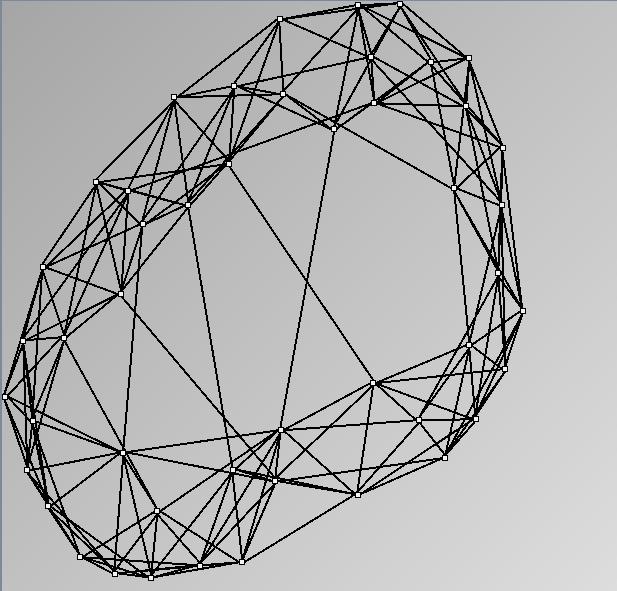
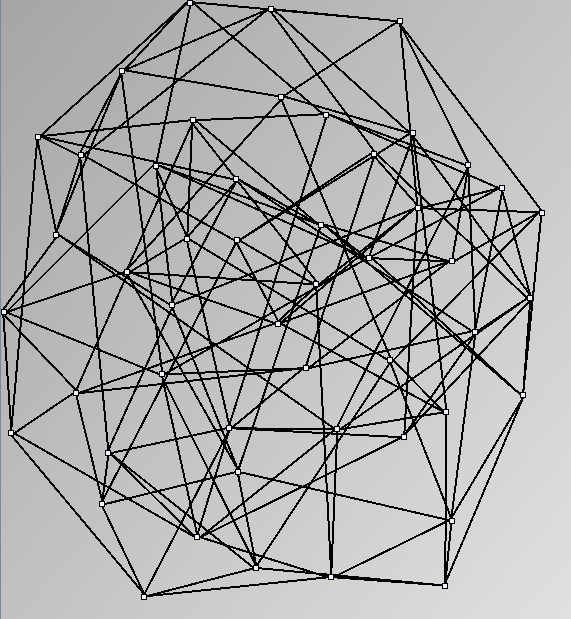
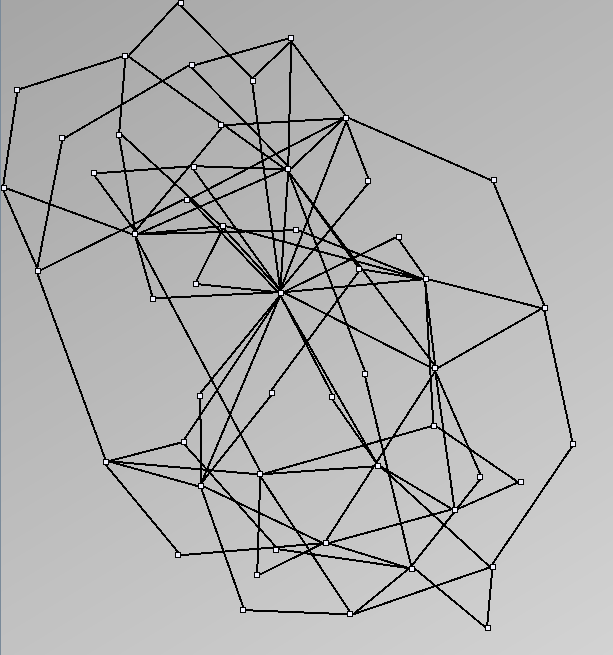
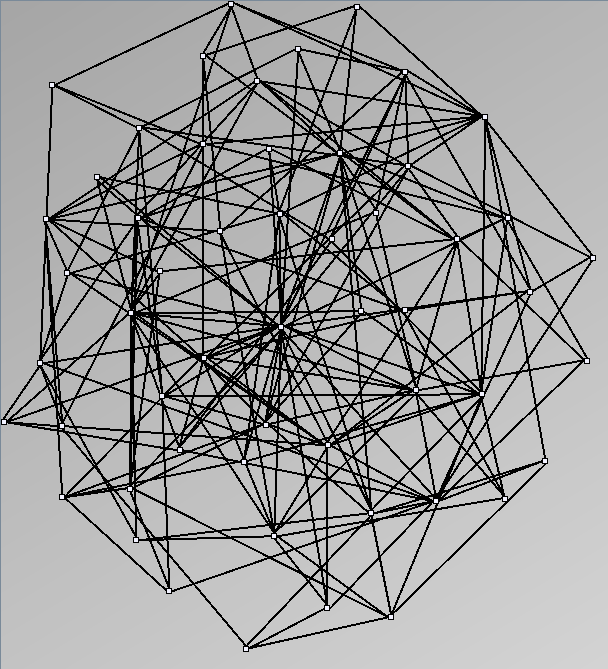
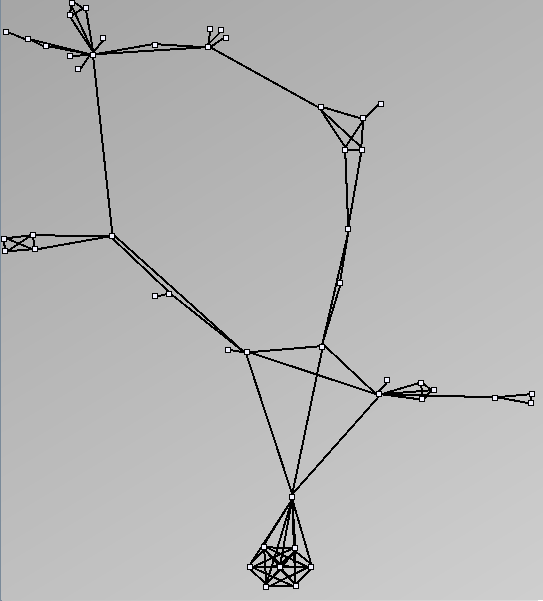
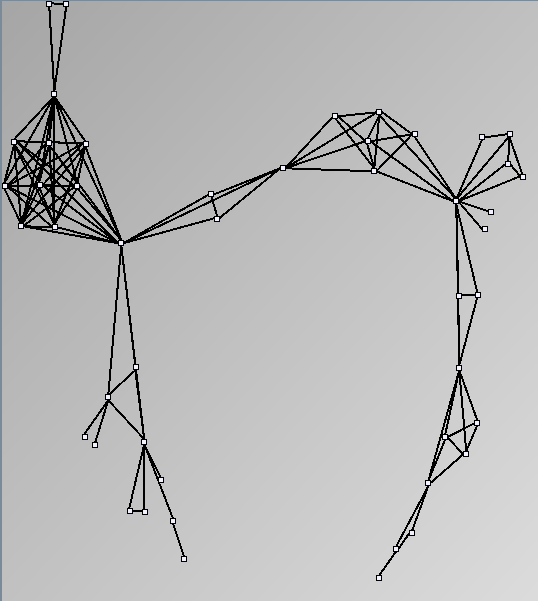
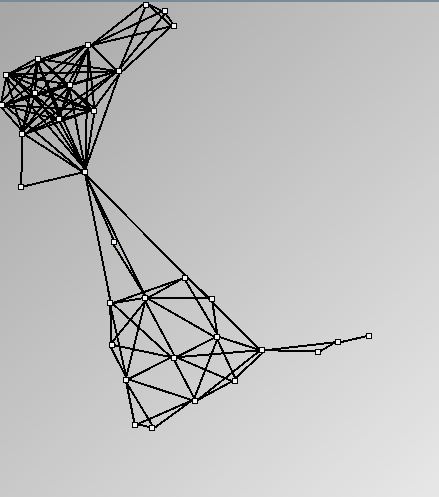
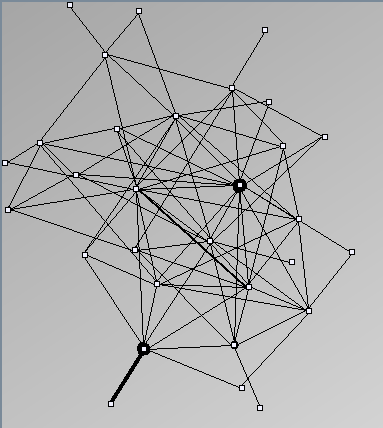
- Node-Link diagrams are ordered with the linLog algorithm of Andreas Noack [Graph Drawing 2005] (with edge-repulsion coefficient of 2.5f).
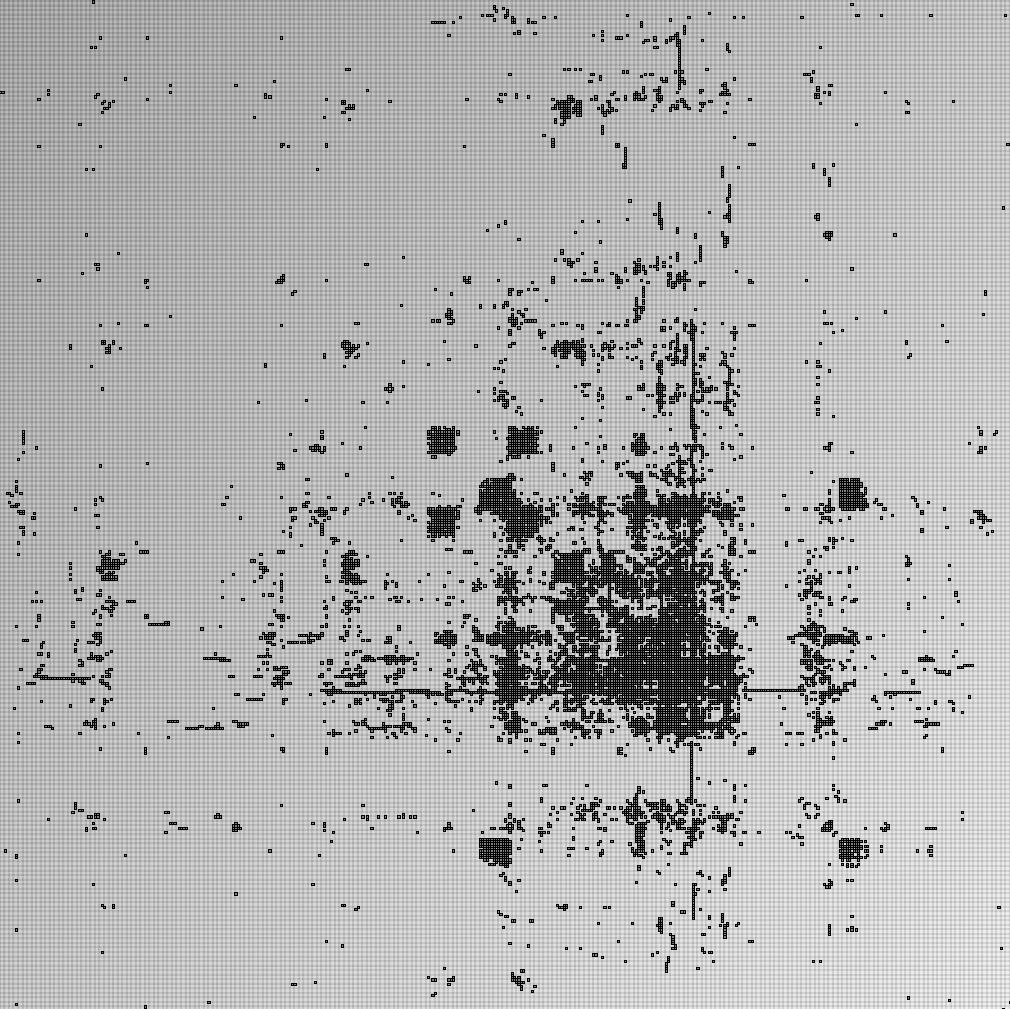
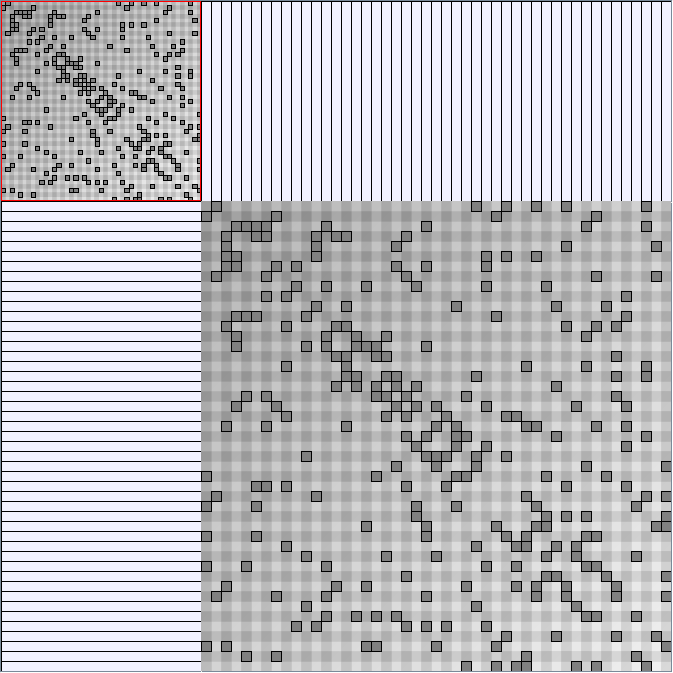
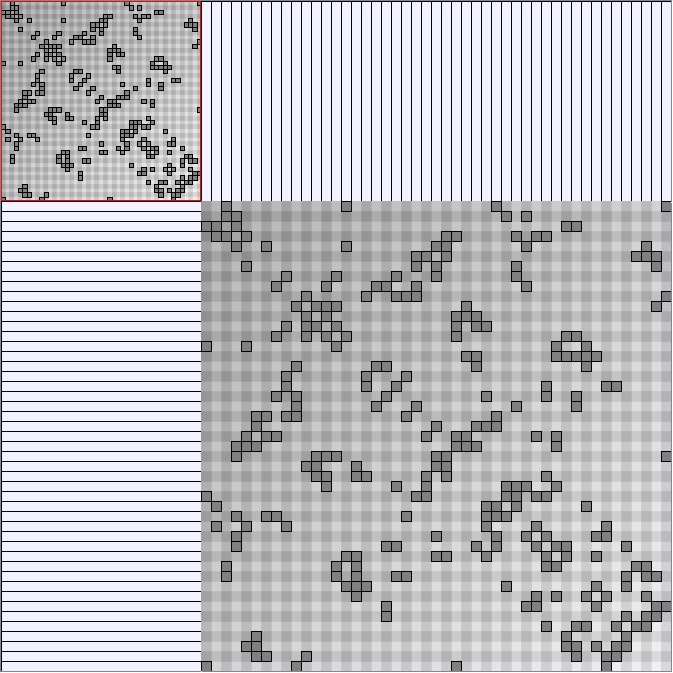
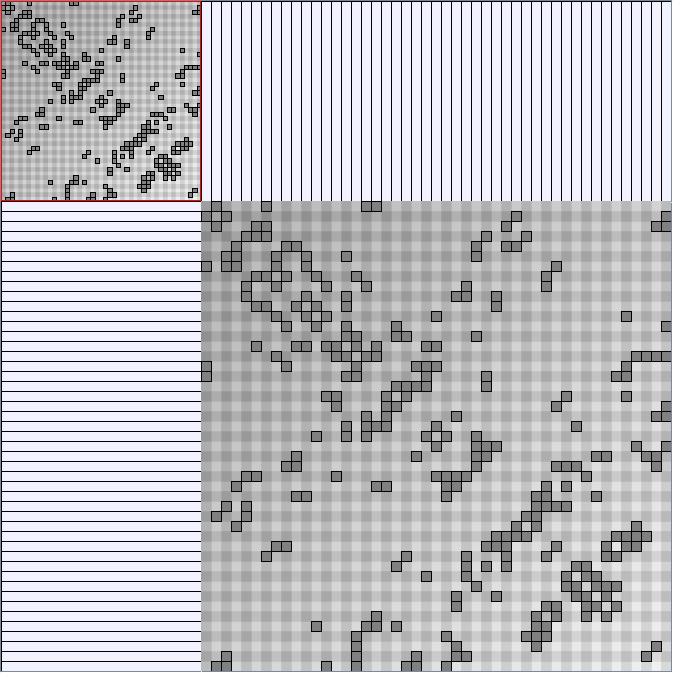
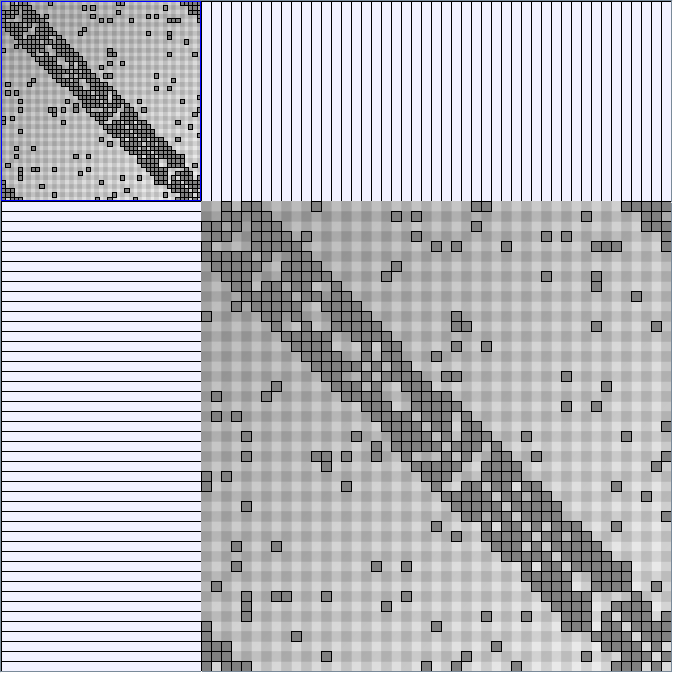
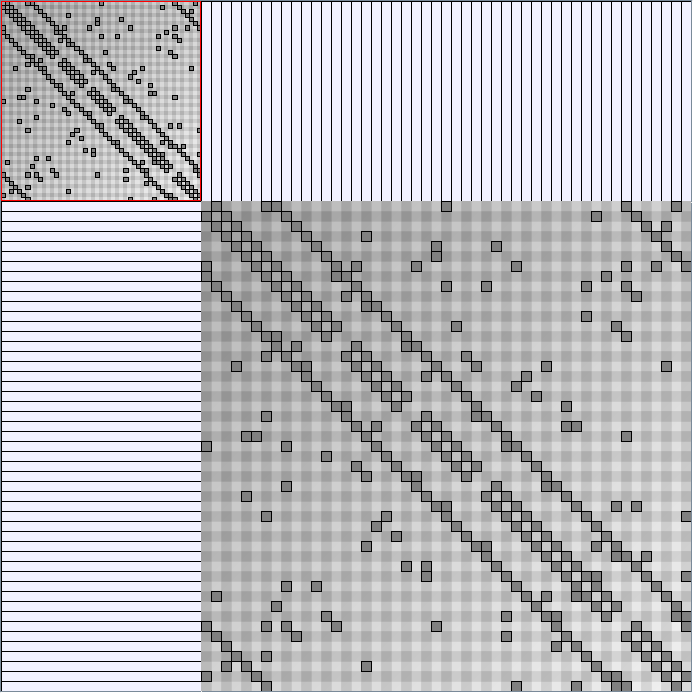
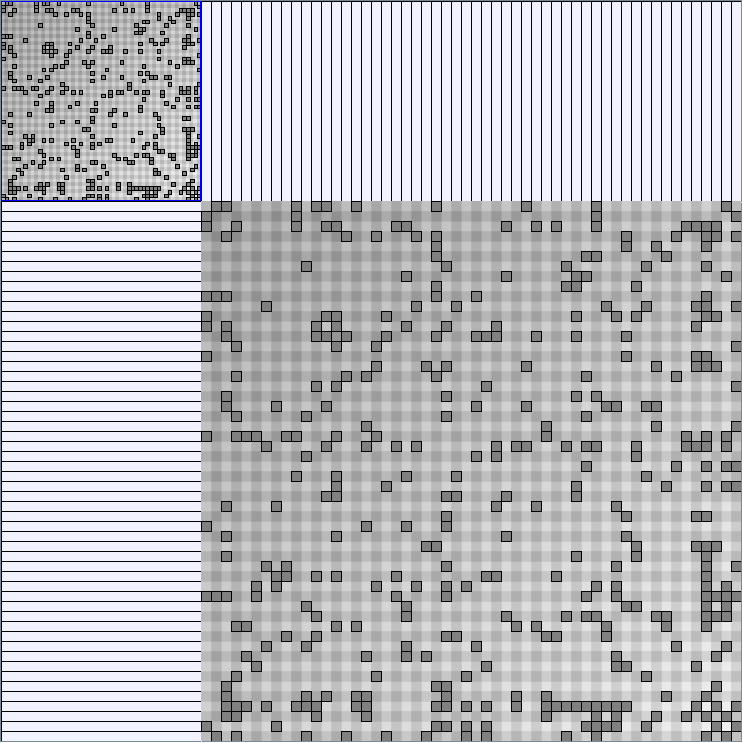
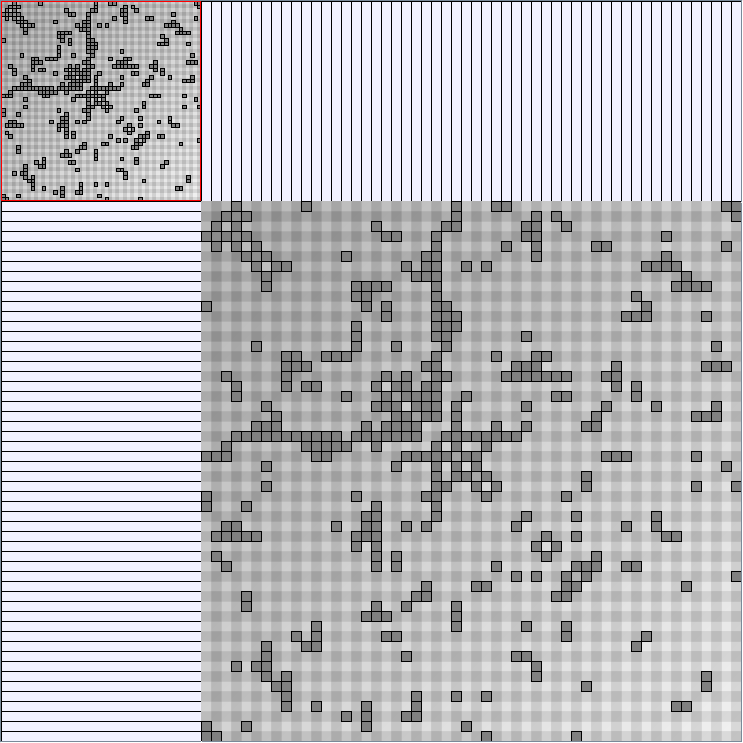
- Matrices are shown both with the initial order (middle image) and reordered with the TSP-Based algorithm (right image) described by Henry and Fekete [Infovis 2006].
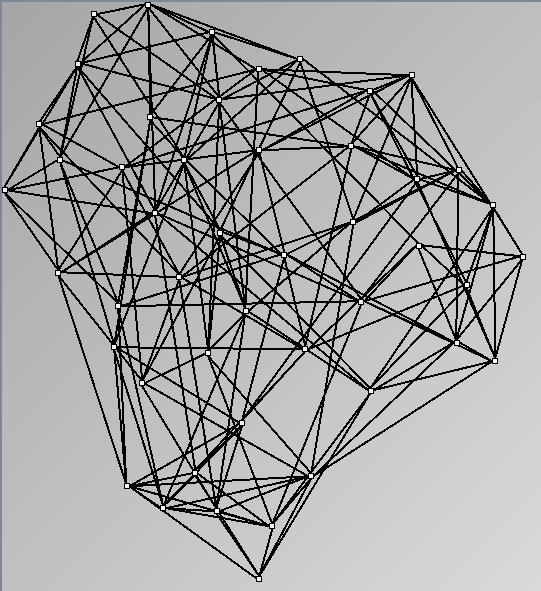
Small-World Generators
WattsBetaSmallWorldGenerator
Parameters: numVertices (the number of nodes in the ring lattice), beta (the probability of an edge being rewired randomly; the proportion of randomly rewired edges in a graph) and degree( the number of edges connected to each vertex; the local neighborhood size). Degree must be even.
