File:KnAVA Model.png: Difference between revisions
(Conceptual Model of Knowledge-Assisted Visual Analytics. The model is divided into two spaces (machine and human) and describes knowledge generation, conversion, and exploitation within the visual analytics discourse, in terms of processes: analysis A...) |
(full source) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Conceptual Model of Knowledge-Assisted Visual Analytics. | Conceptual Model of Knowledge-Assisted Visual Analytics. | ||
The model is divided into two spaces (machine and human) and describes knowledge generation, conversion, and exploitation within the visual analytics discourse, | The model is divided into two spaces (machine and human) and describes knowledge generation, conversion, and exploitation within the visual analytics discourse, in terms of | ||
in terms of processes: analysis A, visualization V, externalization | processes: analysis A, visualization V, externalization X, perception/cognition P, and exploration E; | ||
X, perception/cognition P, and exploration E; containers: explicit | containers: explicit knowledge Ke, data D, specification S, and tacit knowledge Kt; and a non-persistent artifact: image I. | ||
knowledge Ke, data D, specification S, and tacit knowledge Kt; | |||
and a non-persistent artifact: image I. | |||
== Copyright status: == | == Copyright status: == | ||
== Source: == | == Source: == | ||
Federico, P.; Wagner, M.; Rind, A.; Amor-Amorós, A.; Miksch, S. and Aigner, W., The Role of Explicit Knowledge: A Conceptual Model of Knowledge-Assisted Visual Analytics, Proc. 2017 IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), IEEE, In Press. | |||
Latest revision as of 12:55, 2 August 2017
Summary[edit]
Conceptual Model of Knowledge-Assisted Visual Analytics.
The model is divided into two spaces (machine and human) and describes knowledge generation, conversion, and exploitation within the visual analytics discourse, in terms of processes: analysis A, visualization V, externalization X, perception/cognition P, and exploration E; containers: explicit knowledge Ke, data D, specification S, and tacit knowledge Kt; and a non-persistent artifact: image I.
Copyright status:[edit]
Source:[edit]
Federico, P.; Wagner, M.; Rind, A.; Amor-Amorós, A.; Miksch, S. and Aigner, W., The Role of Explicit Knowledge: A Conceptual Model of Knowledge-Assisted Visual Analytics, Proc. 2017 IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), IEEE, In Press.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:54, 2 August 2017 | 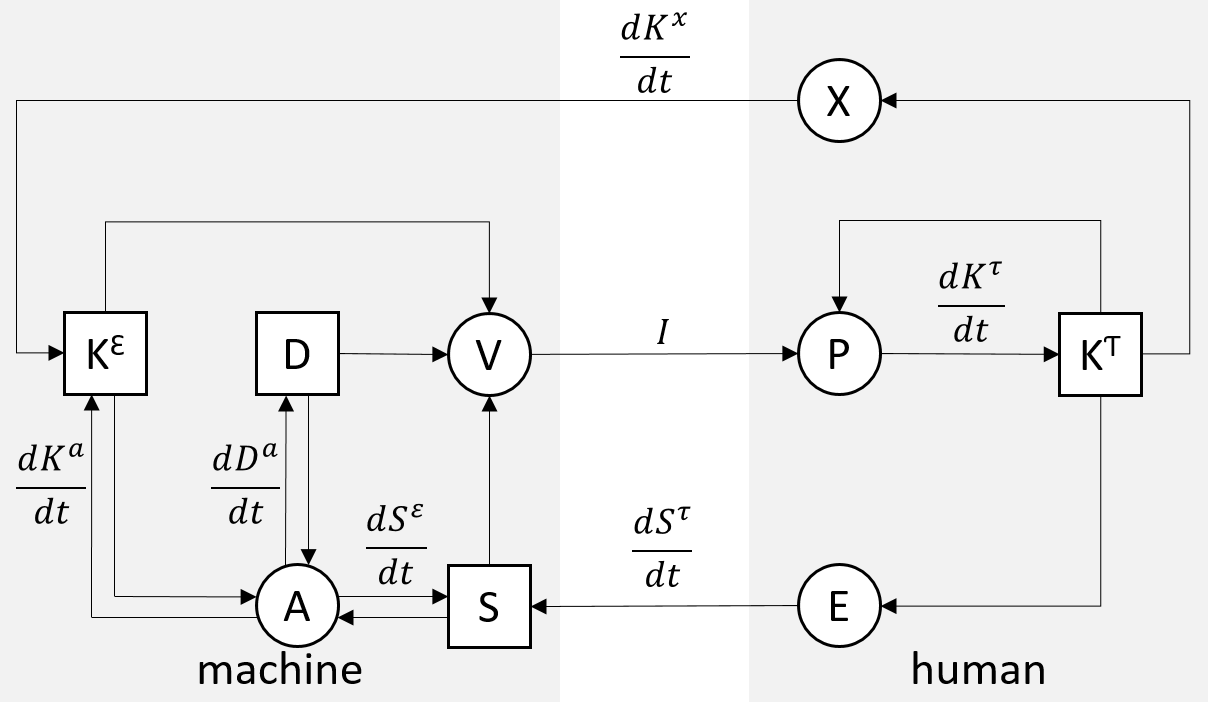 | 1,209 × 702 (42 KB) | Arind (talk | contribs) | Conceptual Model of Knowledge-Assisted Visual Analytics. The model is divided into two spaces (machine and human) and describes knowledge generation, conversion, and exploitation within the visual analytics discourse, in terms of processes: analysis A... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: