Circle Packing: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
== Suitable Datatypes == | == Suitable Datatypes == | ||
Suitable Datatypes for this visualization technique are (large) hierarchical data structures. | Suitable Datatypes for this visualization technique are (large) hierarchical data structures. | ||
== Important Citations == | == Important Citations == | ||
{{Quotation|The visualization of hierarchical information structures is an important topic in the visualization community. Most of the work concentrated on the challenge to display large | {{Quotation|The visualization of hierarchical information structures is an important topic in the visualization community. Most of the work concentrated on the challenge to display large hierarchies in a comprehensible form.| [Wang, W. et al., 2006]}} | ||
hierarchies in a comprehensible form.| [Wang, W. et al., 2006]}} | |||
{{Quotation|The circles of different radii are suitable for representing large numbers of brother nodes. There is no overlapping between any two circles, which ensures each circle is | {{Quotation|The circles of different radii are suitable for representing large numbers of brother nodes. There is no overlapping between any two circles, which ensures each circle is visible. The circles are to be packed as close as possible to save display space. A new circle is always placed outside the front-chain and beside the circle whose center is nearest to the origin, which ensures that the shape of front-chain is basically convex like a circle.| [Wang, W. et al., 2006]}} | ||
visible. The circles are to be packed as close as possible to save display space. A new circle is always placed outside the front-chain and beside the circle whose center is nearest to the origin, which ensures that the shape of front-chain is basically convex like a circle.| [Wang, W. et al., 2006]}} | |||
Revision as of 11:46, 24 April 2007
Authors
- Hongan Wang
- Guozhong Dai
- Weixin Wang
- Hui Wang
Short description
figures
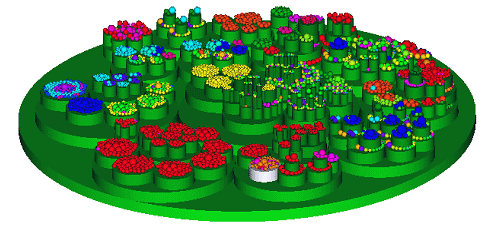
The tree nodes at different levels are represented by nested circles. Brother nodes are packed into the root node. If a node has children they are packed into it.
Packing circles with random radii. The shape is basically convex.
3D nested cylinders and spheres
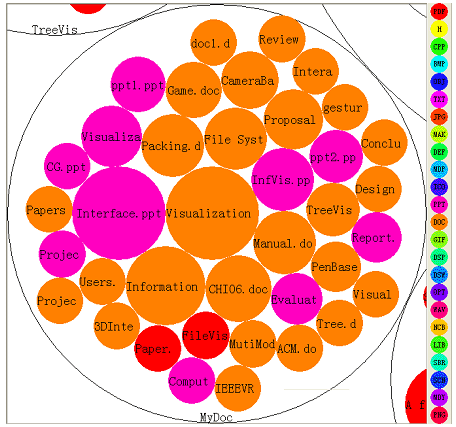
Userinterface: directories are represented by white circles.
The Color of the inner circles shows the filetype and the file sizes determine the radii.
Suitable Datatypes
Suitable Datatypes for this visualization technique are (large) hierarchical data structures.
Important Citations
Evaluation
Internal Links
External Links
References
[Wang, W. et al. 2006] Wang et al. Visualization of large hierarchical data by circle packing. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in computing systems, pages 517-520, Montréal, Québec, Canada, 2006: ACM Press.