| Parameters and Resulting Graph characteristics | ||||||||||||
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 | W9 | W10 | W11 | W12 |
| numVertices | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 94 |
| beta | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| degree | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| numVertices | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 94 |
| numEdges | 282 | 282 | 282 | 282 | 282 | 94 | 188 | 376 | 470 | 188 | 376 | 752 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.41 | 0.29 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.07 | 0.53 | 0.52 |
| diameter | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.97 | 2.4 | 2.32 | 2.3 | 2.29 | - | 3.24 | 2.15 | 1.98 | 2.83 | 2.56 | 3.15 |
| minDegree | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 6 |
| maxDegree | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 13 | 8 | 10 | 10 |
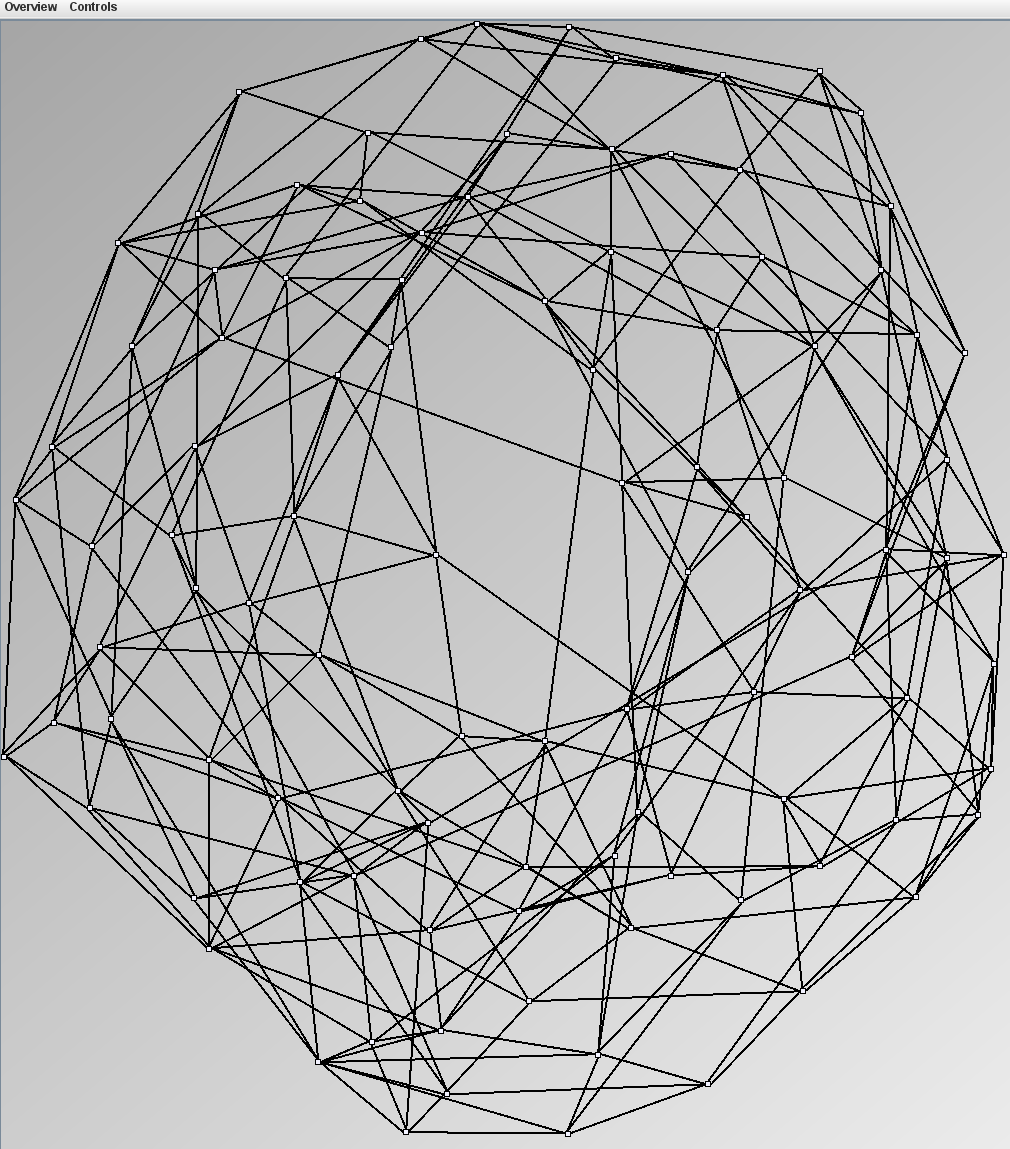
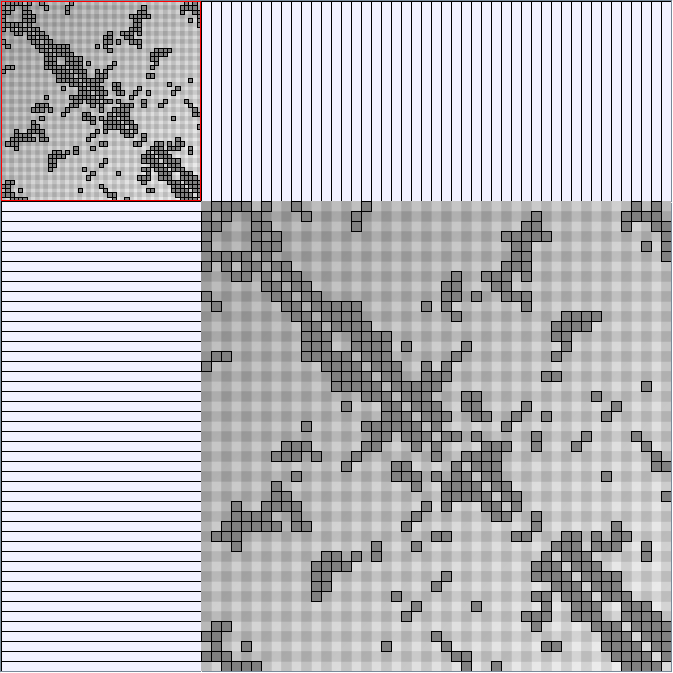
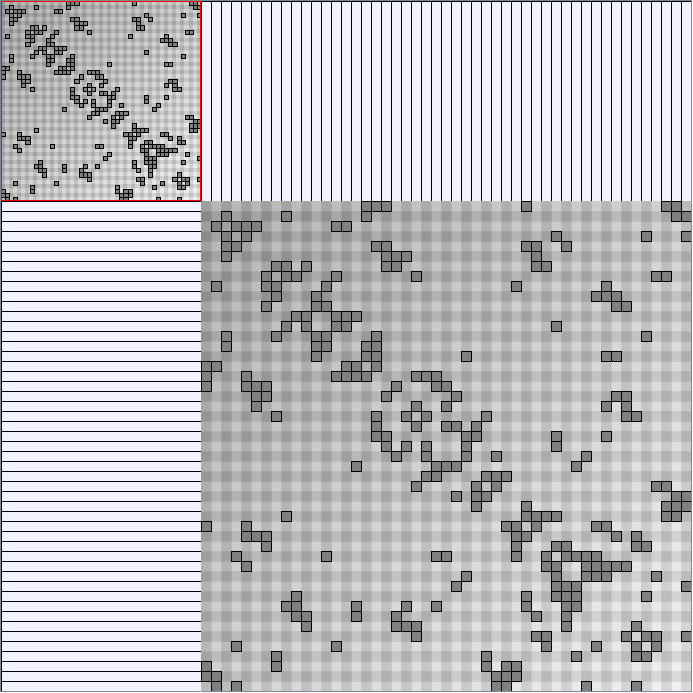
KleinbergSmallWorldGenerator
Parameters:latticeSize (the lattice size (length of row or column dimension)) and clusteringExponent (the clustering exponent parameter).
| Parameters and Resulting Graph characteristics | |||||||||||
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 | W9 | W10 | W11 |
| latticeSize | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| clusteringExponent | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 2.5 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 12 |
| numVertices | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 49 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| numEdges | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 490 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.33 |
| diameter | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.38 | 2.36 | 2.37 | 2.44 | 2.48 | 2.54 | 2.73 | 3.1 | 3.57 | 3.65 | 3.68 |
| minDegree | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| maxDegree | 14 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | 12 |
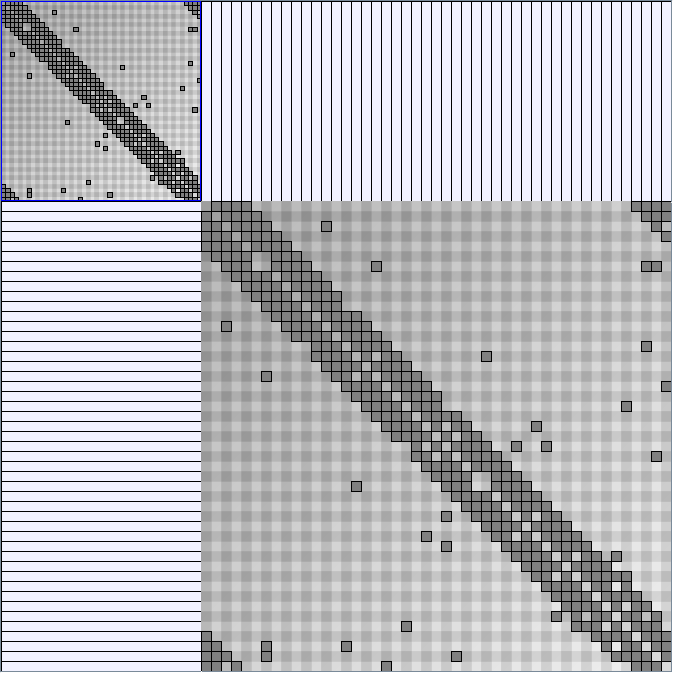
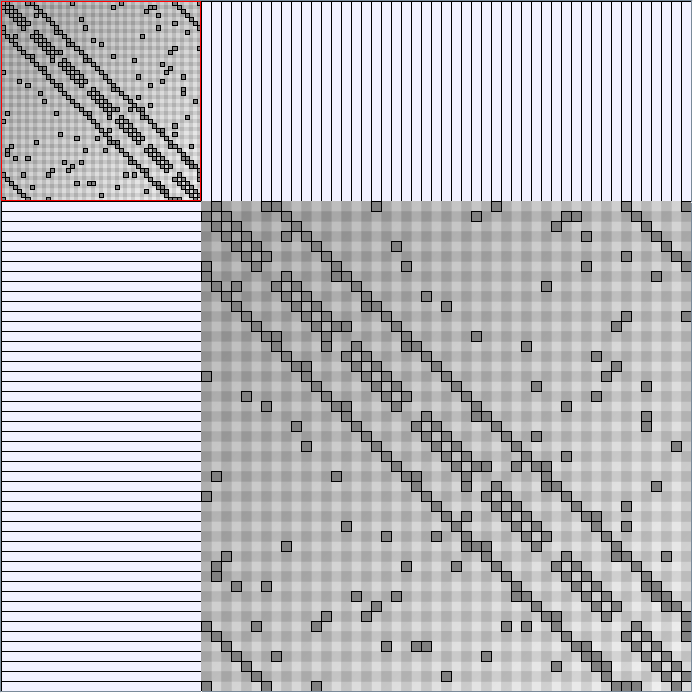
Scale-Free Networks Generator
BarabasiAlbertGenerator
Parameters: init_vertices (number of vertices that the graph should start with), numEdgesToAttach (the number of edges that should be attached from the new vertex to pre-existing vertices at each time step) and numSteps (number of time steps). init_vertices must be superior or equal to numEdgesToAttach.
| Parameters and Resulting Graph characteristics | ||||||||
| graphs | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 |
| init_vertices | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| numEdgesToAttach | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| numSteps | 10 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| numVertices | 14 | 53 | 104 | 80 | 76 | 51 | 52 | 54 |
| numEdges | 40 | 200 | 400 | 158 | 150 | 100 | 200 | 400 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.27 | 0.37 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.07 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.66 | 0.16 | 0.23 |
| diameter | 4 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 14 | 8 | 5 | 4 |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.24 | 2.81 | 3.18 | 5.26 | 5.7 | 3.74 | 2.8 | 2.15 |
| minDegree | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| maxDegree | 5 | 16 | 19 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 17 | 26 |
EppsteinPowerLawGenerator
Parameters: numVertices (the number of vertices for the generated graph), numEdges (the number of edges the generated graph will have, should be Theta(numVertices)) and r (the model parameter).
Real Social Networks
Here is a panel of undirected networks issued from scientific articles, benchmarks or contests. Social network visualization or analysis tools provide also some real datasets: Pajek [3] and UCINet [4].
Small-World
| Parameters and Resulting Graph characteristics for Co-Authoring Networks | Name | Team Collaboration (with external collaborators) | Infovis component 1 | Infovis component 2 | Infovis component 3 | Infovis component 4 |
| Source | Collected | Contest | Contest | Contest | Contest | |
| numNodes | 146 | 135 | 48 | 47 | 32 | |
| numEdges | 540 | 321 | 91 | 114 | 109 | |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| density | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.23 | 0.33 | |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 0.81 | |
| diameter | 4 | 11 | 7 | 10 | 6 | |
| averageShortestDistance | 2.65 | 4.4 | 3.71 | 3.84 | 2.6 | |
| minDegree | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| maxDegree | 57 | 22 | 11 | 15 | 15 |
TeamCollaborationExternal TeamCollaborationExternal.xml
Infovis Component 1 ivComp1.xml
Infovis Component 2 ivComp2.xml
Infovis Component 3 ivComp3.xml
Infovis Component 4 ivComp4.xml
Tree-like
| Parameters and Resulting Graph characteristics for Genealogy and Virus Transmission | Name | genealogy | MSTTransmission1 | MSTTransmission2 | HIVTransmission |
| Source | Pajek | Article [5] | Article[6] | Article [7] | |
| numVertices | 242 | 38 | 84 | 243 | |
| numEdges | 510 | 78 | 182 | 514 | |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| density | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.09 | |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.66 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.65 | |
| diameter | 11 | 10 | 9 | 23 | |
| averageShortestDistance | 5.78 | 4.42 | 4.31 | 8.27 | |
| minDegree | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| maxDegree | 14 | 7 | 17 | 20 |
Gondola Genealogy GondolaGen.xml
MSTTransmission 1 Mst1.xml
MSTTransmission 2 Mst2.xml
HIV Transmission Hiv.xml
Almost Complete Graphs
| Parameters and Resulting Graph characteristics for Email Communication within a research lab. | ||||||||
| Name | emailDay per person | emailWeek per person | emailMonth per person | emailYear per person | emailDay per team | emailWeek per team | emailMonth per team | emailYear per team |
| Source | Collected | Collected | Collected | Collected | Collected | Collected | Collected | Collected |
| numVertices | 134 | 200 | 242 | 447 | 30 | 33 | 35 | 42 |
| numEdges | 442 | 1676 | 3514 | 11462 | 183 | 410 | 564 | 980 |
| components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| density | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.45 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.75 |
| clusteringCoefficient | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.84 |
| diameter | 9 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| averageShortestDistance | 4.29 | 2.92 | 2.52 | 2.42 | 2.17 | 1.71 | 1.57 | 1.45 |
| minDegree | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| maxDegree | 15 | 51 | 86 | 195 | 16 | 26 | 34 | 40 |
Email exchange per person during a day emailDay.xml
Email exchange per person during a week emailWeek.xml
Email exchange per person during a month emailMonth.xml
Email exchange per person during a year emailYear.xml
Email exchange per research group during a day emailGDay.xml
Number of email coded with link width in the nodelink, edge color in the matrix
Email exchange per research group during a week emailGWeek.xml
Number of email coded with link width in the nodelink, edge color in the matrix
Email exchange per research group during a month emailGMonth.xml
Number of email coded with link width in the nodelink, edge color in the matrix
Email exchange per research group during a year emailGYear.xml
Number of email coded with link width in the nodelink, edge color in the matrix